Why don't we fall into the center of the earth? | #aumsum #kids #science #education #children
TLDRThis script delves into the concepts of balanced and unbalanced forces, using everyday experiences like standing on Earth and the act of falling to illustrate the principles. It explains how the gravitational force pulls objects towards the Earth's center, but the normal force exerted by the ground balances it out, preventing us from falling into the center. The discussion highlights the importance of resultant forces and how they dictate the state of motion or rest of an object, ultimately demonstrating the intricate balance of forces at play in our daily lives.
Takeaways
- 🌐 Forces are pushes or pulls that act on objects, influencing their motion or balance.
- ⚖️ Balanced forces occur when the resultant force is zero, keeping an object in a state of rest or uniform motion.
- ⚙️ Unbalanced forces exist when the resultant force is not zero, leading to a change in an object's motion.
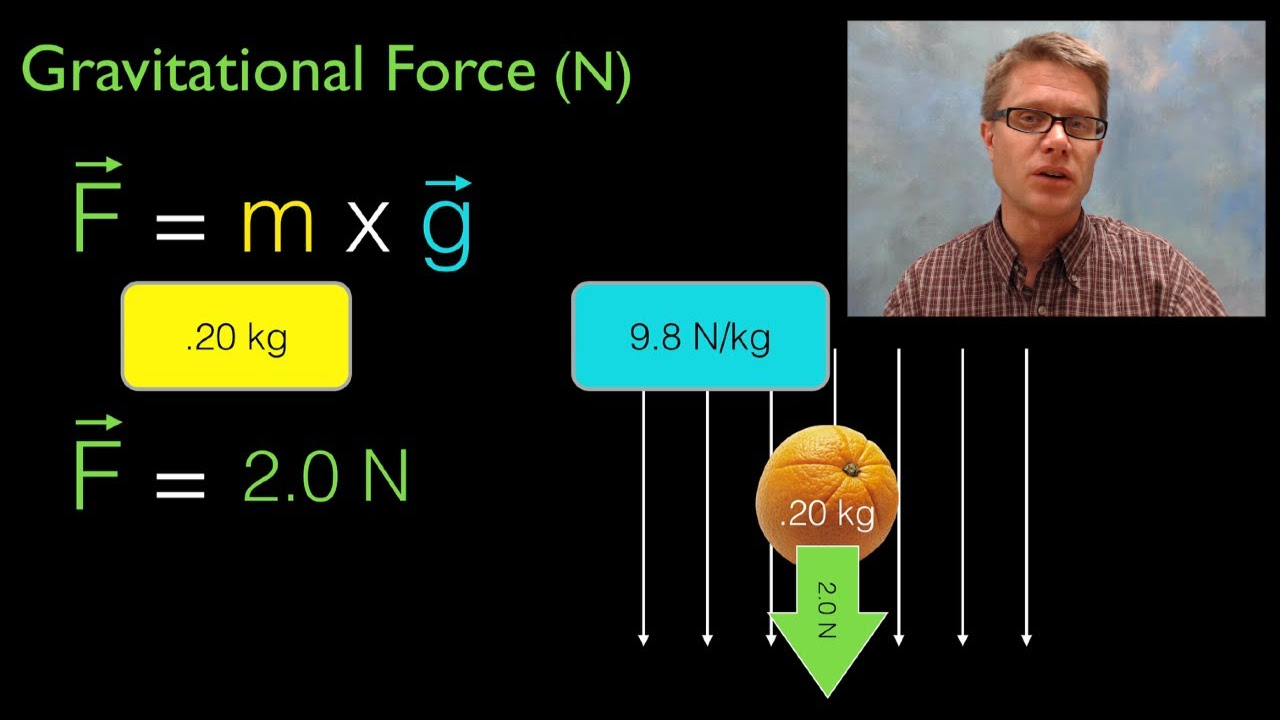
- 🌍 On Earth, all objects experience gravitational force, which pulls them towards the center of the planet.
- 🔄 When an object is falling, the gravitational force is unopposed, resulting in unbalanced forces and a non-zero resultant force.
- 🛡️ The normal force is the upward force exerted by the ground when in contact, balancing the downward gravitational pull.
- 🔧 The normal force is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the gravitational force, creating a balanced situation.
- 🧍 Balanced forces prevent us from falling into the center of the Earth by counteracting the gravitational pull.
- 🏋️♂️ In a balancing act, as demonstrated, the performer's skill ensures that the forces acting on their body remain balanced, preventing a fall.
- 📈 The resultant force's direction and magnitude determine whether forces are balanced or unbalanced and the subsequent motion of the object.
Q & A
What is the primary reason we don't fall into the center of the earth?
-We don't fall into the center of the earth because of the normal force exerted by the ground, which is equal and opposite to the gravitational force pulling us downwards, resulting in a net force of zero that keeps us balanced on the earth's surface.
How do balanced forces relate to our stability on the earth's surface?
-Balanced forces are crucial for our stability on the earth's surface because when the forces acting on us, such as the gravitational force and the normal force from the ground, are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, they cancel each other out, resulting in a net force of zero that prevents us from falling into the earth.
What is the difference between balanced and unbalanced forces?
-Balanced forces occur when the resultant force of all the forces acting on an object sums up to zero, meaning there is no change in the object's state of motion. Unbalanced forces, on the other hand, have a non-zero resultant force, causing a change in the object's state of motion.
What happens when an object is subjected to unbalanced forces?
-When an object is subjected to unbalanced forces, its state of motion changes. This could mean the object starts moving, accelerates, decelerates, or changes direction, depending on the nature and direction of the unbalanced forces acting upon it.
How does the gravitational force of the earth affect objects on its surface?
-The gravitational force of the earth pulls all objects downwards towards the center of the earth. This force is what gives weight to objects and prevents them from floating away into space.
What is the normal force, and how does it interact with gravitational force?
-The normal force is the force exerted by a surface, like the ground, when in contact with an object. It pushes upwards against the object and is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to the gravitational force. Together, they create balanced forces that keep us from falling into the earth.
Why do we not feel the earth's rotation despite its significant speed?
-We do not feel the earth's rotation because everything on the earth, including the atmosphere and us, is spinning with the earth at the same constant rate. This uniform motion means that there is no relative motion between us and the earth's surface, so we do not perceive the movement.
What is an example of balanced forces in everyday life?
-An example of balanced forces can be seen when pushing against a wall. If the wall does not move and neither do you, it means that the force you exert on the wall and the force the wall exerts on you are balanced, resulting in no movement.
How does the concept of balanced and unbalanced forces relate to Newton's first law of motion?
-According to Newton's first law of motion, an object at rest or in uniform motion will stay at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. This law explains why we don't feel the earth's constant motion and why objects subjected to balanced forces remain in their current state of motion.
What would happen if the earth's rotation were to suddenly stop?
-If the earth's rotation were to suddenly stop, the unbalanced forces would result in catastrophic consequences. The atmosphere would continue moving at the previous speed and could potentially wipe the surface of the planet due to the sudden deceleration.
How does the moon's gravitational pull affect the earth's rotation?
-The moon's gravitational pull acts as a drag on the earth's rotation, causing tidal friction. This interaction slowly transfers energy into the moon's orbit and causes the earth to lose a tiny fraction of its rotational speed every day, leading to the occasional need to add an extra second to our clocks to keep them synchronized with the earth's rotation.
Outlines
🌐 Introduction to Balanced and Unbalanced Forces
This paragraph introduces the concept of balanced and unbalanced forces. It begins with a question about standing on Earth without falling into its center, leading to an explanation of forces. Forces are defined as pushes or pulls exerted on an object. The paragraph explains that when multiple forces on an object result in a net force of zero, the forces are balanced. Conversely, if the net force is not zero, the forces are unbalanced. It uses the example of a falling person to illustrate unbalanced forces, where gravitational force overpowers other forces. The paragraph also discusses the gravitational force pulling objects downwards and the normal force exerted by the ground, which pushes us upwards. It concludes by explaining how balanced forces, such as the normal force balancing gravity, prevent us from falling into the center of the Earth.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Balanced Forces
💡Unbalanced Forces
💡Gravitational Force
💡Normal Force
💡Resultant Force
💡Push or Pull
💡Force
💡Object
💡Earth
💡Center of the Earth
💡Motion
Highlights
Exploration of balanced and unbalanced forces as they relate to our daily experiences.
Discussion on how we stand on Earth without falling into its center due to the effect of forces.
Explanation of the concept of force as a push or a pull exerted on an object.
Insight on the variety of forces acting on every object on Earth.
Definition of balanced forces where the resultant force is zero.
Clarification of unbalanced forces when the resultant force is not equal to zero.
Analysis of the forces acting on a falling object, identifying them as unbalanced.
Discussion on Earth's gravitational force pulling objects downwards towards its center.
Explanation of how the normal force, exerted by the ground, counteracts gravity.
Elucidation on the normal force being equal and opposite to gravity, resulting in a net force of zero.
Understanding that balanced forces prevent us from falling into the center of the Earth.
Illustration of the safe landing of an individual due to the interplay of forces.
Questioning why we fall on the ground instead of into the Earth's center, prompting further exploration.
Introduction to the concept of normal force as an upward push exerted by a surface in contact.
Explanation of how balanced forces, such as the normal force against gravity, keep us grounded.
Highlighting the practical application of understanding these forces to explain everyday phenomena.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Balanced and unbalanced forces | Forces and Newton's laws of motion | Physics | Khan Academy

High School Physics - Vertical Circular Motion

GCSE Physics Revision "Newton's First Law of Motion"
Gravitational Force
High School Physics - Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation

Gravity Compilation: Crash Course Kids
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: