What is Current? An Explanation
TLDRThe video script offers a clear and concise explanation of the concept of electric current, emphasizing its definition as the rate of charge flow past a point in a circuit. It distinguishes between the general notion of electrons flowing and the technical definition involving charge rate and time. The script also introduces related terms such as voltage, resistance, capacitance, and charge, and their relevance in understanding circuits and calculations, particularly with Ohm's law and the capacitor equation. The importance of knowing these terms is highlighted for accurate problem-solving and comprehension in electrical studies.
Takeaways
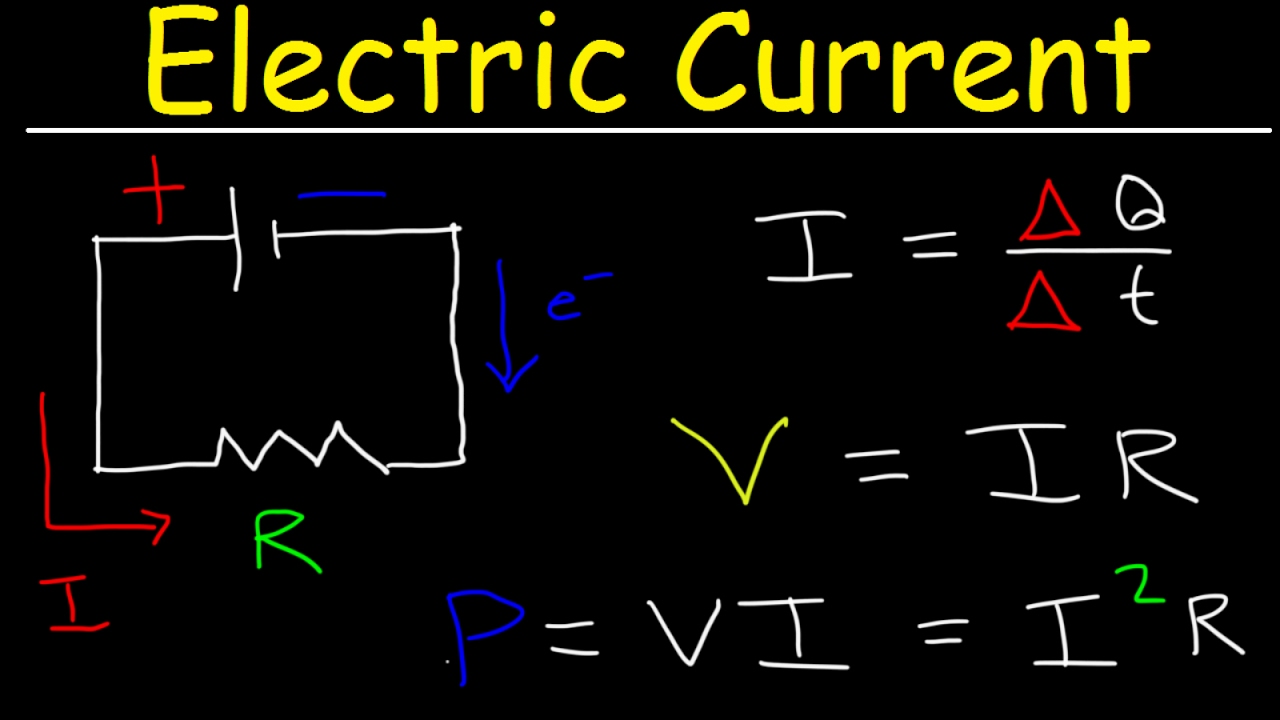
- 📌 Current is the rate of flow of charge past a given point in an electric circuit.
- 🔋 The unit for charge is the Coulomb, and current measures the number of Coulombs passing a point per second.
- ⚡ The symbol for current is 'I', which is used in Ohm's law (V=IR) to represent the current in the circuit.
- 🏎️ Voltage is the electrical potential difference and is represented by the symbol 'V'.
- 🛡️ Resistance is symbolized by 'R' and is part of Ohm's law, indicating how much a circuit resists the flow of current.
- 🔋 Capacitance is represented by 'C' and is related to the amount of charge a circuit can store.
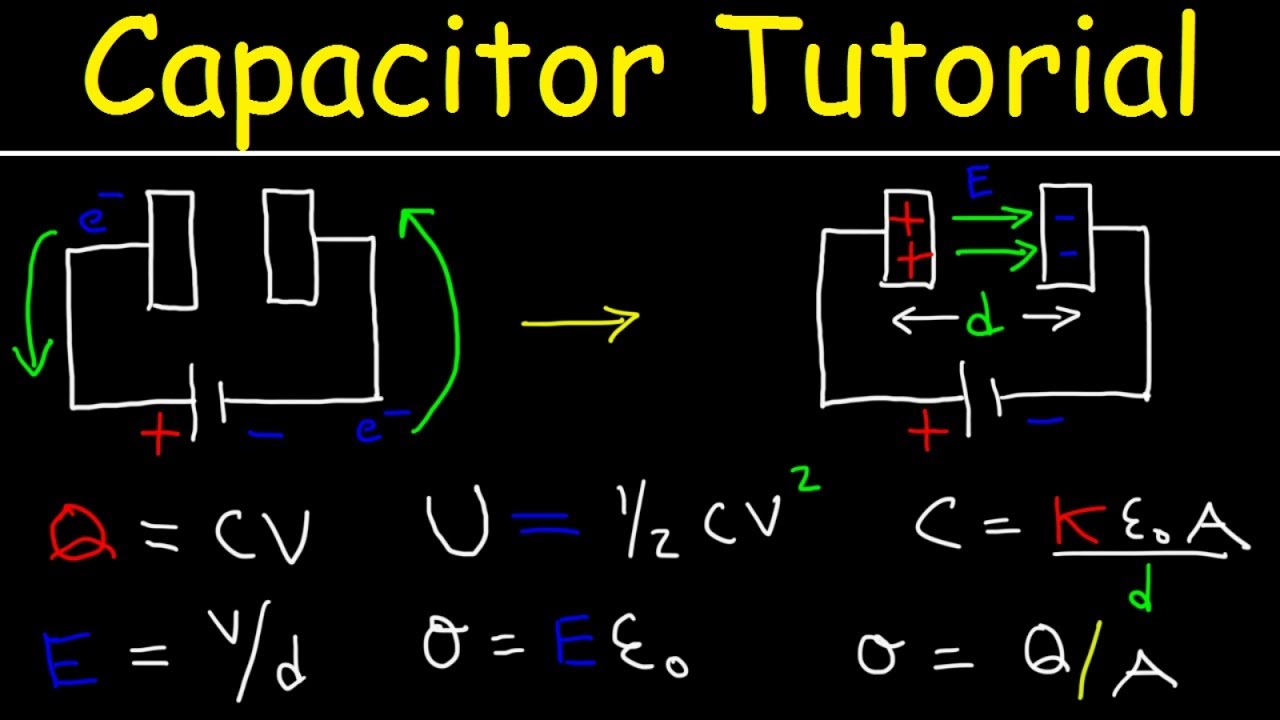
- ⚙️ The capacitor equation is Q=CV, where 'Q' stands for charge, 'C' for capacitance, and 'V' for voltage.
- 🌟 '1 ampere' (abbreviated as 'a') is equivalent to 1 Coulomb of charge flowing past a point every second.
- 📈 Understanding the meaning behind electrical terms is crucial for accurate problem-solving and comprehension.
- 🎓 The video aims to provide a general background on current and related electrical concepts.
- 👍 The presenter encourages viewers to engage by liking and commenting if they found the video helpful.
Q & A
What is the general definition of current?
-The general definition of current is the rate of flow of charge past a given point in an electric circuit.
What are the key terms associated with circuits that one needs to understand?
-The key terms associated with circuits include current, voltage, resistance, capacitance, and charge.
How is current related to Ohm's law?
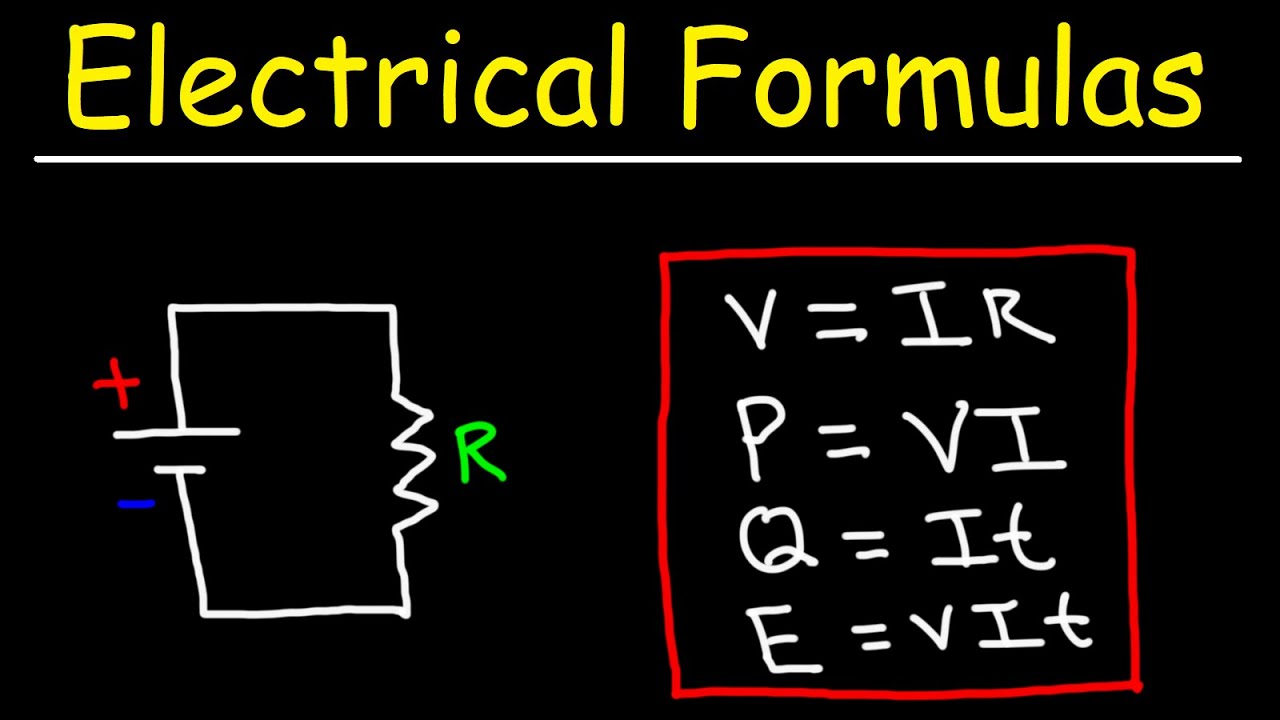
-In Ohm's law, current (I) is related to voltage (V) and resistance (R) by the formula V = I * R, meaning voltage equals the current times the resistance.
What is the unit of charge in an electric circuit?
-The unit of charge in an electric circuit is the Coulomb.
What is the symbol used to represent current?
-The symbol used to represent current is 'I'.
What is the metric unit for current and how is it abbreviated?
-The metric unit for current is the ampere, which is often abbreviated as 'A'.
What does 1 ampere represent in terms of charge flow?
-1 ampere represents 1 Coulomb of charge flowing past a point every second, or equivalently, 4 coulombs per second.
How can one visualize the concept of current?
-One can visualize current as the number of electrons flowing past a point in a circuit every second.
What is the relationship between charge and electrons in the context of current?
-In the context of current, charge is directly related to the number of electrons; the charge is the number of electrons that are flowing past a point in the circuit.
Why is understanding the meaning behind the calculations important?
-Understanding the meaning behind the calculations is important because it allows one to comprehend not just the answers, but also the concepts and principles that underpin the workings of electric circuits.
What does the term 'Coulomb' signify in the context of electric circuits?
-In the context of electric circuits, a 'Coulomb' signifies a unit of electric charge, and it is the quantity that is flowing past a point in the circuit in the definition of current.
Outlines
🌟 Introduction to Current and Circuit Terminology
This paragraph introduces the topic of current in the context of electrical circuits. It emphasizes the importance of understanding the definition of current, as well as related terms such as voltage, resistance, capacitance, and charge. The speaker aims to provide a general overview of these concepts, especially in relation to Ohm's law (V=IR) and the capacitor equation (Q=CV). The goal is to ensure that viewers not only know how to perform calculations but also have a solid grasp of the underlying principles, such as the meaning of current as the rate of charge flow past a given point in a circuit.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡current
💡Ohm's law
💡voltage
💡resistance
💡capacitor
💡capacitance
💡charge
💡Coulomb
💡ampere
💡electrons
💡electric circuit
Highlights
The video aims to provide a general understanding of current in electrical circuits.
Current is often defined as the flow of electrons, but a more specific definition involves the rate of flow of charge.
The rate of flow implies a consideration of time and is measured in coulombs passing a point every second.
The unit for charge is the Coulomb, and the unit for current is the ampere, often abbreviated as 'amp'.
The symbol for current is 'I', and it is used in Ohm's law (V=IR) to calculate voltage and resistance.
Capacitors are also discussed in relation to the equation Q=CV, where Q is charge, C is capacitance, and V is voltage.
Understanding the meaning of current, voltage, and other terms is emphasized for correctly solving electrical problems.
1 ampere is equivalent to 1 Coulomb of charge flowing past a point every second.
The video stresses the importance of not just getting the right answer, but also understanding the concepts behind the calculations.
The speaker encourages viewers to think about current in terms of the number of electrons flowing past a point every second.
The video serves as a general background on the concept of current before delving into more complex topics.
The speaker plans to cover more detailed calculations and applications in future videos.
The video is intended to help viewers gain a better understanding of electrical terms such as current, voltage, resistance, and capacitance.
The speaker invites viewers to engage with the content by liking the video or leaving comments if they found it helpful.
The video concludes with a thank you to the viewers and an anticipation for the next video.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: