Chemical Reactions (3 of 11) Combustion Reactions, An Explanation
TLDRThis video delves into the concept of combustion reactions, highlighting their role in releasing energy. It explains how elements or compounds react with oxygen to form oxides and produce heat, using the reaction of magnesium with oxygen as an example. The video further clarifies that while the reaction between magnesium and oxygen was previously described as synthesis, it can also be viewed as combustion. The most common combustion reactions involve hydrocarbons reacting with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water. The video demonstrates the balancing of these reactions using methane and pentane as examples. It concludes with exciting demonstrations of combustion reactions, emphasizing the visual appeal and energy release associated with these chemical processes.
Takeaways
- 🔥 Combustion reactions involve an element or compound reacting with oxygen to form an oxide and release heat.
- 🌟 The reaction of magnesium with oxygen to form magnesium oxide is an example of both a synthesis and a combustion reaction.
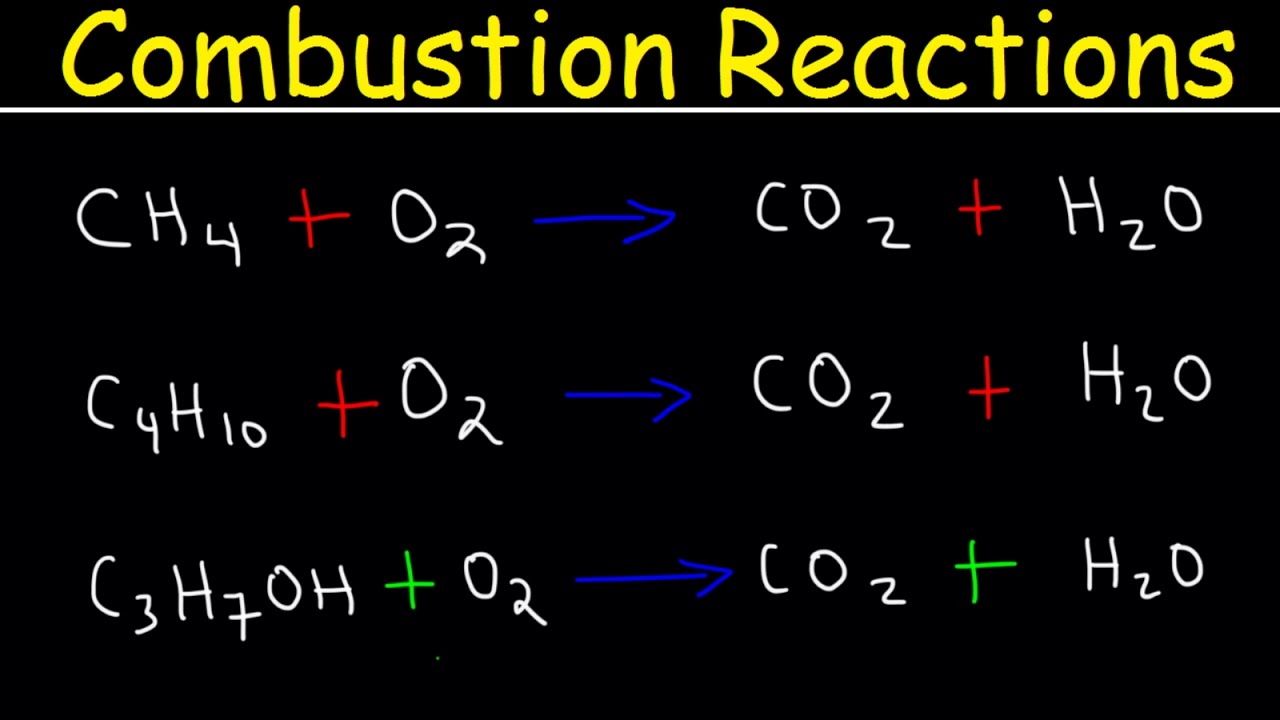
- 📈 The general form of a hydrocarbon combustion reaction involves a hydrocarbon (carbon and hydrogen chain) reacting with oxygen to produce water and carbon dioxide.
- 🔍 Balancing a chemical equation starts with balancing the carbon and hydrogen elements, followed by balancing the oxygen.
- 🐴 Methane (CH4) combusts with oxygen to form water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2), with a balanced equation of CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O.
- 🛢️ Pentane (C5H12) combusts with oxygen to form water and carbon dioxide, with a balanced equation of 2C5H12 + 13O2 → 10CO2 + 12H2O.
- 🎯 The key to balancing chemical equations is ensuring the correct ratio of reactants and products to maintain the law of conservation of mass.
- 💡 Combustion reactions are exothermic, meaning they release energy, often in the form of heat and light.
- 🚀 Hydrocarbon combustion is a common type of reaction with significant applications in energy production and chemical engineering.
- 🧪 The script also mentions fun and visually impressive combustion reactions, such as the methane Mamba and the whoosh bottle, which are popular demonstrations of the release of energy.
Q & A
What is a combustion reaction?
-A combustion reaction is a chemical reaction where an element or compound reacts with oxygen to form an oxide and produces heat.
How does the reaction of magnesium with oxygen illustrate the concept of a combustion reaction?
-The reaction of magnesium with oxygen to produce magnesium oxide serves as an example of a combustion reaction because it involves an element reacting with oxygen to form an oxide, releasing heat in the process.
What is the difference between a synthesis reaction and a combustion reaction?
-While both synthesis and combustion reactions involve the combination of elements, a synthesis reaction typically refers to the formation of a single product from two or more reactants, whereas a combustion reaction specifically involves the reaction with oxygen to produce an oxide and release heat.
What is the general form of a combustion reaction involving hydrocarbons?
-The general form of a combustion reaction involving hydrocarbons is hydrocarbon (composed of carbon and hydrogen) plus oxygen, which produces water and carbon dioxide as the products.
How do you balance the chemical equation for the combustion of methane (CH4)?
-To balance the chemical equation for the combustion of methane, you start by balancing the carbon atoms, which are already balanced with one. Then, you balance the hydrogen atoms by placing a coefficient of 2 in front of water (H2O) to have four hydrogen atoms on both sides. Finally, you balance the oxygen atoms by having two oxygen molecules (O2) on the reactant side and adding a coefficient of 2 in front of the carbon dioxide (CO2) on the product side to have four oxygen atoms, resulting in a balanced equation.
What is the balanced chemical equation for the combustion of pentane (C5H12)?
-The balanced chemical equation for the combustion of pentane is: C5H12 + 8O2 → 5CO2 + 6H2O. Here, five carbon atoms from pentane react with eight oxygen molecules to produce five molecules of carbon dioxide and six molecules of water.
Why is it important to balance chemical equations?
-Balancing chemical equations is important because it ensures that the law of conservation of mass is followed, meaning the number of atoms of each element must be the same on both the reactant and product sides of the equation. This reflects the reality that atoms are neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
What are some common products of hydrocarbon combustion?
-The common products of hydrocarbon combustion are carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O), which result from the reaction of hydrocarbons with oxygen.
What types of combustion reactions were demonstrated in the video?
-The video demonstrated combustion reactions involving methane (CH4), hydrogen gas in a balloon, and the 'whoosh bottle' experiment, all of which release energy in the form of heat and light.
What is the significance of combustion reactions in everyday life?
-Combustion reactions are significant in everyday life as they are the basis for many energy-releasing processes such as internal combustion engines in cars, the burning of fuels for heat and light, and various industrial processes that rely on the release of energy from the reaction of substances with oxygen.
How does the concept of a combustion reaction relate to the energy transformation?
-In a combustion reaction, chemical energy stored in the reactants is transformed into thermal energy (heat) and sometimes light energy, which is released during the reaction. This energy transformation is a key aspect of many practical applications, from heating our homes to powering vehicles.
Outlines
🔥 Introduction to Combustion Reactions
This paragraph introduces the topic of combustion reactions, explaining it as a process where an element or compound reacts with oxygen to form an oxide and release heat. The example of magnesium reacting with oxygen to form magnesium oxide is provided to illustrate a synthesis reaction that can also be considered a combustion reaction. The most common type of combustion reaction is described as the reaction of a hydrocarbon with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water, presenting the general form of this reaction.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Combustion Reaction
💡Hydrocarbon
💡Oxide
💡Synthesis Reaction
💡Balancing Chemical Equations
💡Carbon Dioxide
💡Water
💡Energy Release
💡Methane
💡Pentane
💡Chemical Demonstrations
Highlights
Combustion reactions are discussed in detail, focusing on their role in producing heat and oxides.
The reaction of magnesium metal with oxygen to form magnesium oxide is mentioned as an example of a synthesis reaction that can also be considered a combustion reaction.
The general form of a combustion reaction involving hydrocarbons is explained, where carbon dioxide and water are the typical products.
A step-by-step process for balancing chemical equations is demonstrated, starting with balancing carbon and hydrogen, followed by oxygen.
Methane (CH4) is used as an example to illustrate the balancing of a combustion reaction, resulting in water and carbon dioxide.
The importance of balancing oxygen atoms is emphasized to ensure the correct stoichiometry in chemical reactions.
Pentane (C5H12) is presented as another example, showing how to balance a more complex hydrocarbon combustion reaction.
The concept of a balanced chemical equation for the combustion of pentane in oxygen is provided, with the correct stoichiometric coefficients.
Demonstrations of combustion reactions are mentioned as a way to visually engage with the topic and highlight the release of energy.
The video includes practical examples such as the 'methane Mamba' and 'whoosh bottle' to illustrate the fun and engaging aspects of combustion reactions.
The video aims to educate viewers on the fundamental principles of combustion reactions in an accessible and entertaining way.
The video content is designed to appeal to a broad audience, making complex scientific concepts more understandable and enjoyable.
The educational value of the video is emphasized, with a focus on clear explanations and practical applications of combustion reactions.
The video concludes with a reminder of the educational purpose and an invitation to return for future content.
The transcript provides a comprehensive overview of combustion reactions, suitable for educational purposes and for those interested in chemistry.
The video's approach to teaching chemistry is highlighted, emphasizing the combination of theoretical knowledge and practical demonstrations.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: