Quantitative Data Analysis 101 Tutorial: Descriptive vs Inferential Statistics (With Examples)
TLDRThis video script offers a comprehensive guide to quantitative data analysis, breaking down its fundamentals and demystifying the process. It explains the difference between descriptive and inferential statistics, their purposes, and common statistical methods such as t-tests, ANOVA, correlation, and regression analysis. The script emphasizes the importance of selecting the right statistical methods based on data type and research questions, and provides practical examples to illustrate key concepts, aiming to build confidence in approaching quantitative research.
Takeaways
- 📊 Quantitative data analysis involves examining numerical data using statistical methods.
- 🔍 It's divided into two main branches: descriptive statistics and inferential statistics.
- 📈 Descriptive statistics describe the sample data, focusing on measures like mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and skewness.
- 🔮 Inferential statistics make predictions about the population based on the sample data.
- 🧐 Common inferential methods include t-tests, ANOVA, correlation analysis, and regression analysis.
- 🎯 The choice of statistical methods depends on the type of data collected and the research questions or hypotheses.
- 📝 Understanding the level of measurement (nominal, ordinal, interval, ratio) and the shape of the data (normal distribution vs. skewness) is crucial for selecting appropriate methods.
- 🚫 Misusing statistical methods not suited to the data type can lead to meaningless results.
- 💡 Descriptive statistics are essential for understanding data shape and informing the choice of inferential methods.
- 📝 The research aims and questions should guide the selection of statistical methods rather than personal preference or familiarity.
- 📚 Further exploration of statistical methods and resources is available on the Grad Coach blog and related links.
Q & A
What is quantitative data analysis?
-Quantitative data analysis is the process of analyzing data that is numerically based or can be easily converted into numbers without losing meaning. It involves using statistical methods to interpret and draw conclusions from the data.
What are the three main purposes of quantitative analysis?
-Quantitative analysis is generally used for three purposes: to measure differences between groups, to assess relationships between variables, and to test hypotheses in a scientifically rigorous way.
What is the difference between descriptive and inferential statistics?
-Descriptive statistics focus on describing the sample data, providing details and summaries like mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and skewness. Inferential statistics, on the other hand, aim to make predictions about the entire population based on the findings within the sample.
What are some common statistical tests used in descriptive statistics?
-Common statistical tests used in descriptive statistics include the mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and skewness.
What is the role of t-tests in inferential statistics?
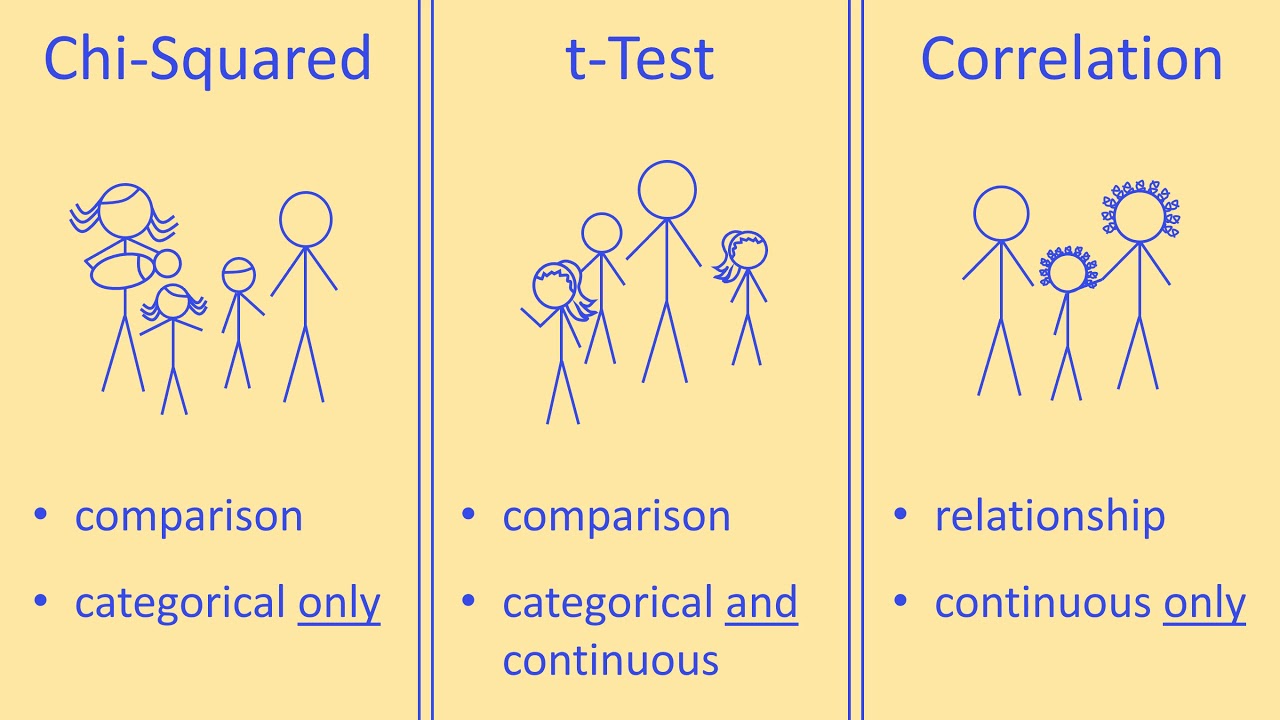
-T-tests in inferential statistics are used to compare the means of two groups of data to assess whether they are different to a statistically significant extent.
What does ANOVA stand for and what does it do?
-ANOVA stands for Analysis of Variance. It is a statistical test similar to a t-test but allows for the comparison of means across multiple groups rather than just two.
How does correlation analysis work in inferential statistics?
-Correlation analysis assesses the relationship between two variables, determining whether one variable increases, decreases, or remains the same as the other variable changes.
What is the difference between correlation and regression analysis?
-While both correlation and regression analysis assess the relationship between variables, regression analysis goes further to understand the cause and effect between variables, not just whether they move together.
How do you choose the right quantitative analysis methods for your research?
-To choose the right quantitative analysis methods, consider the type of data you have, the level of measurement, the shape of the data, and your specific research questions and hypotheses. Ensure that the chosen methods align with these factors and the assumptions required by each statistical method.
Why are descriptive statistics important in research?
-Descriptive statistics are important because they provide a macro and micro view of the data, help spot potential errors, and inform which inferential statistical methods can be used based on the data's shape and distribution.
What are the four levels of measurement in data collection?
-The four levels of measurement in data collection are nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. Each level corresponds to different types of data and has specific statistical methods that can be applied.
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Quantitative Data Analysis
This paragraph introduces the topic of quantitative data analysis, explaining that it involves analyzing numerical data using statistical methods. It mentions that the video will cover what quantitative data analysis is, popular methods, how to choose the right methods, and tips to avoid common pitfalls. The speaker, Emma, welcomes viewers to Grad Coach TV, a platform aimed at demystifying academic research, and offers coaching services for dissertations and research projects.
📊 Understanding Descriptive and Inferential Statistics
This section delves into the two main branches of quantitative analysis: descriptive and inferential statistics. Descriptive statistics are used to describe the sample data, while inferential statistics make predictions about the entire population based on the sample. The paragraph explains the concepts of population and sample and emphasizes the importance of understanding these terms to differentiate between the two branches of statistics. It sets the stage for a deeper exploration of each branch in the subsequent paragraphs.
📈 Descriptive Statistics: Roles and Common Tests
Descriptive statistics are highlighted as crucial for understanding the details of the sample data. The paragraph outlines common statistical tests used in descriptive statistics, such as the mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and skewness. It provides a practical example of body weight data to illustrate these statistics in action. The importance of descriptive statistics is emphasized, noting their role in providing a comprehensive view of the data, identifying potential errors, and informing the choice of inferential statistical methods.
🔍 Inferential Statistics: Predictions and Hypothesis Testing
Inferential statistics are introduced as tools for making predictions about the population based on sample data. The paragraph discusses two common types of predictions: differences between groups and relationships between variables. It explains the use of inferential statistics in hypothesis testing and emphasizes the importance of the sample's composition for accurate inferences. The section also provides an overview of common inferential statistical methods, including t-tests, ANOVA, correlation analysis, and regression analysis, with examples to illustrate their applications.
🛠 Choosing the Right Quantitative Analysis Methods
This section guides viewers on how to select appropriate statistical methods for their research. It emphasizes the importance of considering the type of data collected, the level of measurement, and the shape of the data. The paragraph also highlights the need to align the choice of statistical methods with research questions and hypotheses. It advises against forcing a specific method into research without considering these factors and encourages viewers to explore a range of methods to find the most suitable ones for their research needs.
🎓 Recap and Conclusion
The video concludes with a recap of the key points covered, including the definition of quantitative data analysis, the distinction between descriptive and inferential statistics, common statistical metrics, and the process of choosing the right statistical methods based on data type and research objectives. The speaker encourages viewers to engage with the content, use the resources provided, and consider the coaching services offered for research support. The video ends with a call to action for viewers to like, comment, and subscribe for more research-related content.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Quantitative Data Analysis
💡Descriptive Statistics
💡Inferential Statistics
💡Population and Sample
💡Mean
💡Median
💡Mode
💡Standard Deviation
💡Skewness
💡T-Tests
💡ANOVA
Highlights
Quantitative data analysis is the process of analyzing numerical data, which can include both categorical and numerical data.
Quantitative analysis is generally used for three purposes: measuring differences between groups, assessing relationships between variables, and testing hypotheses in a scientifically rigorous way.
Descriptive statistics and inferential statistics are the two main branches of statistical methods used in quantitative analysis.
Descriptive statistics focus on describing the sample data, while inferential statistics aim to make predictions about the entire population based on the sample findings.
Common descriptive statistical metrics include the mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and skewness.
T-tests, ANOVA, correlation analysis, and regression analysis are common inferential statistical methods used to make predictions about the population.
The choice of statistical methods should align with the type of data collected, the research questions, and the hypotheses.
Understanding the level of measurement and the shape of the data is crucial for selecting appropriate statistical methods.
Descriptive statistics serve a critical role in research by providing a macro and micro-level view of the data, helping to spot potential errors, and informing the choice of inferential statistical methods.
The population in statistics refers to the entire group of interest, while the sample is the subset of that population that is actually accessed for data collection.
The concept of normal or parametric distribution and non-normal or non-parametric distribution is important in understanding the shape of data for statistical analysis.
Statistical methods have their own assumptions and limitations, which must be considered when choosing the right analysis method.
The composition of the sample is crucial for inferential statistics, as it affects the representativeness and usefulness of the findings.
Grad Coach TV aims to demystify and simplify the often intimidating world of academic research.
The video provides a comprehensive breakdown of quantitative analysis, making it accessible for those who may avoid numbers and math.
Practical examples, such as body weight data, are used to illustrate the application of descriptive statistics in understanding data sets.
The video emphasizes the importance of not rushing past descriptives to get to inferential methods, as this can lead to flawed results.
The video concludes with a recap of the key points discussed, reinforcing the understanding of quantitative data analysis and its application in research.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Inferential Statistics FULL Tutorial: T-Test, ANOVA, Chi-Square, Correlation & Regression Analysis

How to Use SPSS: Choosing the Appropriate Statistical Test
Choosing a Statistical Test for Your IB Biology IA

Choosing a Statistical Test

Descriptive Statistics: FULL Tutorial - Mean, Median, Mode, Variance & SD (With Examples)
PRACTICAL RESEARCH 1 - Qualitative and Quantitative Research - EP.5 (Research Simplified)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: