Calculus AB/BC – 6.6 Applying Properties of Definite Integrals
TLDRIn this educational video, Mr. Bean explores the properties of definite integrals, using visual examples to explain how to calculate the area under a curve. He covers the effects of reversing limits, constant multiplication, and the addition and subtraction of integrals. The video also touches on more complex topics like piecewise functions and absolute values, emphasizing the importance of practice and the use of a calculator for accurate calculations.
Takeaways
- 📚 Properties of definite integrals are explored, including the effects of changing limits and the impact of constants.
- 🔄 When the limits of integration are reversed, the sign of the integral changes, as demonstrated by the example of integrating from 0 to 12 versus from 12 to 0.
- 🎯 The area under a curve from a specific point to the same point (e.g., from a to a) results in zero, as there is no width in the interval.
- 🔢 Multiplying the function by a constant factor moves the constant to the front of the integral, following a similar rule to the constant rule in derivatives.
- 📈 The properties of integrals allow for breaking up the integration interval (e.g., from a to c and then from c to b) and adding the results.
- ➕ The addition and subtraction properties of integrals enable the separate calculation of integrals for different functions and the combination of their results.
- 🤔 Sometimes, based on the given information, it's not possible to determine the value of an integral, which is an acceptable answer on exams like the AP exam.
- 📊 Piecewise functions are treated like regular functions when calculating definite integrals; their geometric shapes are used to find the area under the curve.
- 🏷️ Absolute value functions create V-shaped graphs and are treated as piecewise functions, with the integral representing the area under the curve up to a certain point.
- 🧮 The use of a calculator is essential for calculating integrals, especially when the shapes are complex or not easily calculated by hand.
- 🛠️ Practice with a calculator is crucial for mastering the calculation of integrals, and students should familiarize themselves with the specific functions of their calculator model.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is the properties of definite integrals and how they can be used to calculate the area under a curve.
How does Mr. Bean introduce the concept of definite integrals in the video?
-Mr. Bean introduces the concept of definite integrals by discussing the area under a curve and using an example of a definite integral from 0 to 12, explaining how to account for areas under the x-axis.
What is the significance of reversing the limits of integration in the video's examples?
-Reversing the limits of integration changes the sign of the area under the curve. This is important because it affects how the area is calculated when moving from one point to another in the opposite direction.
What happens when the lower and upper limits of a definite integral are the same?
-When the lower and upper limits of a definite integral are the same, the area under the curve is zero, as there is no width to the region being integrated.
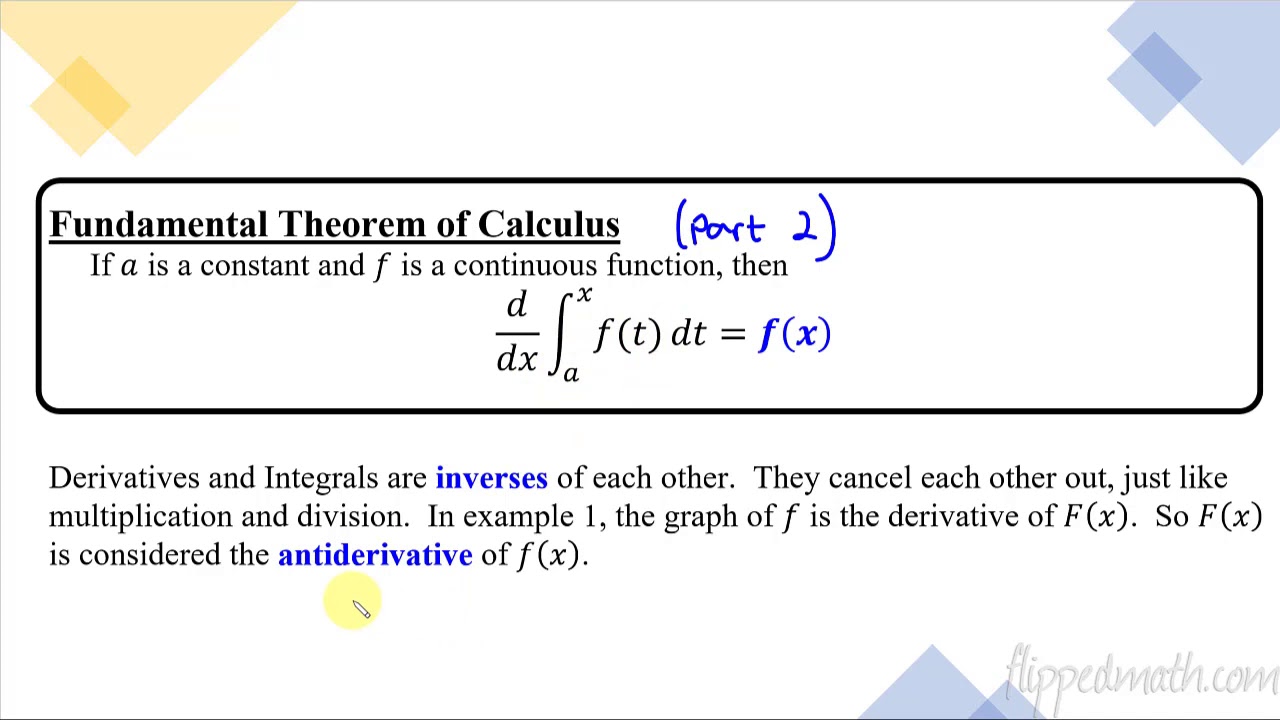
How does the video explain the property of multiplying a definite integral by a constant?
-The video explains that when a definite integral is multiplied by a constant, the constant can be factored out and brought to the front of the integral, similar to the constant rule with derivatives.
What is the rule for integrating over a piecewise function as explained in the video?
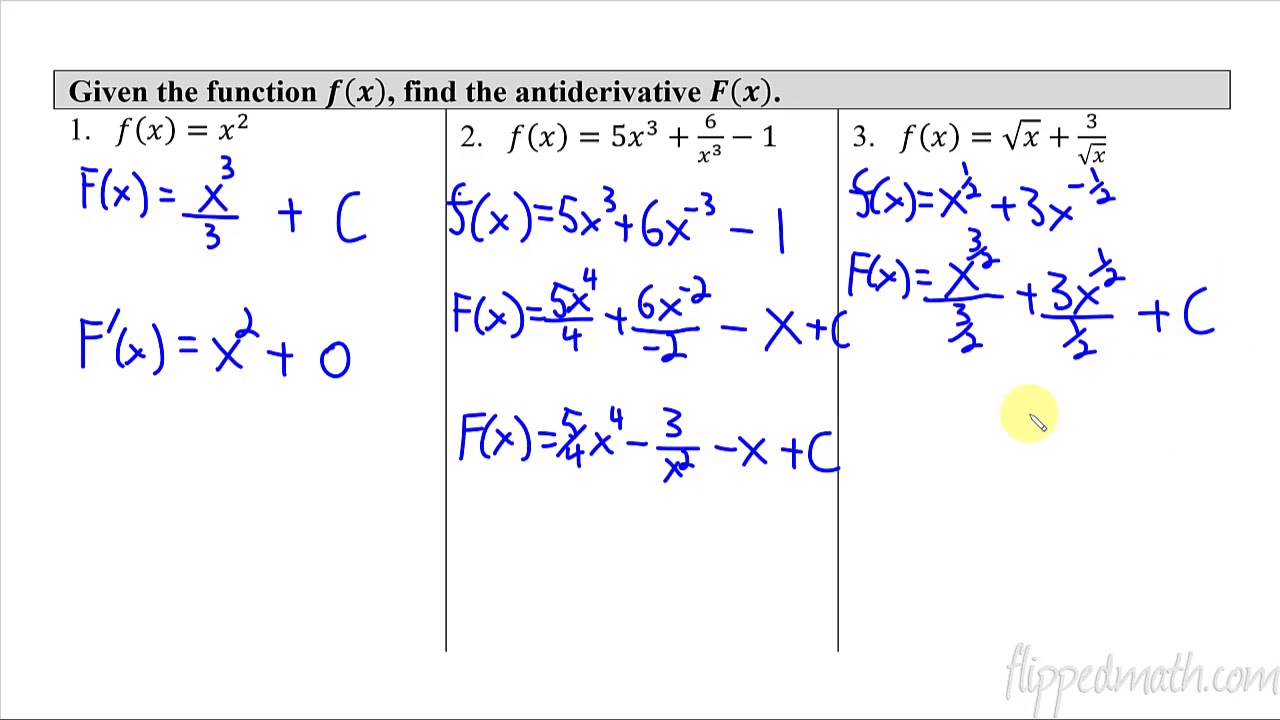
-The rule for integrating over a piecewise function is to treat each piece of the function separately, calculating the area under each piece and then summing these areas to find the total area under the curve.
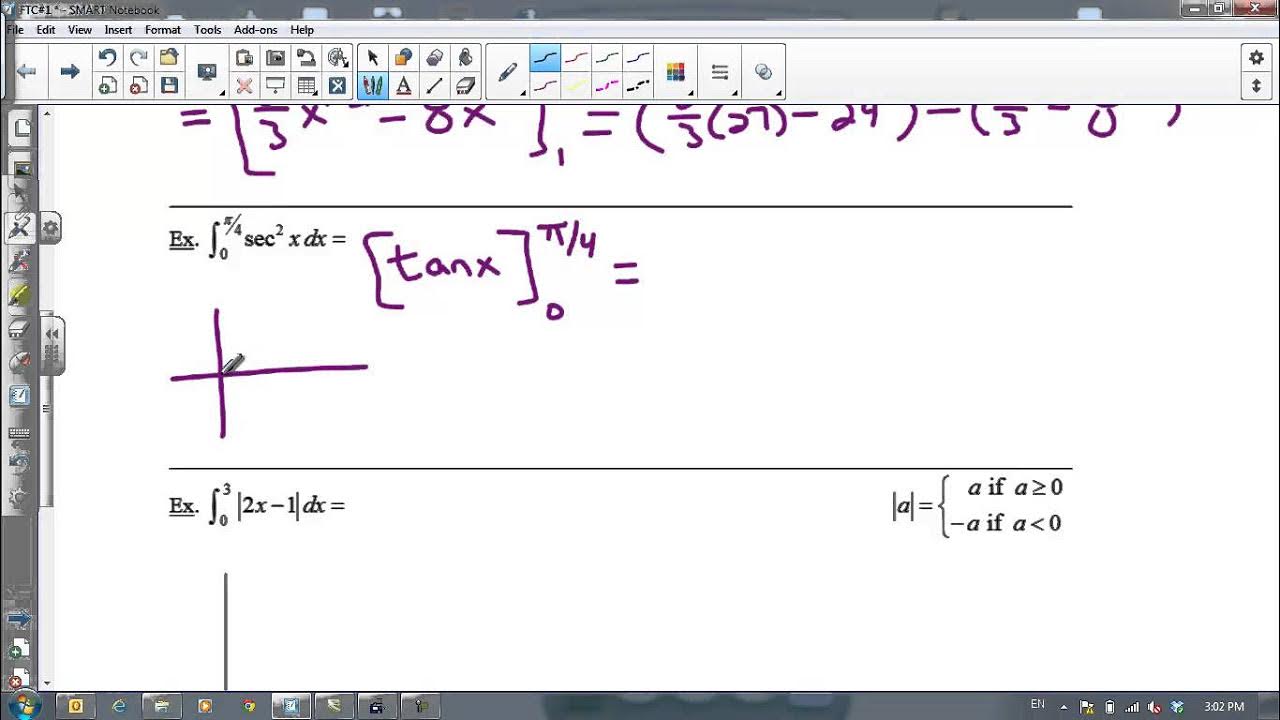
How does the video demonstrate the difference between taking the absolute value of an integral and integrating the absolute value of a function?
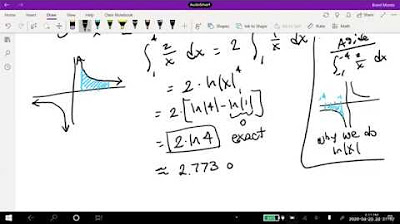
-The video shows that taking the absolute value of an integral means calculating the integral and then taking the absolute value of the result, making all areas positive. In contrast, integrating the absolute value of a function means that the negative areas under the x-axis are flipped to become positive, changing the result significantly.
Why does Mr. Bean emphasize the use of a calculator for certain integrals in the video?
-Mr. Bean emphasizes the use of a calculator for certain integrals because it is a fast and easy way to calculate the area under the curve when a geometric approach is not straightforward or when the calculator is allowed in an exam setting.
What is the specific example given in the video for demonstrating the use of a calculator to find an integral?
-The specific example given is the integral of (x - 1) square root from 2 to 3. Mr. Bean demonstrates how to use a calculator to find this integral, showing that the result is approximately 1.218 or 1.219.
What advice does Mr. Bean give for practicing the concepts discussed in the video?
-Mr. Bean advises viewers to practice sketching graphs, understanding piecewise functions, and using a calculator to calculate integrals, especially when it is allowed in an exam setting.
Outlines
📚 Properties of Definite Integrals
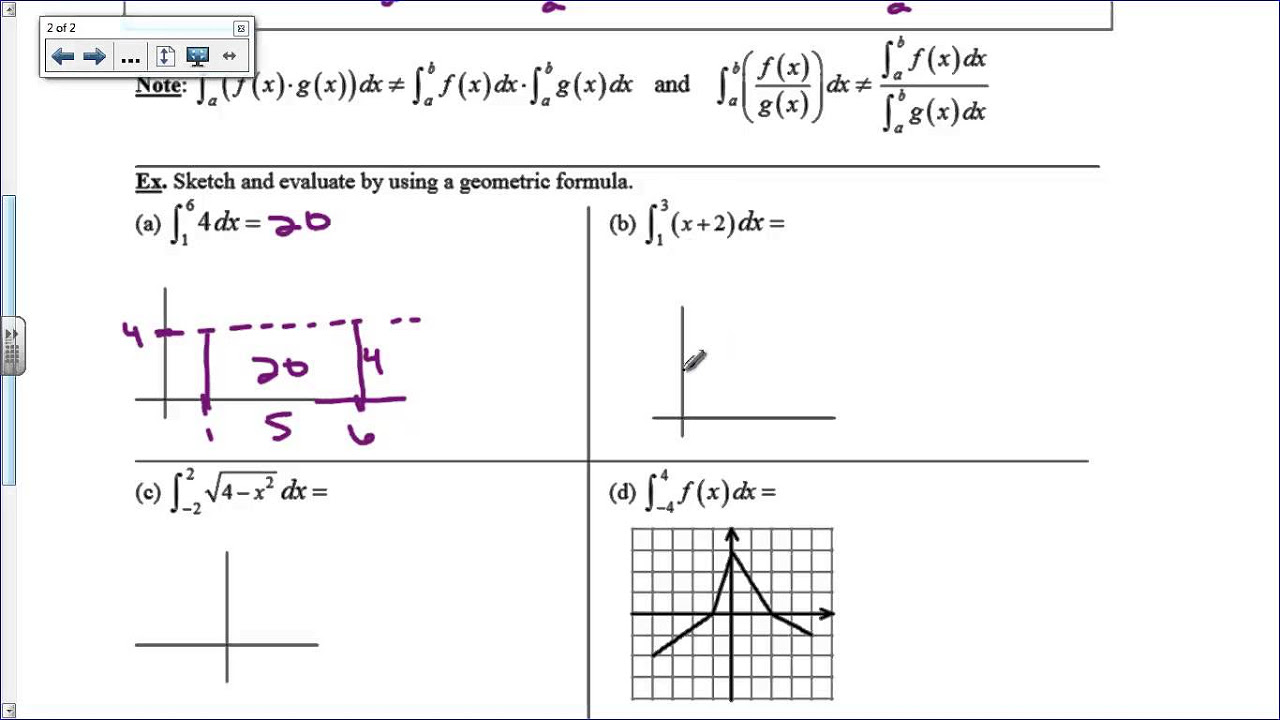
This paragraph introduces the properties of definite integrals, using examples to illustrate how integrals work with areas under curves. Mr. Bean explains how to calculate the area from 0 to 12 and how the area changes when the limits of integration are reversed. He also discusses the properties of integrals when the limits are the same (resulting in zero), and when constants are involved in the integration process. The concept of breaking down an integral into smaller parts (from a to c and then c to b) is also explained, along with the basic operations of addition and subtraction of integrals.
🔢 Solving Integrals with Different Limits
In this section, the speaker continues to explore definite integrals by demonstrating how to solve them when the limits of integration are different. He uses the properties of integrals to manipulate expressions and find solutions. The paragraph covers the calculation of integrals with negative limits, the addition of integrals from different intervals, and the concept of 'cannot be determined' when there's insufficient information. The speaker also introduces piecewise functions and explains how to calculate the area under such functions, emphasizing the importance of geometric understanding.
📊 Absolute Value Functions and Calculator Practice
This paragraph delves into the specifics of dealing with absolute value functions in the context of integration. The speaker clarifies the difference between taking the absolute value of an integral and integrating the absolute value of a function. He provides visual examples and explains how to interpret the results. Additionally, the speaker highlights the importance of calculator usage for solving integrals, especially when it's allowed, and guides through the process of using a calculator to find the area under a curve, specifically for a square root function over a given interval.
🎓 Mastery Check and Next Steps
The final paragraph wraps up the lesson with a mastery check, encouraging viewers to practice the concepts learned. The speaker advises on the use of calculators for quick and easy calculations of integrals, especially when they are allowed in assessments. He also previews upcoming lessons, hinting at more in-depth exploration of calculating areas under curves by hand, and encourages viewers to practice sketching graphs and using calculators to solidify their understanding of the material.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Definite Integrals
💡Properties of Integrals
💡Area Under the Curve
💡Piecewise Functions
💡Absolute Value Functions
💡Calculus
💡Limits
💡Constant Multiplication
💡Geometry
💡Calculator
💡Master Check
Highlights
Introduction to the properties of definite integrals and their applications.
Explanation of how the area under a curve can be calculated using definite integrals.
Illustration of how the definite integral from 0 to 12 is computed.
Discussion on reversing limits of integration and the resulting change in sign of the integral.
Explanation of what happens when the lower and upper limits of integration are the same.
Clarification on multiplying the integral by a constant and the effect it has on the result.
Demonstration of how to break down an integral into smaller parts when the limits are not in order.
Introduction to the property of addition for integrals and how to apply it.
Explanation of the subtraction property for integrals and its application.
Example of how to deal with piecewise functions in the context of integration.
Discussion on the treatment of absolute value functions in integration.
Explanation of the difference between taking the absolute value of the integral and integrating the absolute value of a function.
Emphasis on the importance of practicing the calculation of integrals using a calculator.
Demonstration of how to use a calculator to find the area under a curve defined by a function.
Explanation of the graphical approach to understanding the area under the curve of a square root function.
Conclusion and encouragement to practice the concepts learned in the lesson.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: