Introduction to Organic Chemistry
TLDRThis script delves into the history and fundamentals of organic chemistry. Initially, compounds were categorized based on their natural or artificial origins into organic and inorganic groups. The vital force theory, proposed by Berzelius in 1809, posited that organic compounds could only be synthesized by living organisms. However, Friedrich Wöhler debunked this theory in 1828 by creating urea in a lab, earning him the title 'Father of Organic Chemistry.' The script clarifies that organic chemistry focuses on the study of carbon and hydrogen compounds and their derivatives, while also noting exceptions like carbides, carbonates, and cyanides that contain carbon but are not considered organic.
Takeaways
- 🌿 Organic compounds were historically obtained from living organisms, such as carbohydrates from plants and proteins from animals.
- 🏜 Inorganic compounds were derived from non-living sources, including salts, sulfates, and nitrates.
- 💡 The vital force theory, proposed by Berzelius in 1809, suggested that organic compounds could only be synthesized by living organisms and not in a laboratory.
- 🔬 Friedrich Wöhler disproved the vital force theory in 1828 by synthesizing urea, an organic compound, from inorganic substances in a laboratory.
- 🧪 Wöhler's synthesis of urea marked the beginning of organic chemistry as a scientific discipline.
- 🔍 Organic chemistry is defined as the branch of chemistry that studies carbon and hydrogen compounds and their derivatives.
- 🌐 The study of organic chemistry encompasses two main areas: carbon and hydrogen compounds, and their derivatives.
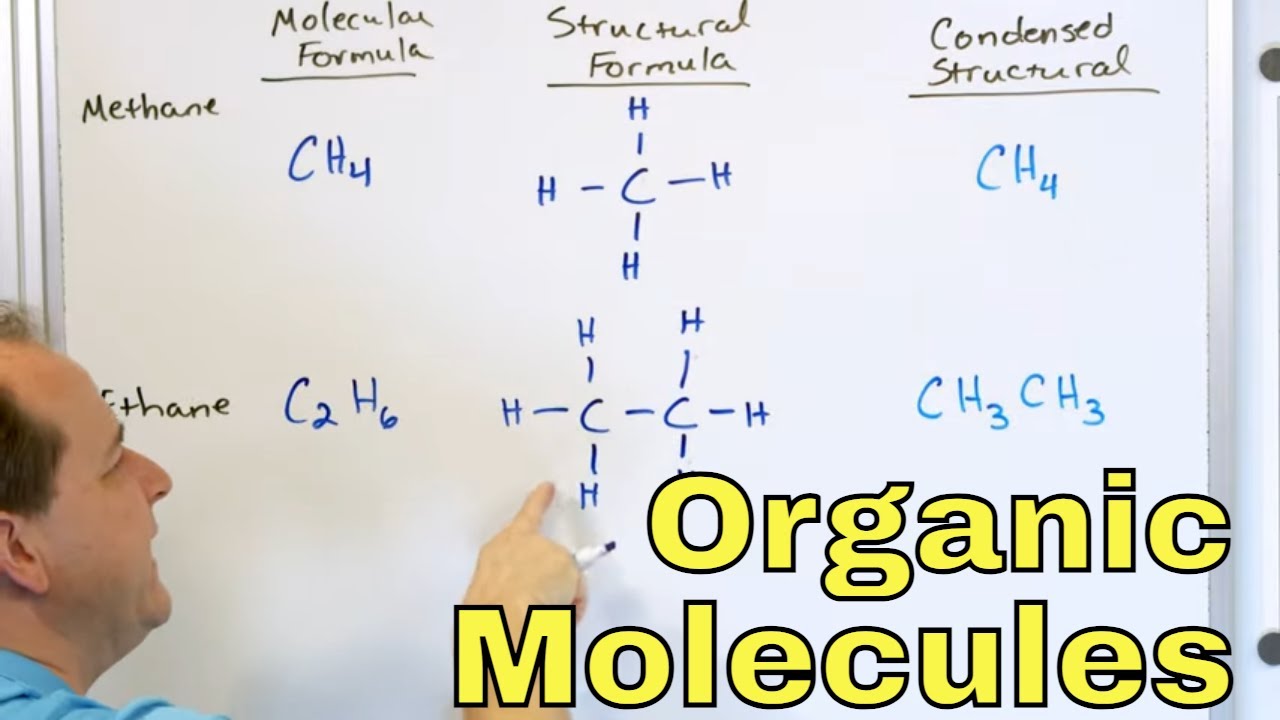
- 📚 Methane (CH4) is an example of a carbon and hydrogen compound, while carbon tetrabromide (CBr4) is a derivative of methane, illustrating the concept of organic derivatives.
- ❗ Not all carbon-containing compounds are organic; exceptions include carbides, carbonates, and cyanides.
- 📘 The script emphasizes the importance of understanding the distinction between organic and inorganic compounds and the historical development of organic chemistry.
Q & A
What were the two main groups of compounds classified by scientists based on their sources in the past?
-The two main groups were organic compounds, which were obtained from living organisms, and inorganic compounds, which were obtained from non-living sources.
What is an example of an organic compound obtained from plants?
-Carbohydrates, such as sucrose, are examples of organic compounds obtained from plants.
What is an example of an inorganic compound?
-Table salt, calcium sulfate, and potassium nitrate are examples of inorganic compounds.
What theory did Berzelius present in 1809 regarding the synthesis of organic compounds?
-Berzelius presented the vital force theory, which stated that organic compounds could only be synthesized by living organisms and not in the laboratory.
Who is credited with breaking the vital force theory, and how did they do it?
-Friedrich Wöhler is credited with breaking the vital force theory by synthesizing urea, the first organic compound prepared in a laboratory, from ammonium cyanide in 1828.
What is the significance of Wöhler's synthesis of urea in the history of organic chemistry?
-Wöhler's synthesis of urea marked the beginning of organic chemistry as a scientific discipline and demonstrated that organic compounds could be synthesized artificially.
What is the definition of organic chemistry according to the script?
-Organic chemistry is the branch of chemistry that studies carbon and hydrogen compounds and their derivatives.
What are the two main areas of study in organic chemistry mentioned in the script?
-The two main areas of study in organic chemistry are carbon and hydrogen compounds, such as methane (CH4), and their derivatives, such as carbon tetra bromide (CBr4).
What is an example of a compound containing carbon that is not considered an organic compound?
-Examples of compounds containing carbon that are not considered organic include carbides like aluminum carbide, carbonates like calcium carbonate, and cyanides like sodium cyanide.
Why is it important to note that some carbon-containing compounds are not organic?
-It is important to note that not all carbon-containing compounds are organic because the distinction helps to clarify the scope and definition of organic chemistry, focusing on compounds that are primarily based on carbon-hydrogen bonds.
How did the script describe the role of Friedrich Wöhler in the field of organic chemistry?
-The script described Friedrich Wöhler as the 'father of organic chemistry' due to his groundbreaking synthesis of urea, which opened a new chapter in the field.
Outlines
🌿 Introduction to Organic Chemistry
This paragraph introduces the historical classification of compounds into organic and inorganic, based on their sources. Organic compounds were thought to be derived only from living organisms, such as carbohydrates from plants and proteins from animals, while inorganic compounds were from non-living sources like salts and nitrates. The vital force theory of 1809 posited that organic compounds could only be synthesized by living organisms and not in a laboratory. However, this theory was debunked by Friedrich Wöhler in 1828 when he synthesized urea, an organic compound, from inorganic substances, marking a significant breakthrough and earning him the title 'Father of Organic Chemistry.' The paragraph also defines organic chemistry as the study of carbon and hydrogen compounds and their derivatives, distinguishing it from compounds containing carbon but not classified as organic, such as carbides, carbonates, and cyanides.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Organic Chemistry
💡Inorganic Compounds
💡Vital Force Theory
💡Friedrich Wöhler
💡Urea
💡Ammonium Cyanide
💡Carbon and Hydrogen Compounds
💡Derivatives
💡Carbides
💡Carbonates
💡Cyanides
Highlights
Introduction to the historical classification of compounds into organic and inorganic based on their sources.
Organic compounds were initially believed to be obtained solely from living organisms, such as carbohydrates from plants and proteins from animals.
Inorganic compounds were thought to be derived from non-living sources like salts, sulfates, and nitrates.
Berzelius' vital force theory of 1809 claimed that organic compounds could only be synthesized by living organisms.
The vital force theory suggested that laboratory synthesis of organic compounds like sucrose was impossible.
The belief in a god-given power exclusive to living organisms for synthesizing organic compounds hindered the exploration of organic chemistry.
Friedrich Wöhler's 1828 experiment with ammonium cyanide disproved the vital force theory by synthesizing urea, an organic compound, in the laboratory.
Urea, previously thought to be exclusively synthesized by living organisms, became the first man-made organic compound.
Friedrich Wöhler is recognized as the father of organic chemistry for his groundbreaking work.
Organic chemistry is defined as the study of carbon and hydrogen compounds and their derivatives.
Methane (CH4) is an example of a carbon and hydrogen compound studied in organic chemistry.
Conversion of methane to carbon tetra bromide (CBr4) demonstrates the study of derivatives in organic chemistry.
Certain carbon-containing compounds, such as carbides, carbonates, and cyanides, are classified as inorganic despite containing carbon.
The importance of distinguishing between organic and inorganic compounds based on their chemical properties, not just their carbon content.
The hope expressed for a clear understanding of the fundamental concepts of organic chemistry.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: