GCSE Physics Revision "Contact and Non-contact Forces"
TLDRThis educational video introduces the concept of forces, differentiating between contact and non-contact forces. It explains that forces are pushes or pulls with both magnitude and direction, measured in Newtons. Contact forces, such as tension, friction, and normal contact force, occur when objects touch, exemplified by a tug-of-war and an airplane landing. Non-contact forces act over a distance, including gravitational, electrostatic, and magnetic forces, with examples like the attraction between charged objects and the International Space Station's pull on Earth. The video encourages viewers to practice identifying these forces through provided exercises.
Takeaways
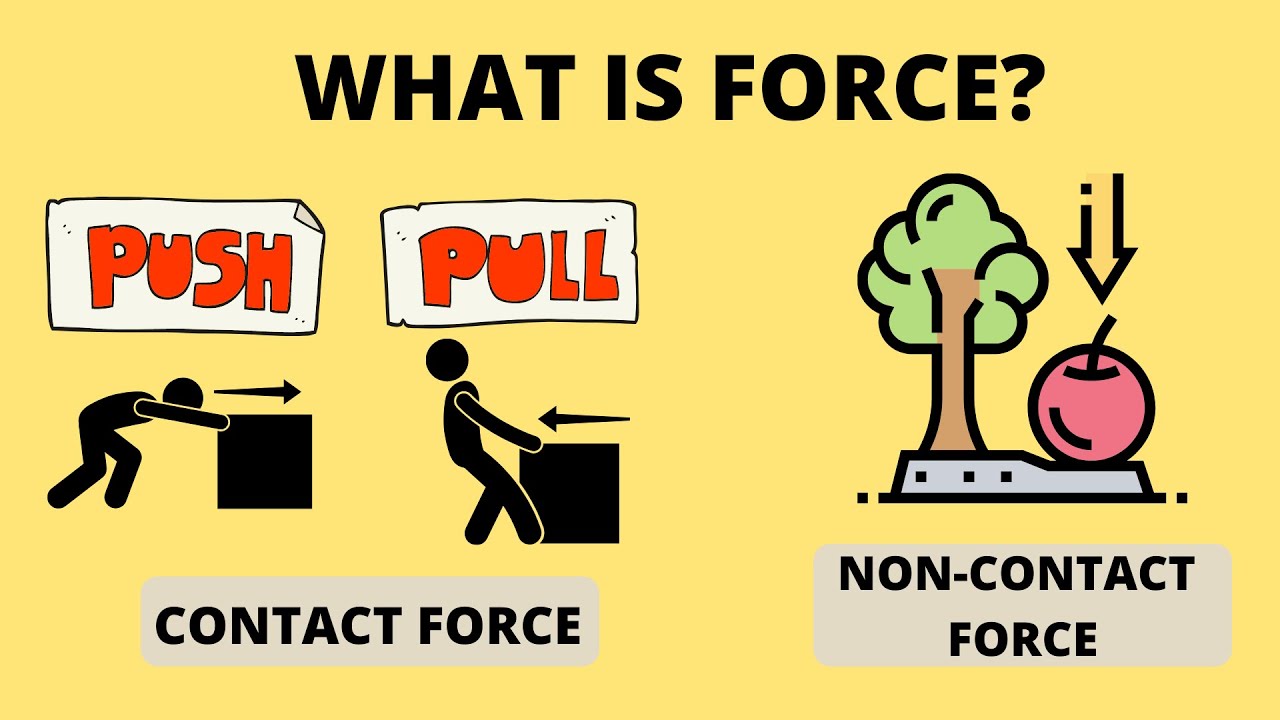
- 📚 A force is defined as a push or pull acting on an object due to interaction with another object.
- 📈 Forces have both magnitude (size) and direction, making them vector quantities.
- 🔩 The unit of force is the Newton, named after Sir Isaac Newton.
- 🤲 Contact forces occur when two objects are physically touching each other.
- 🌐 Examples of contact forces include tension in a rope, friction between surfaces, and air resistance.
- 🚫 Non-contact forces act between objects that are not physically touching.
- 🌍 Gravitational force is a non-contact force that attracts all objects to each other, such as between the Earth and the International Space Station.
- 💥 Electrostatic force is a non-contact force between charged objects, with opposite charges attracting and like charges repelling.
- 🔮 Magnetic force is the third type of non-contact force experienced by objects in a magnetic field.
- 📖 The concept of normal contact force is introduced, which is the upward force exerted by a surface on an object resting on it.
- 📚 The script suggests that there are plenty of practice questions on contact and non-contact forces in the accompanying workbook.
Q & A
What is the definition of force?
-Force is a push or pull that acts on an object due to the interaction with another object. It has both magnitude, or size, and direction, making it a vector quantity.
What is the unit of force?
-The unit of force is the Newton.
How can forces be categorized?
-Forces can be categorized into two main types: contact forces and non-contact forces.
What is an example of a contact force?
-Tension in a rope is an example of a contact force, as it occurs when two objects are physically touching.
What are three types of contact forces mentioned in the script?
-Three types of contact forces mentioned are tension, friction, and air resistance.
What is the normal contact force?
-The normal contact force is the upward force exerted by a surface on an object in contact with it, such as the table exerting a force on the lump in the example given.
What is a non-contact force?
-A non-contact force is a force that acts on objects that are not in physical contact with each other.
What are three examples of non-contact forces?
-Three examples of non-contact forces are gravitational force, electrostatic force, and magnetic force.
How does the gravitational force work?
-Gravitational force attracts all objects to each other, such as the force between the International Space Station and the Earth.
What happens when two charged objects interact through electrostatic force?
-Objects with opposite charges experience an electrostatic force of attraction, while objects with the same type of charge experience an electrostatic force of repulsion.
What is the significance of understanding contact and non-contact forces?
-Understanding contact and non-contact forces is important for solving problems in physics and for explaining various phenomena in everyday life and engineering applications.
Outlines
📘 Introduction to Forces and Contact Forces
The video begins by introducing the concept of a force, defined as a push or pull acting on an object due to interaction with another object. It emphasizes that forces have both magnitude and direction, making them vector quantities, and their unit is the Newton. The video categorizes forces into contact and non-contact forces, with the aim of helping viewers identify these types in an exam setting. It then delves into contact forces, explaining that they occur when two objects physically interact. Examples of contact forces include tension in a rope, friction between water and an airplane, air resistance acting on a skydiver, and the normal contact force exerted by a table on an object resting on it.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Force
💡Contact Forces
💡Non-Contact Forces
💡Friction
💡Air Resistance
💡Normal Contact Force
💡Gravitational Force
💡Electrostatic Force
💡Magnetic Force
💡Vector Quantity
💡Newton
Highlights
The definition of force as a push or pull acting on an object due to interaction with another object.
Forces have both magnitude and direction, making them vector quantities.
The unit of force is the Newton.
Forces are categorized into contact and non-contact forces.
Contact forces occur when two objects are physically touching.
Tension in a rope is an example of a contact force.
Friction is a contact force that acts between the water and an airplane during landing.
Air resistance is a contact force experienced by a skydiver falling through the air.
Normal contact force is the upward force exerted by a surface on an object in contact with it.
Non-contact forces act between objects that are physically separated.
Gravitational force is a non-contact force that attracts all objects to each other.
Electrostatic force is a non-contact force between charged objects.
Objects with opposite charges experience an electrostatic force of attraction.
Objects with the same charge type experience an electrostatic force of repulsion.
Magnetic force is a non-contact force experienced by objects in a magnetic field.
There are plenty of questions on contact and non-contact forces in the revision workbook.
The revision workbook can be accessed by clicking the link provided.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: