AP Physics B Kinematics Presentation #12
TLDRThe video script discusses the analysis of a position versus time graph to determine an object's velocity. It clarifies that velocity is the slope of the graph, calculated by the change in position over time. By selecting two points on the graph, the script calculates a constant velocity of 5 meters per second. It then systematically eliminates incorrect choices regarding the object's velocity, concluding that the correct answer is 'c', indicating the object's velocity remains unchanged, as the graph's slope is constant and non-zero.
Takeaways
- 📊 The script discusses how to interpret a position versus time graph to determine the motion of an object.
- 🔍 It emphasizes the importance of identifying the type of graph before attempting to answer the question.
- 🏃 The script focuses on velocity, which is a key concept in understanding the object's motion.
- ❌ It dismisses option 'e' (more information is required) early, assuming that the given data is sufficient for analysis.
- 📐 The script explains that velocity can be calculated as the change in position over the change in time.
- 📈 It demonstrates the calculation of velocity by selecting two points on the graph and determining the slope.
- 🔢 The example provided calculates a velocity of 5 meters per second from the given position-time graph.
- 📉 The script refutes options 'a' and 'b', stating that the velocity does not increase or decrease since the slope is constant.
- 🚫 It clarifies that option 'd' is incorrect because the object has a non-zero velocity and is not at rest.
- 🎯 The correct answer, according to the script, is 'c', indicating that the object's velocity remains unchanged.
- 📝 The script concludes by highlighting that the given information is adequate to deduce the correct answer without needing more data.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the script?
-The main topic discussed in the script is how to analyze a position versus time graph to determine the velocity of an object and answer a multiple-choice question based on the graph.
What is the first step suggested in the script for solving the problem?
-The first step suggested is to determine the type of graph provided, which in this case is a position versus time graph.
Why can we eliminate option 'e' at the beginning of the problem-solving process?
-Option 'e' stating more information is required can be eliminated initially because if all other options are wrong, it would be the last resort. The script implies that the given information should be sufficient to make a determination.
How is velocity related to the graph in the script?
-Velocity is related to the graph as the slope of the line in a position versus time graph, which represents the change in position over the change in time.
What method does the script use to calculate velocity from the graph?
-The script uses the method of selecting two points on the graph, calculating the change in position and change in time, and then determining the slope of the line, which is the velocity.
What is the calculated velocity from the example given in the script?
-The calculated velocity from the example is 5 meters per second, obtained by dividing the change in position (40 meters) by the change in time (8 seconds).
Why is option 'a' incorrect according to the script?
-Option 'a' is incorrect because the script proves that the velocity is constant at 5 meters per second and does not increase.
Why is option 'b' incorrect based on the script's explanation?
-Option 'b' is incorrect because it suggests the velocity decreases, but the script establishes that the velocity remains constant.
What does option 'c' state and why is it correct according to the script?
-Option 'c' states that the object's velocity stays unchanged, which is correct because the script demonstrates that the velocity is constant at 5 meters per second with an unchanging slope.
Why is option 'd' not the correct answer in the context of the script?
-Option 'd' is incorrect because it suggests the object is at rest, but the script shows that the object has a non-zero velocity and is therefore moving.
What does the script imply about the sufficiency of the information provided for the problem?
-The script implies that the information provided is sufficient to deduce the correct answer, making option 'e' unnecessary in this context.
Outlines
📈 Understanding Velocity from a Position-Time Graph
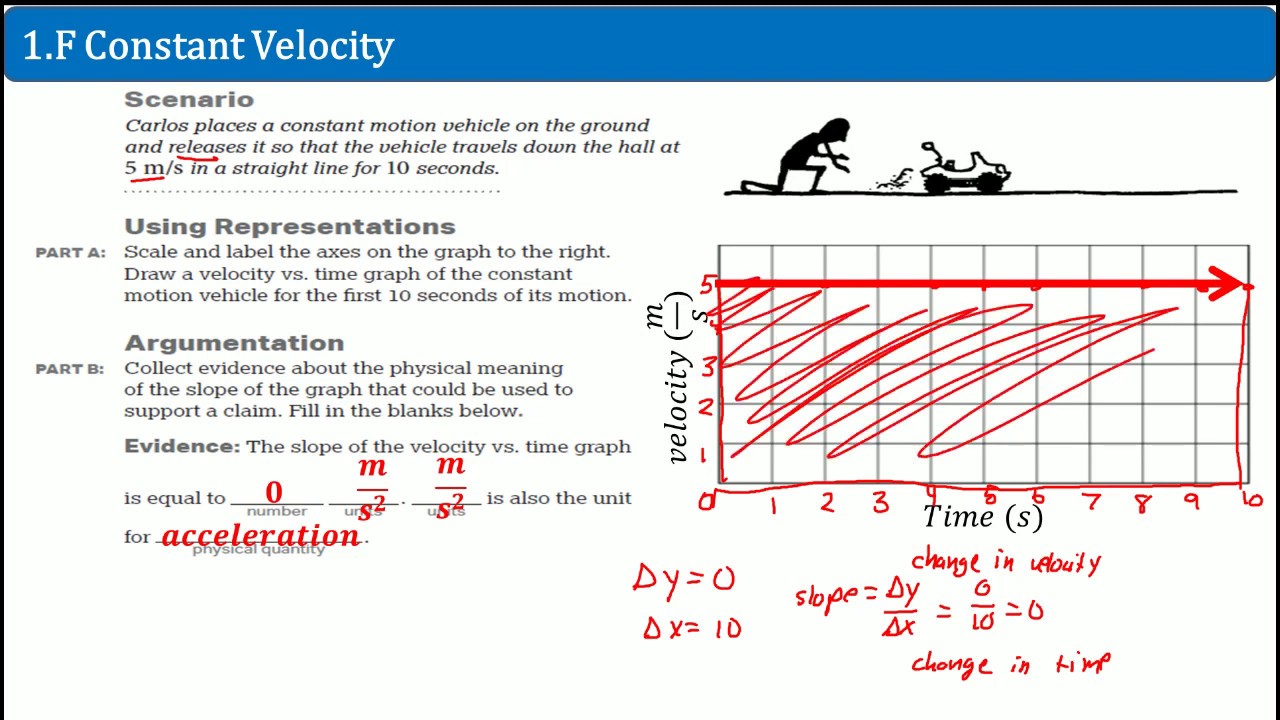
This paragraph explains how to determine the state of an object's motion from a position versus time graph. The speaker clarifies that velocity is the rate of change of position with respect to time. By selecting two points on the graph and calculating the slope, the speaker deduces a constant velocity of 5 meters per second. The explanation refutes options a and b, which suggest increasing or decreasing velocity, and dismisses option d, which implies the object is at rest. The correct answer, according to the analysis, is option c, which states that the object's velocity remains unchanged.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Velocity
💡Position-Time Graph
💡Slope
💡Acceleration
💡Deceleration
💡Rest
💡Constant Velocity
💡Change in Position
💡Change in Time
💡More Information Required
Highlights
The problem involves determining the state of an object's velocity from a position versus time graph.
Choices involve changes in velocity or the possibility of needing more information.
The key to solving the problem is understanding the relationship between velocity and the slope of the position-time graph.
Velocity is calculated as the change in position over the change in time.
Selecting two points on the graph helps determine the slope, which represents velocity.
The final position is 40 meters at a time of eight seconds.
The initial position and time are both zero, simplifying the calculation of velocity.
The calculated velocity is 5 meters per second, derived from the slope of the graph.
The slope of the graph remains constant, indicating a constant velocity.
Choice A (velocity increases) is incorrect due to the constant velocity.
Choice B (velocity decreases) is also incorrect for the same reason.
Choice C (velocity stays unchanged) is correct, as the velocity is constant at 5 m/s.
Choice D (object at rest) is incorrect because the velocity is non-zero.
Choice E (more information required) is not applicable as the graph provides sufficient data.
The correct answer is C, as the velocity of the object remains unchanged throughout the motion.
The problem-solving process emphasizes the importance of understanding the concept of velocity in physics.
The method used in the transcript is a practical application of physics principles to interpret graphical data.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: