Types Of Forces
TLDRIn this informative session of HighSchoolScience101, the focus is on the concept of forces in physics. The video explains forces as interactions that can change an object's motion, shape, or direction and categorizes them into contact and non-contact forces. It provides examples of contact forces like friction and non-contact forces such as magnetism, static electricity, and gravity. The explanation includes the role of atoms, electrons, and the concept of magnetic poles and gravitational fields, enhancing the viewer's understanding of these fundamental physical concepts.
Takeaways
- 🌟 A force is an interaction that can cause an object to move, stop, slow down, change direction, or change shape.
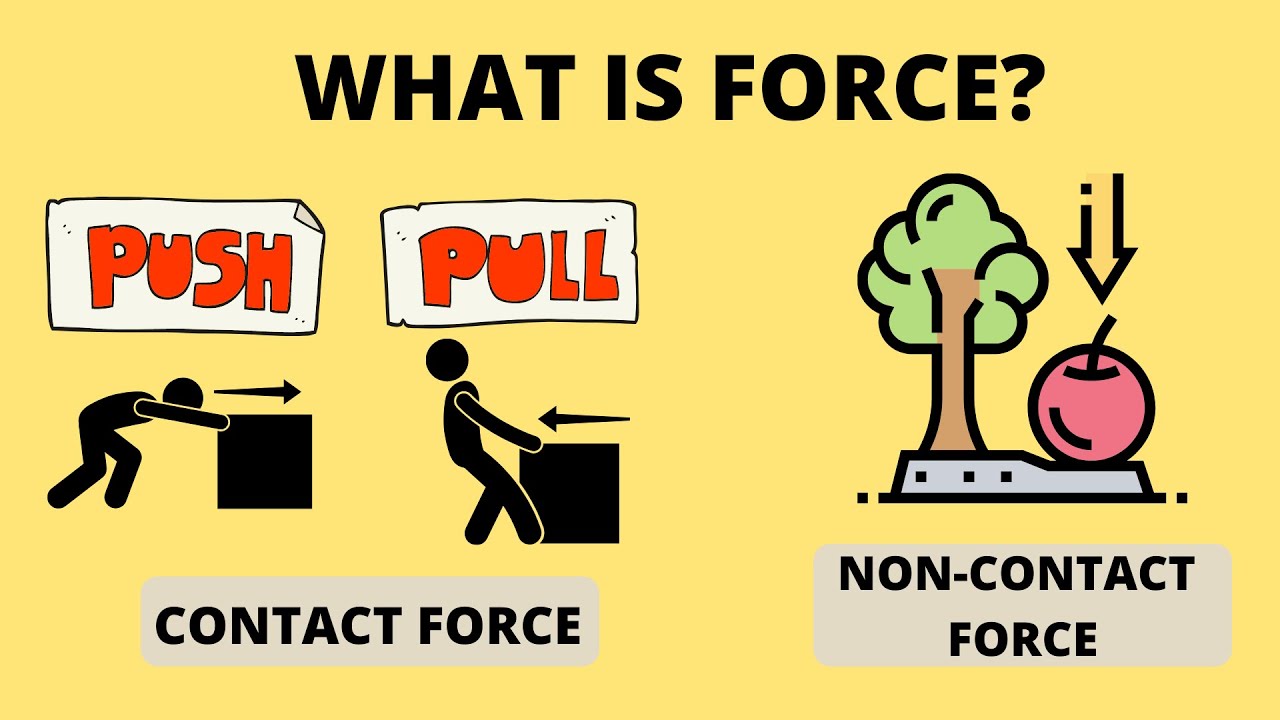
- 🤲 Forces are classified into two main groups: contact forces and non-contact forces.
- 👐 Contact forces require physical contact between two surfaces, like pushing or pulling on an object.
- 🔄 Friction is an example of a contact force that acts when surfaces rub against each other.
- 🧲 Magnetism is a non-contact force that acts through an invisible field and can affect objects without touching them.
- 🔴🔵 Magnets have North and South poles, and opposite poles attract each other while like poles repel.
- ⚡ Static electricity is another non-contact force that occurs when electrons are transferred from one object to another, causing attraction between objects with opposite charges.
- 🌐 Gravity is a non-contact force that affects all objects with mass, and its strength depends on the mass of the objects and the distance between them.
- 🪐 The gravitational pull is more noticeable with larger masses, like planets, moons, and stars.
- 📉 The distance between two objects has a stronger impact on gravitational attraction than their masses.
- 📚 Future videos may cover concepts of balanced and unbalanced forces in more detail.
Q & A
What is a force in physics?
-A force is an interaction that can cause an object to start or stop moving, slow down, change direction, or change shape. It can be a push, pull, or twist.
What are the two main groups of forces?
-The two main groups of forces are contact forces, which require physical contact, and non-contact forces, which do not require physical contact.
Can you provide an example of a contact force?
-An example of a contact force is applying physical force to putty to change its shape, where there is direct contact between the hand and the putty.
What is friction and how is it related to contact forces?
-Friction is a force that opposes the relative motion or tendency of such motion of two surfaces in contact. It is a byproduct of contact forces.
What is magnetism and how does it differ from contact forces?
-Magnetism is a non-contact force that acts between magnets without them having to touch. It involves an invisible magnetic field around the object.
Why are some materials magnetic while others are not?
-Materials like iron, nickel, or cobalt have electrons that spin in the same direction around the nucleus, creating a magnetic field and making the object magnetic.
What are the two poles of a magnet and how do they interact?
-Every magnet has a North pole and a South pole. Opposite poles (North and South) attract each other, while the same type of poles (two Norths or two Souths) repel each other.
What is static electricity and how does it work?
-Static electricity is a non-contact force that occurs when electrons move from one object to another, leaving one object positively charged and the other negatively charged, which then attract each other.
What is gravity and how does it affect objects?
-Gravity is a non-contact force that acts between any objects that have mass. It pulls them towards each other, with the strength of the attraction depending on the mass of the objects and the distance between them.
How does the distance between two objects affect their gravitational attraction?
-The gravitational attraction between two objects decreases as the distance between them increases. The larger the distance, the weaker the gravitational force.
What are balanced and unbalanced forces?
-Balanced forces occur when the net force on an object is zero, meaning the object is either at rest or moving at a constant velocity. Unbalanced forces result in a net force, causing the object to accelerate or decelerate.
Outlines
🚀 Introduction to Forces and Their Types
This paragraph introduces the concept of forces in physics, explaining that forces are interactions causing objects to move, stop, change direction, or shape. It distinguishes between contact and non-contact forces, using examples like hand shaping putty for contact forces and magnetism for non-contact forces. The explanation also touches on the atomic level, discussing how electrons contribute to magnetic properties in certain materials and the concept of poles in magnets. Additionally, it briefly introduces static electricity as another non-contact force, describing how electrons transfer between objects and create attraction between charged materials.
🌌 Gravity and the Influence of Mass and Distance
The second paragraph delves into gravity as a non-contact force, clarifying that every object with mass possesses a gravitational field. It contrasts the often perceived association of gravity with celestial bodies by highlighting that gravity acts between all objects, regardless of size. The summary emphasizes the dual factors of mass and distance in determining the strength of gravitational attraction, with distance having a more significant impact. The paragraph concludes by mentioning the potential for future content on balanced and unbalanced forces, providing a teaser for upcoming videos.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Force
💡Interaction
💡Contact Forces
💡Non-Contact Forces
💡Magnetism
💡Friction
💡Electrons
💡Static Electricity
💡Gravity
💡Mass
💡Distance
Highlights
Force is an interaction that can cause an object to start moving, speed up, stop moving, slow down, change direction, or change shape.
Forces can be classified into two main groups: contact and non-contact forces.
Contact forces require physical contact between two surfaces, such as pushing or pulling.
Friction is an example of a contact force and is discussed in more detail in another video.
Non-contact forces act on objects without physical contact, such as magnetism.
Magnetism is a non-contact force where magnets affect each other without touching.
Objects made of iron, nickel, or cobalt can become magnetic due to the alignment of electrons.
Every magnet has a North pole and a South pole, with opposite poles attracting each other.
Static electricity is a non-contact force that occurs when electrons are transferred from one object to another.
Charged objects can attract or repel each other based on their positive or negative charge.
Rubbing objects together can result in a transfer of electrons, causing static electricity.
Gravity is a non-contact force that affects all objects with mass, including the attraction between people and objects.
The gravitational pull is stronger with larger masses and closer distances between objects.
The universal law of gravitation, proposed by Isaac Newton, states that any object with mass has a gravitational field.
The video briefly introduces the concept of balanced and unbalanced forces, suggesting a future video on the topic.
The video aims to provide a basic understanding of different types of forces and their effects on objects.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: