Example calculating t statistic for a test about a mean | AP Statistics | Khan Academy
TLDRIn this educational transcript, Rory conducts a t-test to investigate his suspicion that teachers in his district have less than five years of experience on average. With a sample of 25 teachers, a sample mean of four years, and a standard deviation of two years, Rory calculates the test statistic for his hypothesis. Assuming a normal distribution and meeting all conditions for inference, he aims to determine if the p-value supports rejecting the null hypothesis of a five-year mean experience, suggesting an alternative of less experience.
Takeaways
- 🔍 Rory is testing a hypothesis about the average years of experience of teachers in his school district, suspecting it's less than five years.
- ⚠️ The null hypothesis states that the average experience is exactly five years, while the alternative hypothesis suggests it's less than five years.
- 📝 Rory has a sample size of 25 teachers, with a sample mean of four years and a sample standard deviation of two years.
- 📊 To test his hypothesis, Rory is using a t-test, which is appropriate for means when the population standard deviation is unknown.
- 🧐 The significance test will determine the probability of getting a sample mean as low or lower than observed, assuming the null hypothesis is true.
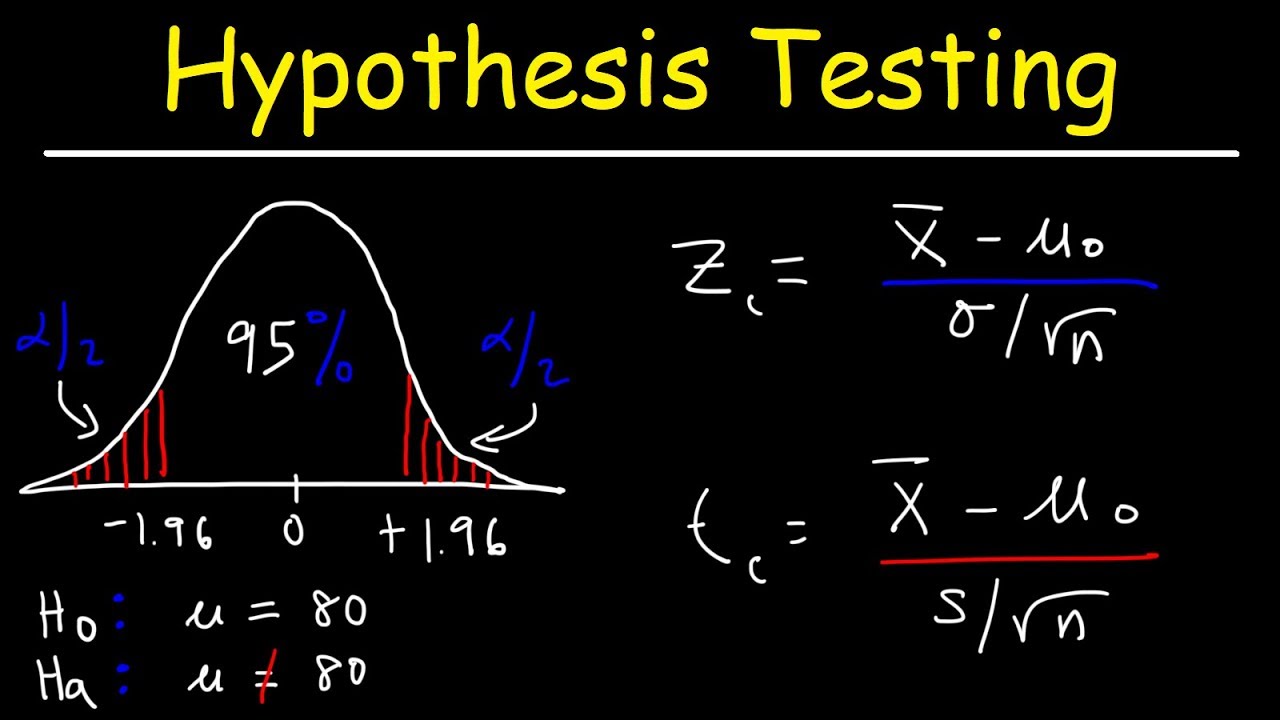
- 📐 The t-statistic is calculated by subtracting the assumed mean from the sample mean and dividing by the standard error of the mean, which is the sample standard deviation divided by the square root of the sample size.
- 🔢 Rory's t-statistic calculation involves a numerator of -1 (4 - 5) and a denominator of √(2/25), resulting in a t-value of -2.5.
- 📚 Rory will look up this t-value in a t-distribution table to find the corresponding p-value, which represents the probability of observing such a low sample mean.
- 🚫 If the p-value is below a predetermined significance level (commonly 5% or 1%), Rory will reject the null hypothesis, supporting his suspicion of less than five years of average experience.
- 🤔 The script reminds us that all conditions for inference have been met, including the assumption of a random sample and the normality of the sampling distribution.
- 🔄 The conditions also imply that the observations are independent, possibly with replacement, or that the sample size is less than 10% of the population.
Q & A
What is Rory's null hypothesis regarding the average years of experience of teachers in his school district?
-Rory's null hypothesis is that the mean number of years of experience for teachers in his school district is five years.
What is Rory's alternative hypothesis in relation to the teachers' years of experience?
-Rory's alternative hypothesis is that the true mean of years of experience for teachers in his school district is less than five years.
How many teachers did Rory sample to test his hypothesis?
-Rory sampled 25 teachers to test his hypothesis.
What was the sample mean of years of experience for the teachers Rory surveyed?
-The sample mean of years of experience for the teachers Rory surveyed was four years.
What was the sample standard deviation of years of experience in Rory's sample?
-The sample standard deviation of years of experience in Rory's sample was two years.
What type of test does Rory plan to conduct to analyze the sample data?
-Rory plans to conduct a t-test on the mean to analyze the sample data.
Why might Rory choose a t-test instead of a z-test for his analysis?
-Rory chooses a t-test because the population standard deviation is unknown, which is a common scenario when working with sample data rather than the entire population.
What is the formula for calculating the t-test statistic based on Rory's scenario?
-The formula for calculating the t-test statistic is (Sample Mean - Assumed Population Mean) / (Sample Standard Deviation / √Sample Size).
What is the calculated t-test statistic value for Rory's test?
-The calculated t-test statistic value for Rory's test is -2.5.
How does Rory determine whether to reject the null hypothesis based on the t-test statistic?
-Rory will compare the t-test statistic to a t-distribution table to find the associated p-value. If the p-value is below a preset significance level (e.g., 5% or 1%), he will reject the null hypothesis.
What assumptions were made about the sample and population for Rory's t-test to be valid?
-The assumptions made include that the sample was truly random, the individual observations were independent, the sample size was less than 10% of the population, and the sampling distribution is roughly normal.
Outlines
🔍 Hypothesis Testing for Teacher Experience
Rory, suspecting that teachers in his school district have less than five years of experience on average, decides to test this hypothesis. He sets up a null hypothesis stating the mean experience is five years and an alternative hypothesis suggesting the true mean is less. Using a sample of 25 teachers with a mean of four years and a standard deviation of two years, Rory plans to conduct a t-test. The video explains the process of hypothesis testing, emphasizing the conditions for inference and the calculation of the test statistic. The t-statistic is calculated by taking the difference between the sample mean and the assumed population mean, divided by the sample standard deviation over the square root of the sample size, resulting in a value of -2.5. Rory will then compare this value to a t-distribution to find the p-value, which will determine if the null hypothesis should be rejected.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Null Hypothesis
💡Alternative Hypothesis
💡Sample Mean
💡Sample Standard Deviation
💡t-test
💡Significance Level
💡p-value
💡Test Statistic
💡Sampling Distribution
💡Conditions for Inference
Highlights
Rory suspects that teachers in his school district have less than five years of experience on average.
Null hypothesis is that the mean number of years of experience is five years.
Alternative hypothesis is that the true mean of years of experience is less than five years.
A sample of 25 teachers is used for the t test.
Sample mean is four years, and sample standard deviation is two years.
Significance tests determine the probability of getting a sample mean this low or lower if the null hypothesis is true.
A t test is used instead of a z test due to unknown population standard deviation.
The t statistic is calculated using the formula (sample mean - assumed mean) / (sample standard deviation / sqrt(sample size)).
The calculated t statistic is negative 2.5.
The t value is looked up on a t table to find the p value.
A p value below a preset significance level suggests rejecting the null hypothesis.
If the null hypothesis is rejected, it supports Rory's suspicion of less than five years of experience on average.
All conditions for inference have been met, including random sampling and independence of observations.
The sample size is less than 10% of the population, ensuring the sampling distribution is roughly normal.
The significance level, such as 5% or 1%, is preset before conducting the test.
The t test is a common method for hypothesis testing when dealing with means and unknown population standard deviation.
The process emphasizes the importance of understanding the conditions for conducting a valid t test.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
Calculating Power and the Probability of a Type II Error (A One-Tailed Example)
P-values and significance tests | AP Statistics | Khan Academy
Explaining The One-Sample t-Test

Hypothesis testing and p-values | Inferential statistics | Probability and Statistics | Khan Academy
8.3.2 Testing a Claim About a Mean - Sigma Known and When the Sampling Distribution Isn't Normal
Hypothesis Testing Problems - Z Test & T Statistics - One & Two Tailed Tests 2
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: