What is Force? - Part 2 | Physics | Don't Memorise
TLDRThis video script delves into the concept of force, distinguishing between contact and non-contact forces and their effects on objects. It explains how forces like applied force, friction, air resistance, and normal force are examples of contact forces, while gravitational pull is a non-contact force. The video also explores the various effects of forces, including initiating motion, altering velocity and direction, and changing the shape of objects. It invites viewers to consider the multifaceted impact of forces on the motion and structure of objects, promising an engaging game in the next installment to reinforce understanding.
Takeaways
- 📌 Forces are interactions between objects, not just human actions.
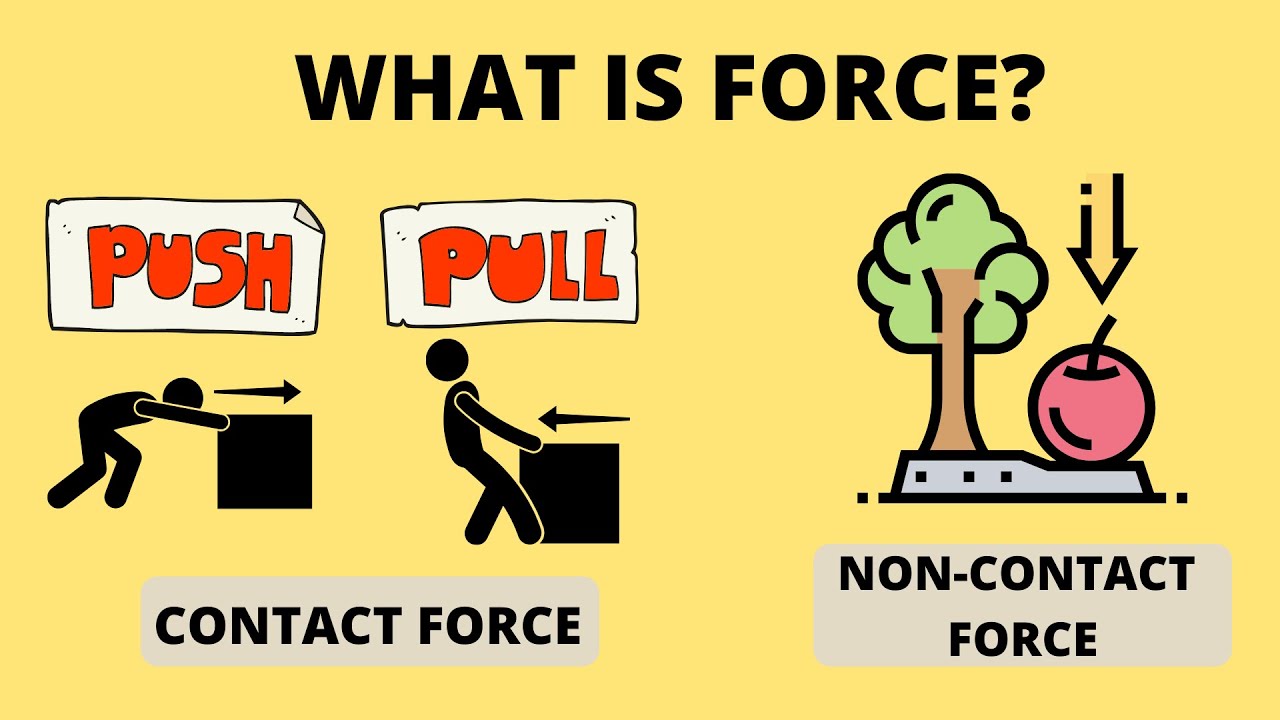
- 🔍 Forces can be categorized into two main types: Contact forces and Non-contact forces.
- 🤺 Contact forces occur when two objects are physically touching each other, like when you kick a ball.
- 🚀 Applied Force is a type of contact force, such as when you kick a ball and it moves.
- 🔄 Friction is a contact force that opposes motion, like when a ball slows down after being kicked.
- 💨 Air resistance is a contact force that affects objects as they move through the air.
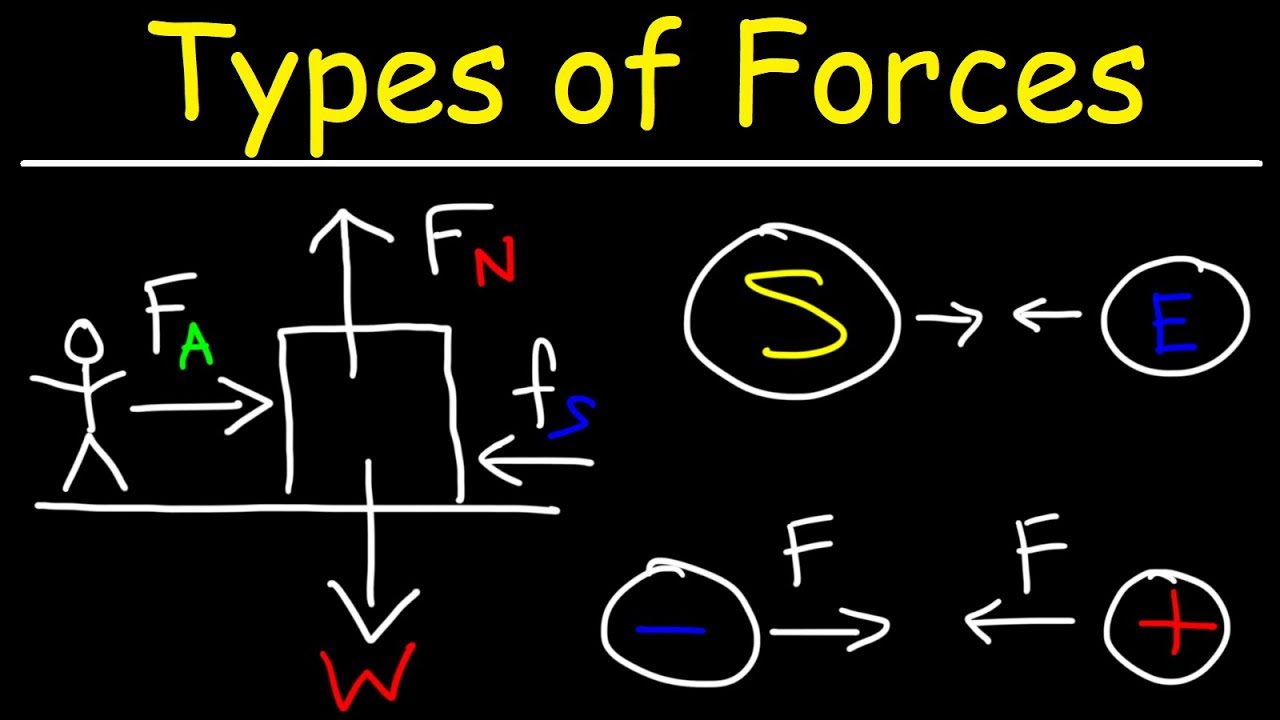
- 🌐 Gravitational force is a non-contact force that acts on objects, pulling them towards the Earth's center, even without direct contact.
- 🧲 Non-contact forces include gravitational, electrical, and magnetic forces that act over a distance.
- 🚶 Force can set a stationary object in motion or stop a moving object.
- 🏃♂️ Force can change the velocity of an object, making it move faster or slower.
- 🔄 Force can change the direction of an object's motion, altering its trajectory.
- 🎾 Force can also change the shape of an object, like compressing a ball.
Q & A
What is the definition of force in physics?
-Force is a push or pull upon an object, resulting from its interaction with another object.
What are the two main types of forces discussed in the video?
-The two main types of forces discussed are contact forces and non-contact forces.
What is an example of a contact force?
-An example of a contact force is the applied force when you kick a ball lying on the ground.
What are the different contact forces acting on a ball when it is rolling on the ground?
-The different contact forces include applied force, frictional force, air resistance, and the normal force.
What is a non-contact force and provide an example?
-A non-contact force is a force that acts on an object without physical contact, such as the gravitational force that pulls objects towards the Earth.
How can a force affect an object that is at rest?
-A force can set a stationary object in motion.
How does force relate to the velocity of a moving object?
-Force can change the velocity of an object, either by increasing it when pushed harder or by stopping the object.
What happens when a force is applied to a spherical ball from both sides?
-The shape of the ball changes, even though its position does not, demonstrating that force can alter the form of an object.
What are the three effects of force that were discussed in the video?
-The three effects of force are: changing the motion state of an object (from rest to motion, changing velocity, or stopping), changing the direction of motion, and changing the shape of an object.
What other types of non-contact forces were mentioned in the video?
-Electrical and magnetic forces were mentioned as examples of non-contact forces.
How can understanding the effects of forces be beneficial?
-Understanding the effects of forces can help us predict and control the behavior of objects, which is crucial in various applications, from sports to engineering and beyond.
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Forces and Their Types
This paragraph introduces the concept of force, clarifying that it is not merely a human action but rather a result of interactions between objects. It distinguishes between two main types of forces: contact forces, which occur through physical interaction, and non-contact forces, which act at a distance. The paragraph provides examples of contact forces, such as applied force, friction, air resistance, and normal force, and introduces gravitational force as an example of a non-contact force. It also sets the stage for discussing the effects of forces in the following content.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Force
💡Contact Forces
💡Non-contact Forces
💡Applied Force
💡Friction
💡Air Resistance
💡Normal Force
💡Gravitational Force
💡Velocity
💡Direction of Motion
💡Shape
Highlights
Force is not merely a human action of pushing or pulling, but rather a result of interactions between objects.
Forces can be categorized into two main types: Contact forces and Non-contact forces.
Contact forces arise from physical interaction between two objects in contact.
An example of a contact force is the applied force when you kick a ball lying on the ground.
Frictional force, which slows down the ball, is another type of contact force.
Air resistance is a contact force that acts on objects moving through the air.
The normal force, acting upward, is a contact force that counteracts gravity.
Non-contact forces act on objects without direct physical contact, such as gravitational pull.
Gravitational force pulls objects towards the center of the Earth, even without contact.
Electrical and magnetic forces are examples of non-contact forces that act at a distance.
Force can initiate motion in a stationary object.
By applying a greater force, an object's velocity can be increased.
Force can also bring a moving object to a stop.
Changing the direction of a moving object is another effect of force.
Force can alter the shape of an object, as exemplified by deforming a sphere.
Understanding the effects of force is crucial for grasping the principles of motion and interaction.
An upcoming video will feature a game to test the comprehension of how forces act on objects.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: