Parallel, Intersection and Perpendicular Line
TLDRThis educational script explores the concepts of parallel, intersecting, and perpendicular lines. It uses the analogy of two cars' paths to illustrate intersecting lines, which meet at a point, forming an angle. The script then introduces perpendicular lines, characterized by a right angle, and demonstrates how to identify them using a model angle. It also addresses the concept of parallel lines, which never intersect, and explains a method to verify their parallelism by measuring the distance between them using perpendicular lines. The lesson concludes with the symbols used to denote perpendicularity and parallelism, effectively teaching viewers how to identify and draw these types of lines.
Takeaways
- 😀 Lines have the property of extending infinitely in both directions.
- 🚗 The concept of intersecting lines is introduced through the analogy of two cars meeting at a point.
- 📐 Intersecting lines form an angle where they meet, which can be identified visually.
- 🔍 A right angle is a specific type of angle formed by intersecting lines, and it can be verified with a model angle.
- ⊥ The symbol used to denote that one line is perpendicular to another is introduced.
- 👀 All lines that intersect and form right angles are classified as perpendicular lines.
- 🤔 Not all lines intersect; some may appear to be non-intersecting within a certain view but will meet if extended.
- 🔄 The concept of parallel lines is introduced, which are lines that never intersect no matter how far they are extended.
- 📏 A method to determine if lines are parallel involves drawing perpendicular lines from one line to another and checking if the perpendicular distances are equal.
- 🔄 The symbol used to denote that one line is parallel to another is explained.
- 📚 The lesson covers the identification and drawing of parallel, intersecting, and perpendicular lines.
Q & A
What is the definition of intersecting lines?
-Intersecting lines are two lines that meet at a point, forming an angle where they cross each other.
How can you visually identify intersecting lines in a scenario like cars moving on a road?
-Intersecting lines can be identified by observing if the paths of the cars meet at a point, forming an angle indicative of their crossing paths.
What is the term for intersecting lines that form a right angle?
-Lines that intersect to form a right angle are called perpendicular lines.
How can you verify if two intersecting lines are perpendicular using a model angle?
-You can verify if two intersecting lines are perpendicular by checking if the angle formed is a right angle, typically 90 degrees, using a model angle or a protractor.
What symbol is used to denote that one line is perpendicular to another?
-The symbol used to denote that line EF is perpendicular to line XY is '⊥', read as 'EF is perpendicular to XY'.
What is the definition of parallel lines?
-Parallel lines are two lines in the same plane that do not meet; they are always the same distance apart and will never intersect.
How can you determine if two lines are parallel, especially when they seem to be moving apart?
-You can determine if two lines are parallel by drawing a perpendicular line from one line to the other and checking if the distance between the two lines remains constant at all points.
What is the method to check if two lines are parallel using perpendicular lines?
-To check if two lines are parallel, draw a perpendicular line from one line to the other at one point, and then draw another perpendicular line from the first line to the second at a different point. If the lengths of these two perpendicular lines are equal, the original lines are parallel.
What symbol is used to denote that one line is parallel to another?
-The symbol used to denote that line GH is parallel to line KL is '∥', read as 'GH is parallel to KL'.
What are the key concepts covered in this lesson about lines?
-The key concepts covered in this lesson are identifying and drawing parallel, intersecting, and perpendicular lines.
Why is it important to understand the concepts of intersecting, perpendicular, and parallel lines in geometry?
-Understanding these concepts is important in geometry as they form the basis for more complex geometrical figures and relationships, and are essential in various mathematical proofs and real-world applications.
Outlines
🚗 Understanding Intersecting, Parallel, and Perpendicular Lines
This paragraph introduces the concepts of intersecting, parallel, and perpendicular lines. It uses the analogy of two cars moving in different directions to explain how lines can intersect at a point, forming an angle. The script clarifies that intersecting lines form an angle, and when this angle is a right angle, the lines are referred to as perpendicular. The paragraph also discusses how to identify parallel lines, which never intersect, by checking if the perpendicular distances between them remain constant. The use of symbols to denote perpendicularity and parallelism is introduced.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Intersecting Lines
💡Perpendicular Lines
💡Parallel Lines
💡Angle
💡Right Angle
💡Model Angle
💡Distance
💡Perpendicular Line
💡Symbol
💡Geometry
💡Extend
Highlights
Lines can be parallel, intersecting, or perpendicular, and they extend infinitely in both directions.
Intersecting lines meet at a point and form an angle.
A right angle is formed when two lines are perpendicular to each other.
Perpendicular lines can be identified by the right angle they form upon intersection.
The symbol used to denote one line being perpendicular to another is introduced.
Not all lines intersect; some may only appear to intersect if extended.
Parallel lines never intersect, no matter how far they are extended.
A method to check if two lines are parallel involves drawing perpendicular lines to one and intersecting it with the other.
If the lengths of two perpendicular lines drawn from one line to another are equal, the original lines are parallel.
The distance between parallel lines remains constant, which is a key characteristic.
The symbol used to denote one line being parallel to another is explained.
The lesson covers how to identify and draw parallel, intersecting, and perpendicular lines.
A practical example using cars and their paths to illustrate intersecting lines is provided.
A practical example using cars and their paths to illustrate perpendicular lines is provided.
A practical example using cars and their paths to illustrate parallel lines is provided.
The importance of extending lines to determine if they are parallel or intersecting is emphasized.
The lesson concludes with a summary of how to identify different types of lines and their relationships.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

PARALLEL, INTERSECTING & PERPENDICULAR LINES | GRADE 4
Parallel, Intersecting, and Perpendicular Lines | Geometry | Math with Mr. J
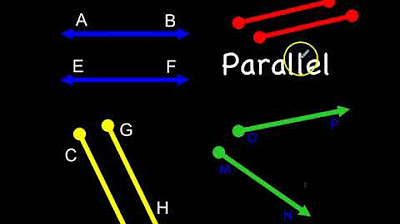
Parallel, Intersecting, & Perpendicular Lines

Parallel Lines and Perpendicular Lines - Nerdstudy

Using Parallel Structures || GRADE 8 || MELC-based VIDEO LESSON | QUARTER 3 | MODULE 6
Parallel & Perpendicular Lines, Alternate Interior & Exterior Angles, Transversals
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: