Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
TLDRThis educational video simplifies organic chemistry reactions, teaching viewers to predict outcomes instead of memorizing. It covers combustion, oxidation, substitution, addition, and esterification reactions, using techniques like balancing equations and understanding reactivity. The script explains how methane, butane, ethanol, and other compounds react, and introduces tests like the bromine water test for distinguishing between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. It also highlights the industrial importance of saponification in soap making.
Takeaways
- 🔍 The video aims to simplify the understanding of various organic chemistry reactions using logical explanations and special techniques.
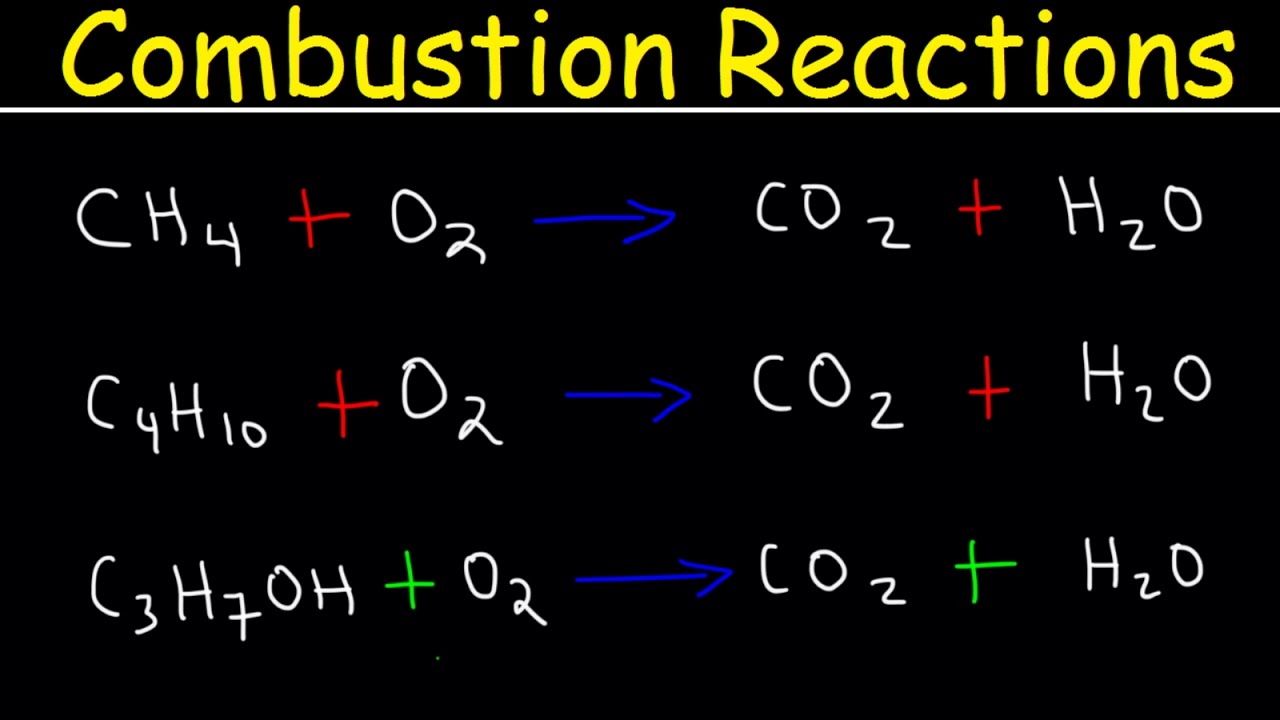
- 🔥 Combustion reactions involve organic compounds reacting with oxygen in the air to produce carbon dioxide, water vapor, and release heat and light energy.
- ⚖️ Balancing chemical equations is crucial for understanding the stoichiometry of reactions, such as in the combustion of methane and butane.
- 🌱 Methane is a component of CNG (Compressed Natural Gas), and butane is used in LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) cylinders, both serving as fuel sources.
- 🍾 Ethanol, or ethyl alcohol, when burned, follows the same combustion principles, producing carbon dioxide and water vapor, and is mixed with petrol in some regions.
- 🍾 Oxidation reactions, such as the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid using oxidizing agents, are controlled processes that differ from the rapid combustion reactions.
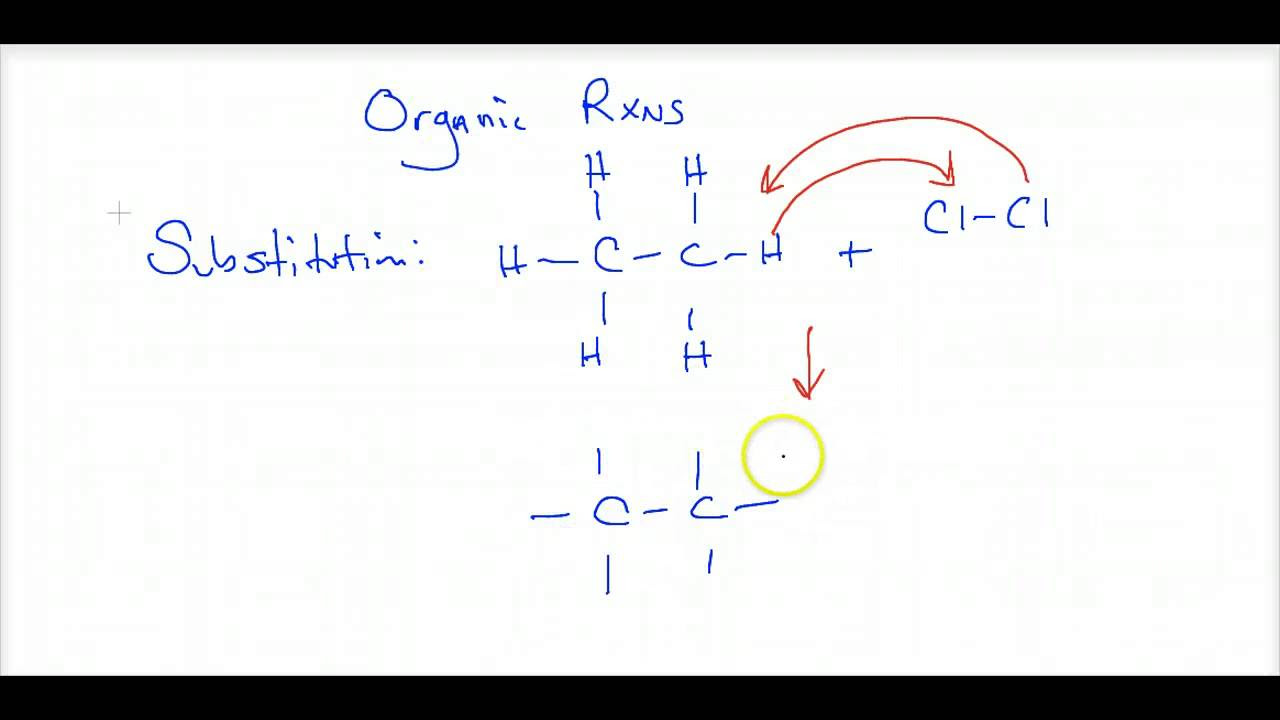
- 💧 Substitution reactions in saturated hydrocarbons like methane involve the replacement of hydrogen atoms with other atoms, such as chlorine, in the presence of sunlight.
- 🔗 Addition reactions in unsaturated hydrocarbons, such as alkenes and alkynes, involve the breaking of double or triple bonds and the addition of atoms like hydrogen.
- 🧪 The bromine water test is used to distinguish between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons based on the decolorization of bromine's reddish-brown color.
- 🍶 Esterification is the reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol to produce an ester and water, which can be identified by their sweet or fruity smell.
- 🧼 Saponification is the reaction of an ester with an alkali, like sodium hydroxide, to produce a sodium salt of the acid and alcohol, which is used in soap manufacturing.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of the video?
-The main purpose of the video is to simplify the understanding of various chemical reactions in organic chemistry, allowing viewers to predict reactions without memorization by explaining the logic and techniques behind each reaction.
What is the significance of balancing chemical equations in the context of the video?
-Balancing chemical equations is crucial as it ensures that the law of conservation of mass is adhered to, meaning the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation, reflecting a valid chemical reaction.
What happens when methane burns in air according to the video?
-When methane burns in air, it reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water vapor, and releases heat and light energy.
How does the presence of limited oxygen affect the combustion of organic compounds?
-In the presence of limited oxygen, the combustion of organic compounds results in the formation of carbon monoxide and water vapor, along with heat and light energy, instead of carbon dioxide.
What is the difference between combustion and oxidation as explained in the video?
-Combustion is a rapid and spontaneous process involving the reaction of a substance with oxygen, usually producing heat and light. Oxidation, on the other hand, is a controlled process where the substance reacts with oxidizing agents to incorporate oxygen into the compound.
What is the product of the oxidation of ethanol with oxidizing agents?
-The oxidation of ethanol with oxidizing agents like potassium permanganate or potassium dichromate results in the formation of ethanoic acid (acetic acid) and water.
What is a substitution reaction in organic chemistry?
-A substitution reaction in organic chemistry is a type of reaction where an atom or a group of atoms in a molecule is replaced by another atom or group of atoms, typically occurring in saturated hydrocarbons.
What is an addition reaction and how does it differ from a substitution reaction?
-An addition reaction is a type of chemical reaction where atoms or groups are added to a double or triple bond in a molecule, converting it into a single bond. It differs from a substitution reaction, where one atom or group replaces another in the molecule.
What happens when ethene (C2H4) reacts with bromine water?
-When ethene reacts with bromine water, an addition reaction occurs where the bromine atoms add across the double bond of ethene, forming 1,2-dibromoethene, and the reddish-brown color of the bromine water fades away.
What is the outcome of the esterification reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol?
-The esterification reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol results in the formation of an ester and water. This reaction is significant as it is used to produce sweet-smelling compounds and is a key process in the manufacture of perfumes and flavorings.
What is the purpose of using concentrated sulfuric acid in certain reactions shown in the video?
-Concentrated sulfuric acid is used as a dehydrating agent in reactions to remove water molecules, thus facilitating the formation of products like ethers or esters, and it can also act as a catalyst to speed up the reaction.
What is the significance of saponification in the soap industry?
-Saponification is a crucial process in the soap industry where fats or oils (esters) are reacted with an alkali like sodium hydroxide to produce soap, which is a sodium salt of a fatty acid, and glycerol. This reaction is essential for the manufacture of soaps and detergents.
Outlines
🔍 Introduction to Organic Chemistry Reactions
The video script introduces the complexity of organic chemistry reactions and offers a simplified approach to understanding them. The speaker promises to explain the logic and techniques behind various reactions, enabling viewers to predict outcomes instead of memorizing reactions. The video covers combustion, oxidation, substitution, and addition reactions, and encourages viewers to like, share, and subscribe for more content, including quizzes and additional resources.
🔥 Combustion Reactions in Organic Chemistry
This paragraph delves into combustion reactions, explaining that they involve the burning of compounds in air, reacting with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water vapor, along with heat and light. The script provides examples with methane and butane, demonstrating how to balance chemical equations. It also touches on the uses of these compounds, such as in CNG and LPG, emphasizing the importance of sufficient oxygen for safe and complete combustion.
🌡 Oxidation and Substitution Reactions
The script moves on to oxidation reactions, contrasting them with combustion by describing them as controlled processes involving oxidizing agents. It details the oxidation of ethanol to ethanoic acid using potassium permanganate or potassium dichromate. Substitution reactions are then introduced, with a focus on saturated hydrocarbons like methane, illustrating how chlorine can substitute hydrogen in the presence of sunlight, resulting in chlorinated hydrocarbons and hydrogen chloride.
💧 Hydrogenation and Addition Reactions
This section discusses addition reactions, particularly hydrogenation, where hydrogen is added to unsaturated hydrocarbons like alkenes and alkynes. The script uses ethene and ethyne as examples, showing how double and triple bonds break and are converted into single bonds with the addition of hydrogen. It also explains the industrial application of hydrogenation in converting oils into saturated fats, a process crucial for the production of certain types of food products.
🧪 Bromine Water Test for Unsaturation
The script introduces a practical test using bromine water to distinguish between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. It explains that the reddish-brown color of bromine fades in the presence of unsaturated compounds due to the addition reaction, while it remains unchanged with saturated compounds. This test is highlighted as a quick and visual method to identify the type of hydrocarbon and is applicable to differentiating between cooking oil and butter.
🍶 Reactions of Ethanol with Various Agents
Ethanol's reactions with different agents are explored, including its combustion to produce carbon dioxide and water, its oxidation to form acetic acid and water, and its reaction with sodium metal in a single displacement reaction to form sodium ethoxide and hydrogen gas. The script also covers the esterification of ethanol with acetic acid, producing ethyl acetate, a sweet-smelling ester that can be used as a test for the presence of carboxylic acids or alcohols.
🧪 Esterification and Reactions of Ethanoic Acid
The script continues with esterification reactions, focusing on the formation of esters from carboxylic acids and alcohols, specifically the production of ethyl esters. It also discusses the reactions of ethanoic acid with sodium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, and sodium hydroxide, resulting in the formation of sodium acetate, carbon dioxide, and water. These reactions are used as tests to identify the presence of ethanoic acid.
🧼 Saponification and Ester Hydrolysis
Saponification is introduced as a reaction where esters react with alkalis like sodium hydroxide to produce soap, a sodium salt of a fatty acid, and alcohol. The script explains that this process is fundamental to the soap industry, where fats or oils are heated with an alkali to produce soap and glycerol. The final reaction involves the esterification of ethanoic acid with ethanol, producing ethyl acetate and water, and is highlighted as a key reaction for testing the presence of carboxylic acids.
🚀 Conclusion and Call to Action
The video concludes by encouraging viewers to apply the learned techniques to predict organic reactions, emphasizing the importance of understanding over memorization. The speaker invites viewers to like, comment, share, and subscribe to the channel for more educational content. Links to additional resources, including a quiz and the speaker's website, are promised in the video description.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Combustion
💡Organic Chemistry
💡Hydrocarbons
💡Ethanol
💡Oxidation
💡Substitution Reaction
💡Addition Reaction
💡Esterification
💡Saponification
💡Bromine Water Test
Highlights
The video aims to simplify organic chemistry reactions using logic and special techniques to predict outcomes without memorization.
Combustion reactions of hydrocarbons produce carbon dioxide, water vapor, and release heat and light energy.
Balancing chemical equations is crucial, and a quick trick is demonstrated for hydrocarbon combustion.
Methane is used in CNG as a fuel, and butane in LPG cylinders, both producing carbon dioxide and water vapor upon combustion.
Ethanol, when burned, follows the same combustion pattern and is mixed with petrol due to its cost-effectiveness and energy production.
Oxidation reactions, unlike combustion, are controlled using oxidizing agents and result in the formation of ethanoic acid from ethanol.
Ethanol can be tested with sodium due to the production of hydrogen gas, which burns with a pop sound.
Substitution reactions in saturated hydrocarbons involve the replacement of hydrogen atoms by other atoms, like chlorine.
Addition reactions in unsaturated hydrocarbons break double or triple bonds, adding atoms like hydrogen across the bond.
Hydrogenation is the process of adding hydrogen to unsaturated fats, converting them into saturated fats.
Bromine water test distinguishes between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons based on the decolorization of bromine.
Esterification is the reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol to produce an ester and water, characterized by a sweet smell.
Saponification is the hydrolysis of esters using an alkali, like sodium hydroxide, to produce a sodium salt of the acid and alcohol.
The video provides a method to predict reactions using the breakdown of reactants into positive and negative ions.
Practical applications of these reactions are highlighted, such as in the soap industry for saponification.
The video concludes with an interactive challenge for viewers to predict the products of a given reaction, fostering engagement.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
Balancing Combustion Reactions

Chemistry | Organic Chemistry | Reactions (Substitution, Addition and Elimination)
Crash Course Regents Chemistry 12 - Reaction Review

Chemical Reactions (3 of 11) Combustion Reactions, An Explanation

Intro to Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: Crash Course Organic Chemistry #37

Chem 51A 10/14/09 Ch. 3. Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Amines
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: