What is a resistor?
TLDRA resistor is a passive electrical component designed to limit the flow of electric current, akin to a constriction in a water pipe that reduces flow. The effect is governed by Ohm's law, which states that resistance equals voltage divided by current. Resistors come in various types, such as fixed, variable, and those sensitive to physical quantities. Applications are vast, including in LED circuits to prevent damage from excessive current. Different resistor types, like carbon film or metal oxide film, offer varying levels of precision, stability, and durability. Resistor values are often indicated by color-coded bands, decipherable through charts or calculators.
Takeaways
- 📌 A resistor is a passive electrical component that primarily limits the flow of electric current.
- 🌊 The function of a resistor can be compared to the resistance created in a water flow within a tube, where narrowing the tube reduces water flow, analogous to reducing electrical current in a circuit.
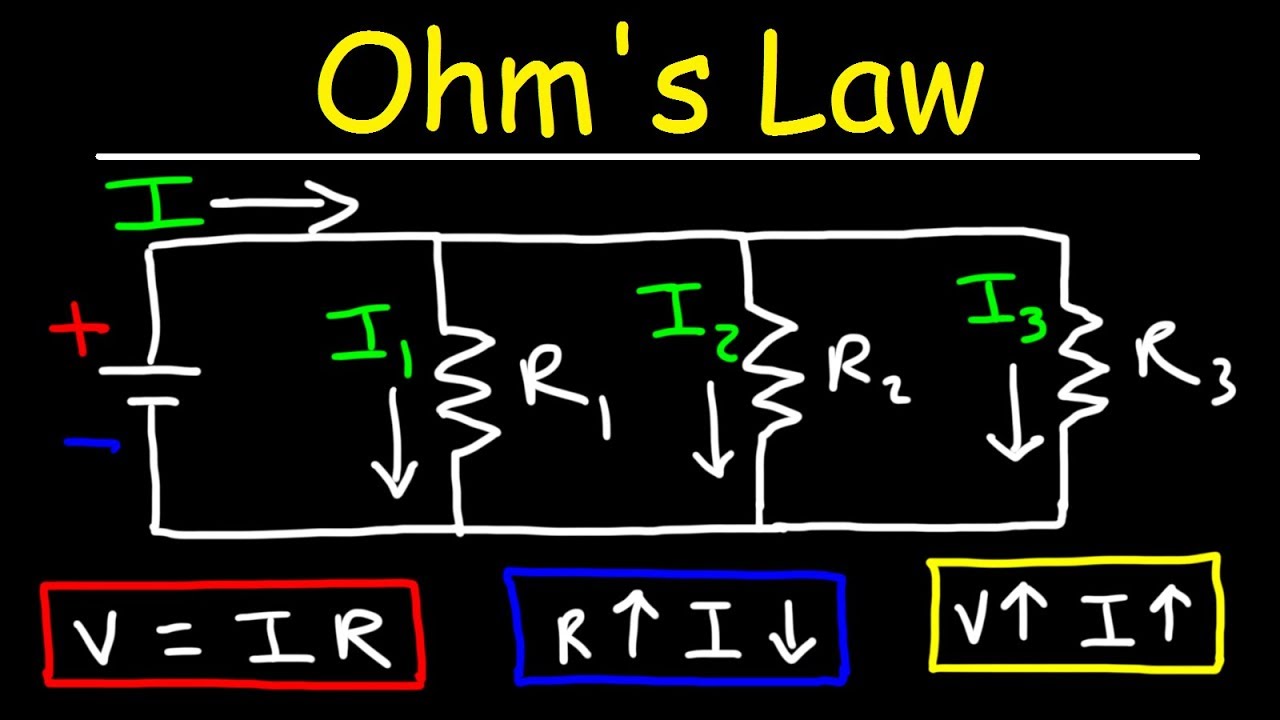
- ⚡电阻器的作用可以通过欧姆定律(Ohm's Law)来描述,即电阻值等于电压除以电流,公式为 V = I * R。
- 🔌 电阻器的标准符号有两种:美国标准(左侧锯齿形)和国际电工委员会(IEC)标准(右侧).
- 🔍 通过一个简单的电路例子(电池和电阻器),展示了电压源产生电流,而电阻器限制电流的大小。
- 💡 应用实例:通过在LED电路中使用电阻器,可以防止LED因电流过大而烧毁,通过计算得出所需电阻值来保护LED。
- 🔄 电阻器有多种类型,包括固定电阻器、可变电阻器(如电位器和变阻器)以及数字电位器,它们根据物理量变化而变化电阻值。
- 📐 电阻器可以根据材料和结构进一步分类,如绕线电阻器、碳复合电阻器、碳膜电阻器、金属膜电阻器、金属氧化物膜电阻器和箔电阻器。
- 🎨 轴向引线电阻器通常带有表示阻值和公差的彩色带,可以通过颜色代码表来解读。
- 🔧 电阻器的颜色代码由四个带组成:第一和第二带表示阻值的前两位数字,第三带表示乘法因子,第四带表示公差。
Q & A
What is the primary function of a resistor?
-The primary function of a resistor is to limit the flow of electric current in an electrical circuit.
What are the standard symbols for resistors in American and International standards?
-The American standard symbol for a resistor is a zigzag line on the left, while the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standard symbol is a rectangle with two diagonal lines on the right.
How does the flow of water through a tube relate to the flow of electric current?
-The flow of water through a tube is analogous to the flow of electric current in an electrical circuit, where the pressure difference causing the water to flow can be compared to the voltage difference causing the flow of electrical current.
What is the effect of a resistor on the electrical current in a circuit?
-A resistor has a higher resistance than the connecting leads, causing a reduced electrical current. This can be visualized as a pressure drop in a water pipe due to a narrow part in the middle, where the pressure on the left is higher than on the right.
What is Ohm's Law and how is it related to resistors?
-Ohm's Law describes the relationship between electrical current, voltage, and resistance. It states that resistance is equal to voltage divided by current, expressed as R = V/I, where R is resistance in ohms, V is voltage in volts, and I is current in amps.
How can a simple circuit with a battery and a resistor be used to explain Ohm's Law?
-In a simple circuit with a battery and a resistor, the voltage source causes a current which is limited by the resistor. For example, if the voltage source is 2 volts and we want a current of 4 amps, the resistance can be calculated using Ohm's Law as R = 2V/4A = 0.5Ω.
What is an example application of a resistor in a circuit?
-An example application of a resistor is in a basic LED circuit. To light a red LED with a 9-volt battery without burning it out, a resistor is placed in the positive lead to limit the current to the LED's specified maximum current, which is 30 milliamps.
What are the different types of resistors and their applications?
-Resistors can be categorized into fixed resistors, which have a constant resistance value, and variable resistors, which have an adjustable resistance value. Variable resistors can be further classified as potentiometers (used as voltage dividers) and rheostats (used to control current). There are also digital potentiometers controlled electronically. Another category includes resistors with varying resistance dependent on physical quantities like light, temperature, or voltage, often used as measurement devices.
How are resistors categorized based on material and construction?
-Resistors can be categorized based on their material and construction into wound resistors, carbon composition resistors, carbon film resistors, metal film resistors, metal oxide film resistors, and foil resistors. Each type has unique characteristics, applications, and levels of accuracy, stability, and durability.
How can the resistance value and tolerance of a resistor be identified using color bands?
-Most axial lead resistors have markings with colored bands to indicate their resistance value and tolerance. The first two bands represent the first two digits of the resistance value, the third band indicates the multiplication factor, and the fourth band signifies the tolerance. For example, a resistor with red, blue, gray, and gold bands has a value of 2.6 mega ohms with a 5% tolerance.
Where can one find more information about resistor types, properties, and the color code?
-More information about different resistor types, their properties, and the color code can be found on websites such as resistorguide.com, which also offers an automatic calculator to decipher the color code.
Outlines
🔌 Understanding Resistors and Their Function
This paragraph introduces resistors as passive electrical components that limit the flow of electric current. It explains the concept using the analogy of water flowing through a tube, where the resistor acts as a constriction, creating a pressure drop similar to a voltage drop in an electrical circuit. The definition of resistance is further clarified through Ohm's Law, which states that resistance is equal to voltage divided by current. The paragraph also describes a simple circuit with a battery and a resistor, illustrating how to calculate resistance to achieve a desired current. The importance of resistors in preventing damage to components, such as LEDs, is highlighted, and the variety of resistor types, applications, and construction materials is briefly mentioned.
🎨 Resistor Types and Color Code
The second paragraph delves into the different types of resistors, including fixed resistors, variable resistors (potentiometers and rheostats), and those with varying resistance based on physical quantities. It explains the construction and characteristics of wound, carbon composition, and film resistors, including metal film resistors. The paragraph also provides an in-depth look at how resistors are marked with colored bands to indicate their resistance value and tolerance, using a carbon composition resistor as an example to explain the resistor color code. The explanation includes how to interpret each color band and its significance, and directs readers to a resource for more information on resistor properties and types.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Resistor
💡Passive Electrical Component
💡Ohm's Law
💡Electric Current
💡Voltage
💡Carbon Film Resistor
💡Color Code
💡LED Circuit
💡Potentiometer
💡Rheostat
💡Resistor Types
Highlights
A resistor is a passive electrical component that primarily limits the flow of electric current.
The standard symbols for resistors are a zigzag line, with the American standard on the left and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standard on the right.
The function of a resistor can be compared to the flow of water through a tube, where the resistor creates resistance similar to a narrow part in the tube.
Ohm's law describes the relationship between electrical current, voltage, and resistance, stating that resistance is equal to voltage divided by current.
A simple circuit with a battery and a resistor can limit the current produced by the voltage source according to Ohm's law.
An example application of a resistor is in an LED circuit, where it prevents the LED from burning out by limiting the current to its specified maximum.
Resistors come in various types, including fixed resistors, variable resistors (potentiometers and rheostats), and those with resistance that varies based on physical quantities.
Fixed resistors are the most common type and are available in axial and Surface-Mounted Device (SMD) packages.
Variable resistors can be adjusted mechanically or controlled electronically, like digital potentiometers.
Resistors can also be categorized by their resistance material and construction, such as wound, carbon composition, carbon film, metal film, and metal oxide film resistors.
Wound resistors are durable and can have very low resistance values but may have higher parasitic reactance at higher frequencies.
Carbon composition resistors were once the most common type but are now used for specific applications due to their ability to withstand high energy pulses.
Carbon film resistors are widely used today for their higher accuracy and better properties compared to carbon composition resistors.
Metal film resistors offer better accuracy, lower temperature coefficients, and improved stability.
Metal oxide film resistors are known for their durability, high-temperature resistance, and reliability.
Foil resistors provide the highest precision and stability with a resistive element made of thin metallic foil.
Axial lead resistors often have color-coded bands to indicate their resistance value and tolerance, which can be deciphered using a resistor color code chart.
The resistor color code can be memorized or an automatic calculator can be used online to interpret the code.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: