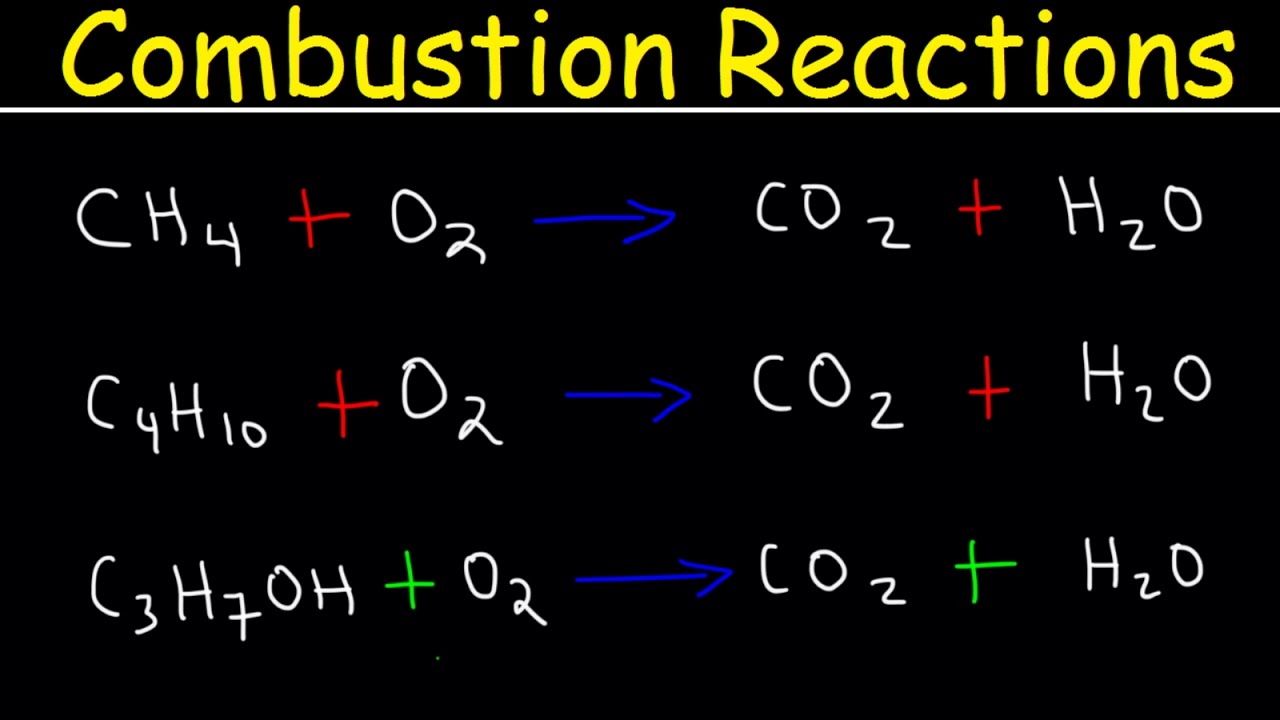
How To Balance Combustion Reactions
TLDRThis video tutorial offers a step-by-step guide to balancing complex combustion reactions, emphasizing the importance of counting oxygen atoms and balancing carbon and hydrogen first. The presenter demonstrates the process using butane and a more challenging compound, C100H202, showing how to adjust coefficients for oxygen last and achieve a balanced equation. The key takeaway is to ensure all oxygens are accounted for, use fractions to correct oxygen balance, and multiply by two for whole number coefficients, making the process accessible and clear.
Takeaways
- 🔍 Start by balancing the carbons and hydrogens in a combustion reaction, leaving the oxygens to be balanced last.
- 📝 Always count all the oxygen atoms on the product side, including those in both carbon dioxide and water (H2O).
- 🔄 Use fractions to balance the oxygen atoms in the equation, ensuring the total number of oxygens on both sides is equal.
- ⚖️ If you want whole numbers for coefficients, multiply the entire equation by an appropriate factor to eliminate fractions.
- 📐 Demonstrated the process of balancing butane combustion, emphasizing the importance of balancing carbon and hydrogen first.
- 📉 Showed an example of balancing a more complex combustion reaction with C100H202, highlighting the step-by-step approach.
- 📚 Stressed the importance of not forgetting to count oxygens in water molecules when balancing combustion reactions.
- 🔑 Provided a method to fix the oxygen balance by using the fraction to adjust the coefficients of the oxygen-containing products.
- 📈 Gave a final example of how to achieve whole number coefficients by multiplying through the equation by 2.
- 👨🏫 Presented by Dr. B, who offered clear instructions and examples for balancing tough combustion reactions.
- 📝 Encouraged viewers to pause and practice balancing the given combustion reactions to reinforce learning.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video script?
-The main topic of the video script is how to balance combustion reactions, specifically focusing on complex organic compounds like butane and a hypothetical compound C100H202.
Why is it important to count all the oxygens on the product side of the equation?
-It is important to count all the oxygens on the product side because it ensures that the oxygen atoms in carbon dioxide and water are accurately accounted for, which is crucial for balancing the equation correctly.
What is the recommended order for balancing atoms in a combustion reaction?
-The recommended order is to balance the carbons and hydrogens first, and then balance the oxygens last.
Why should oxygens be balanced last in a combustion reaction?
-Oxygens should be balanced last because they are often involved in multiple products (like CO2 and H2O), and adjusting for oxygen last helps to ensure that the entire equation is balanced without overcomplicating the process.
What is the purpose of using a fraction to fix the oxygens in the equation?
-Using a fraction to fix the oxygens helps to balance the number of oxygen atoms on both sides of the equation, ensuring that the reaction is chemically accurate.
Why might one want to multiply all coefficients by 2 after balancing the equation?
-Multiplying all coefficients by 2 is done to convert the equation to whole numbers, which are often easier to work with and understand.
What does the script suggest for dealing with complex combustion reactions like C100H202?
-The script suggests following the same process: count all oxygens, balance carbons and hydrogens first, use a fraction to balance oxygens, and then multiply by a whole number to simplify the coefficients if desired.
What is the final step in the script's method for balancing butane combustion?
-The final step is to multiply the entire equation by 2 to convert the coefficients into whole numbers, resulting in coefficients of 2, 25, 16, and 18.
How does the script demonstrate the process of balancing a combustion reaction?
-The script demonstrates the process by walking through the step-by-step method of balancing butane and then applying the same method to a more complex compound, C100H202.
Who is the presenter of the video script?
-The presenter of the video script is Dr. B.
Outlines
🔍 Balancing Combustion Reactions
This paragraph introduces the process of balancing combustion reactions, emphasizing the importance of counting all oxygen atoms on the product side, including those in carbon dioxide and water. The speaker demonstrates how to balance butane by first addressing carbon and hydrogen atoms and then balancing the oxygen atoms last. A step-by-step guide is provided, including multiplying by a fraction to correct the oxygen count and, if desired, adjusting coefficients for whole numbers. The example of butane combustion is used to illustrate these steps.
🧩 Advanced Combustion Reaction Balancing
The paragraph presents a more challenging example of balancing a combustion reaction with the compound C100H202. The speaker guides the audience through the process of balancing the carbon and hydrogen atoms first, then recalculating the oxygen atoms to ensure the equation is balanced. The method of multiplying by a fraction to correct the oxygen count is reiterated, and the example concludes with the balanced equation. The speaker also suggests multiplying the entire equation by two to achieve whole number coefficients, providing the final balanced equation with these coefficients.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Combustion Reactions
💡Balancing Equations
💡Butane
💡Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
💡Hydrogen (H2O)
💡Coefficients
💡Fractions
💡Whole Numbers
💡C100 H202
💡Dr. B
💡Educational Content
Highlights
Balancing combustion reactions can be challenging, but the video provides a method to balance even complex ones like C100H202.
The key to balancing is to balance oxygen atoms last after counting all atoms on each side of the equation.
When balancing butane, the video demonstrates adding oxygens in CO2 and H2O to the product side, emphasizing not to forget this step.
Balancing carbons and hydrogens first before oxygens is a strategic approach shown in the video.
A step-by-step guide is provided to balance butane by first multiplying CO2 by 4 and then adjusting hydrogens accordingly.
Recalculating the number of oxygens after adjusting carbons and hydrogens is crucial to achieve balance.
The video explains how to fix the oxygen balance by using a fraction and then adjusting the coefficients.
Multiplying all coefficients by 2 is suggested for whole number coefficients, making the equation easier to read.
The video provides a balanced equation for butane combustion, demonstrating the effectiveness of the method.
An example of balancing a more complex combustion reaction, C100H202, is given to illustrate the method's applicability.
The importance of counting oxygens in both CO2 and H2O is reiterated for the C100H202 example.
The video shows how to balance carbons and hydrogens first in the C100H202 example, leaving oxygens for last.
A technique using a fraction to balance oxygens in the C100H202 example is demonstrated.
The final step in the C100H202 example is multiplying the equation by 2 to achieve whole number coefficients.
The video concludes with a summary of the key steps to balance combustion reactions effectively.
Dr. B emphasizes the importance of counting oxygens and balancing carbons and hydrogens before oxygens in the method.
The video provides a clear and practical guide to balancing tough combustion reactions, making it accessible to viewers.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: