Algebra Review
TLDRThis video script offers a comprehensive review of algebra fundamentals, perfect for students returning to school. It covers fraction operations, like terms addition and subtraction, variable exponent rules, and solving linear equations. The script also discusses solving inequalities and graphing them, providing a solid foundation for higher-level math courses. The instructor suggests practicing with homework problems for mastery and highlights the importance of effort in learning algebra.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video is an algebra review aimed at preparing students for typical algebra concepts they'll encounter in school.
- 🧩 It starts with a review of fraction operations, emphasizing the importance of finding a common denominator for addition and subtraction, and the process of multiplying and dividing fractions.
- 🔢 The video explains the concept of 'keep change flip' for dividing fractions, which involves keeping the first fraction, changing division to multiplication, and flipping the second fraction.
- ➕ It covers the process of adding and subtracting like terms, highlighting that only terms with the same variable and exponent can be combined.
- 🆚 The script discusses the difference between adding and multiplying unlike terms, using the example of multiplying 5x and 3x squared to result in 15x cubed.
- 📈 The importance of understanding the operations with exponents is highlighted, such as adding exponents when multiplying variables and subtracting them when dividing.
- 🌐 The video provides examples of simplifying expressions with multiple variables and exponents, demonstrating how to cancel out common factors and reduce fractions.
- 🔑 The concept of solving basic equations is introduced, with a focus on isolating the variable to find its value, using operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
- 🔍 The process of solving multi-step equations and those with variables on both sides is explained, emphasizing the need to strategically move terms to one side to simplify the equation.
- 📉 The video touches on solving equations with fractions by eliminating them early in the process, such as multiplying every term by the denominator to create whole numbers.
- 📈 The final part of the script covers inequalities, showing how to represent solutions on a number line and in interval notation, and how to solve basic inequalities by treating them like equations but remembering to flip the inequality sign when multiplying or dividing by a negative number.
Q & A
What is the first step when adding fractions with different denominators?
-The first step is to find a common denominator by adjusting the fractions so they have the same denominator.
How do you add 3/4 and 2/5?
-First, adjust the fractions to have a common denominator of 20. Multiply 3/4 by 5/5 to get 15/20 and 2/5 by 4/4 to get 8/20. Then add the fractions to get 23/20.
What is the method for subtracting fractions?
-To subtract fractions, you need to have the same denominator. Adjust the fractions accordingly, then subtract the numerators.
How do you multiply two fractions, for example, 7/5 and 4/3?
-Multiply the numerators and denominators directly. So, 7 times 4 is 28, and 5 times 3 is 15. The result is 28/15.
How can large numbers in fractions be simplified before multiplication?
-Factor each number and cancel out common factors before multiplying. This simplifies the calculation and reduces the resulting fraction.
What is the 'keep change flip' method used for?
-The 'keep change flip' method is used for dividing fractions. Keep the first fraction the same, change the division to multiplication, and flip the second fraction.
How do you combine like terms in an algebraic expression?
-Combine terms that have the same variable raised to the same power. For example, combine 3x² and 8x² to get 11x².
What happens when you multiply variables with exponents?
-When multiplying variables with exponents, add the exponents. For example, x² * x³ = x⁵.
How do you solve an equation with variables on both sides?
-Move all variables to one side and constants to the other side by adding or subtracting them from both sides, then solve for the variable.
What should you do when solving inequalities involving multiplication or division by a negative number?
-When multiplying or dividing both sides of an inequality by a negative number, reverse the inequality sign.
Outlines
📚 Algebra Basics: Fractions Operations
This section reviews fundamental algebra concepts, focusing on fraction operations. It explains how to add, subtract, multiply, and divide fractions by finding a common denominator or adjusting numerators and denominators accordingly. Examples provided include adding fractions with different denominators, subtracting fractions by creating a common base, and simplifying the results. The process of multiplying fractions without the need for a common denominator and simplifying the product is also discussed, along with the division of fractions using the 'keep, change, flip' method.
🔢 Algebra Review: Variables and Exponents
The paragraph delves into operations with algebraic expressions involving variables. It covers adding and subtracting like terms, such as combining '5x' and '-7x', and explains that unlike terms cannot be combined. The rules of multiplying and dividing variables are discussed, including the addition and subtraction of exponents during these operations. The concept of negative exponents and how to handle them by inverting the variable is also explained, along with examples to illustrate the processes.
🧩 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
This part of the script focuses on simplifying algebraic expressions by multiplying and dividing monomials, binomials, and polynomials. It provides examples of how to multiply expressions with exponents, such as '5x^3 * 7x^4', and how to simplify the results by adding exponents. The process of dividing expressions, like '30x^5 / 48x^9', and canceling out common factors is also covered. The importance of recognizing like terms and combining them correctly is emphasized.
📉 Inequalities and Algebraic Manipulation
The script introduces the concept of inequalities, explaining how to represent them on a number line and how to solve basic inequality equations. It demonstrates solving inequalities by isolating the variable and changing the direction of the inequality when multiplying or dividing by a negative number. The representation of solutions using interval notation and number lines is also discussed, providing examples for both greater than and less than scenarios.
📌 Solving Equations and Inequalities
This section provides a comprehensive guide on solving linear equations and inequalities, including those with fractions and decimals. It explains techniques such as cross-multiplication for equations with fractions, converting decimals to whole numbers by multiplying by a power of 10, and using the 'keep, change, flip' method for dividing fractions. The importance of checking solutions by substituting them back into the original equation is highlighted.
📘 Algebra Course Overview and Resources
The final part of the script offers an overview of an algebra course available on Udemy, covering a wide range of topics from basic arithmetic to complex and imaginary numbers. It outlines the course structure, including sections on linear equations, order of operations, graphing, inequalities, polynomials, factoring, systems of equations, quadratic equations, rational and radical expressions, exponential functions, logarithms, functions, conic sections, and sequences and series. Each section is equipped with video quizzes for review.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Fractions
💡Common Denominator
💡Multiplying Fractions
💡Dividing Fractions
💡Simplifying Fractions
💡Like Terms
💡Exponents
💡Distributive Property
💡Foil Method
💡Linear Equations
Highlights
Review of basic algebra concepts for school preparation, including fraction operations.
Explanation of how to add fractions with different denominators by adjusting to a common denominator.
Subtraction of fractions demonstrated with an example, emphasizing finding a common denominator.
Multiplication of fractions without the need for a common denominator, illustrated through examples.
Simplification of fractions after multiplication, including reducing large numbers for easier calculation.
Division of fractions by 'flipping' the second fraction and multiplying, as per the 'keep change flip' rule.
Combining like terms in algebraic expressions and the distinction between addition and multiplication of unlike terms.
Multiplication of variables and the rule of adding exponents when variables are the same.
Division of variables, where exponents are subtracted, and the concept of negative exponents.
Raising a variable to an exponent and the multiplication of exponents when raising to a power.
Examples of multiplying and simplifying expressions with multiple variables and exponents.
Introduction to solving basic algebraic equations, emphasizing the isolation of variables.
Step-by-step solution of linear equations with multiple steps, including combining like terms.
Solving equations with variables on both sides, demonstrating the process of moving all variables to one side.
Handling equations with parentheses and variables, including the distribution of terms.
Solving equations with fractions by eliminating the fractions early in the process.
Graphing inequalities on a number line and representing solutions using interval notation.
Solving inequalities, including changing the direction of inequality when multiplying or dividing by negative numbers.
Course recommendation for further study in algebra, including various topics and quizzes for practice.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Math Videos: How To Learn Basic Arithmetic Fast - Online Tutorial Lessons

College Physics 1: Lecture 1 - Mathematics Review

Algebra SYSTEM WORD PROBLEM – Let’s solve it step-by-step...
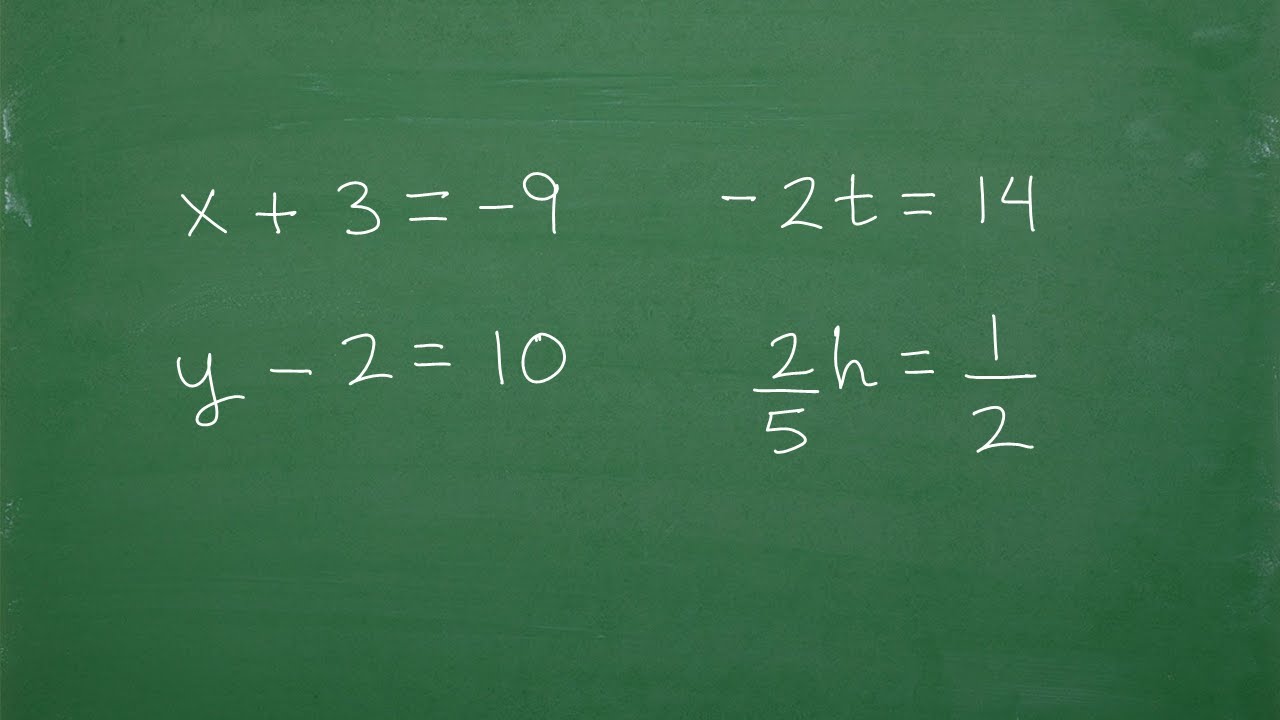
Let’s Solve These Basic Algebra Equations- Step-by-Step…….
Algebra Introduction - Basic Overview - Online Crash Course Review Video Tutorial Lessons

Algebra - How To Solve Equations Quickly!
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: