GCSE Chemistry - Fractional Distillation and Simple Distillation #50
TLDRThis video explores two distillation methods for separating liquid mixtures: simple and fractional distillation. Simple distillation, suitable for mixtures like seawater, uses a flask, thermometer, condenser, and heating device to evaporate and condense pure liquid. Fractional distillation, necessary for mixtures with similar boiling points like methanol, ethanol, and propanol, incorporates a fractionating column with glass rods to separate components by temperature. The process is illustrated with a step-by-step guide, making it accessible and informative.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Simple distillation is used to separate a liquid from a solution, such as obtaining pure water from seawater.
- 🧪 The equipment for simple distillation includes a flask, a bung, a thermometer, a condenser with a water jacket, a beaker, and a heating device.
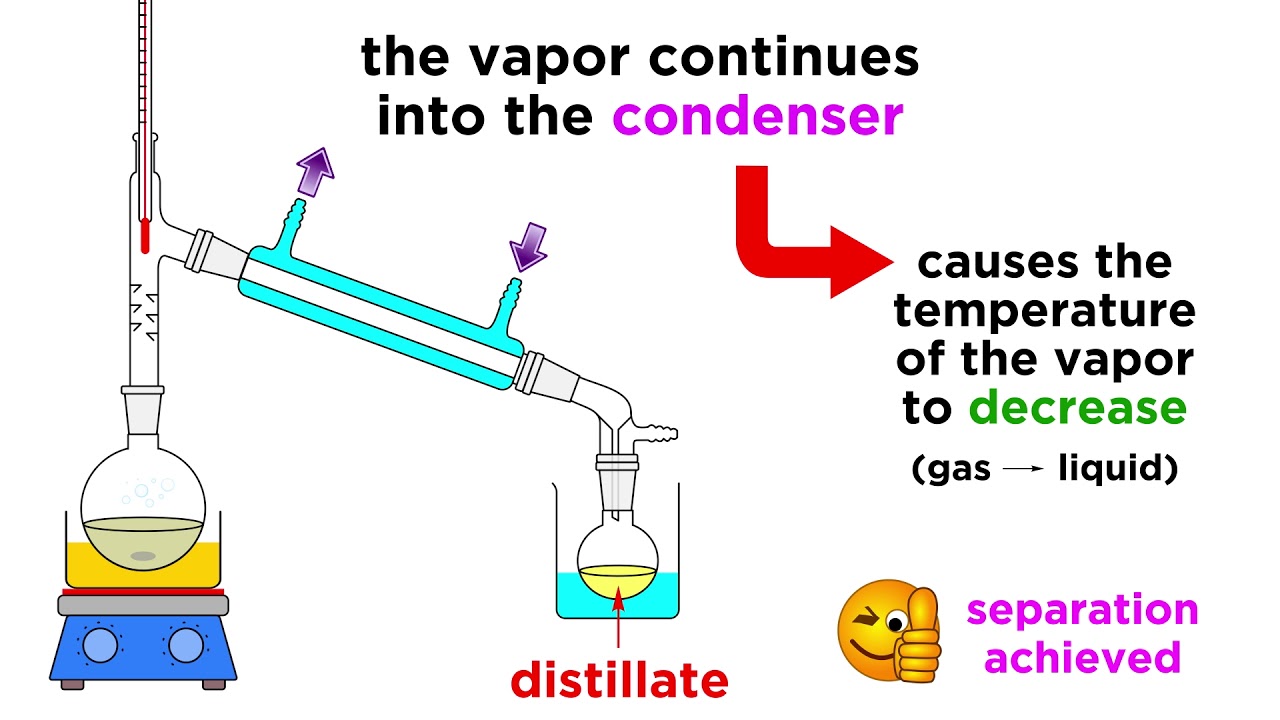
- 🌡 The process involves heating the mixture until the desired liquid evaporates, which then travels to the condenser and condenses back into a liquid.
- 💧 In simple distillation, the condensed liquid is collected in a beaker, leaving behind the non-volatile components like salt in the case of seawater.
- 🤔 Simple distillation is not effective for separating mixtures of liquids with similar boiling points, such as methanol, ethanol, and propanol.
- 🔄 Fractional distillation is the technique for separating mixtures of liquids with similar boiling points.
- 🌡️ Fractional distillation uses a fractionating column filled with glass rods to provide a high surface area for vapors to condense.
- 📏 The fractionating column is taller, resulting in a temperature gradient from the bottom to the top, which is cooler.
- 🔥 Methanol, with the lowest boiling point, is separated first by heating the mixture to around 65 degrees Celsius.
- 🌡️ Ethanol is then separated by raising the temperature to approximately 78 degrees Celsius, leaving behind propanol.
- 📝 The process can be repeated for each component, ensuring the purity of each liquid collected in the beaker.
Q & A
What is the purpose of simple distillation?
-Simple distillation is used for separating a liquid from a solution, such as obtaining pure water from seawater.
What is the primary equipment used in simple distillation?
-The primary equipment includes a flask containing the solution, a bung to seal the flask, a thermometer, a condenser with a water jacket, a beaker to collect the liquid, and a heating device like a Bunsen burner.
How does the condenser work in simple distillation?
-The condenser works by having a main pipe surrounded by a water jacket. Cold water continuously flows through the jacket, cooling the vapor and causing it to condense back into liquid form.
What is the limitation of simple distillation when dealing with liquids with similar boiling points?
-Simple distillation cannot effectively separate liquids with similar boiling points because more than one liquid will evaporate at the same time, preventing the separation into pure substances.
What technique is used to separate mixtures of liquids with similar boiling points?
-Fractional distillation is used to separate mixtures of liquids with similar boiling points.
What is the key feature of a fractionating column in fractional distillation?
-The fractionating column is full of little glass rods that provide a high surface area and is taller, resulting in a temperature gradient from the bottom to the top.
How does the fractionating column help in separating liquids with similar boiling points?
-The fractionating column allows vapors to rise and cool as they come into contact with the glass rods. Liquids with lower boiling points evaporate first and condense, while those with higher boiling points condense back into the flask.
What is the process for separating methanol, ethanol, and propanol using fractional distillation?
-First, heat the mixture to around 65 degrees Celsius to evaporate methanol. Then, raise the temperature to around 78 degrees Celsius to evaporate ethanol. Finally, increase the temperature again to remove propanol.
Why are the liquids shown as green in the video?
-The liquids are shown as green in the video to make it easier to follow along, even though in real life they would be colorless.
How does the temperature control in fractional distillation help in separating specific liquids?
-By controlling the temperature, only the liquid with the boiling point closest to the set temperature will evaporate and be separated, while others will condense back due to the cooler environment in the fractionating column.
What is the final step in the fractional distillation process after separating ethanol?
-The final step is to raise the temperature again to boil off the remaining propanol, ensuring that only pure propanol is left in the flask.
Outlines
🔬 Simple Distillation Process
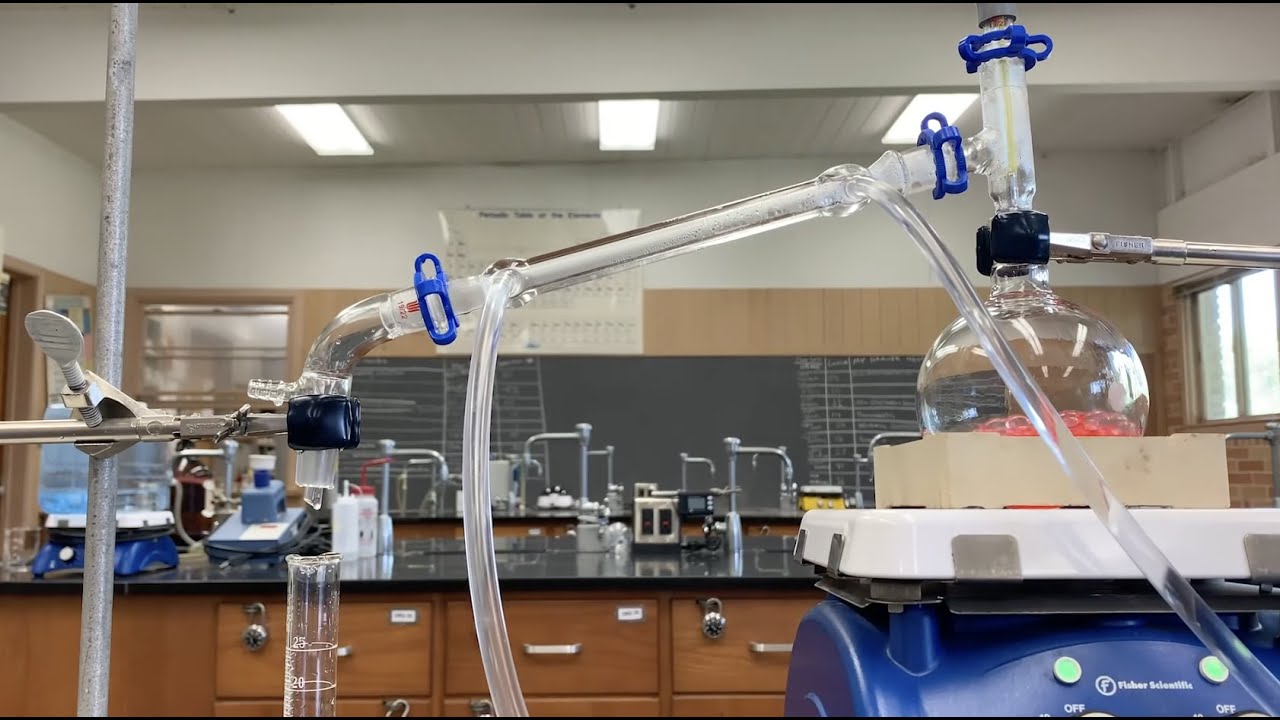
This paragraph introduces simple distillation, a method used to separate a liquid from a mixture, such as obtaining pure water from seawater. The equipment setup includes a flask containing the mixture, sealed with a bung to prevent gas escape, a thermometer to monitor temperature, a condenser with a water jacket for cooling vapors, and a beaker to collect the distillate. The process involves heating the mixture until the desired liquid evaporates, then cooling it in the condenser and collecting the condensed liquid. However, this method is ineffective for separating liquids with similar boiling points, such as methanol, ethanol, and propanol, which necessitates the use of fractional distillation.
🌡️ Fractional Distillation for Complex Mixtures
The second paragraph delves into fractional distillation, a technique for separating mixtures of liquids with similar boiling points. The equipment is similar to simple distillation but includes a fractionating column filled with glass rods to provide a large surface area and a temperature gradient from bottom to top. The process is illustrated using methanol, ethanol, and propanol, which are heated in stages to selectively evaporate and condense each component. Methanol, with the lowest boiling point, is first evaporated and collected, followed by ethanol at a higher temperature. The remaining propanol can be assumed to be pure or further heated to ensure purity. This method effectively separates components of complex mixtures.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Distillation
💡Simple Distillation
💡Fractional Distillation
💡Boiling Point
💡Flask
💡Condenser
💡Beaker
💡Bunsen Burner
💡Fractionating Column
💡Methanol
💡Ethanol
💡Propanol
Highlights
Introduction to two types of distillation for separating mixtures containing liquids.
Simple distillation is used for separating a liquid from a solution, such as pure water from seawater.
Equipment for simple distillation includes a flask, thermometer, condenser, beaker, and heating device.
Process of heating the mixture to evaporate the desired liquid, which then condenses in the condenser.
Use of a fractionating column in fractional distillation for separating liquids with similar boiling points.
Fractional distillation equipment is similar to simple distillation but includes a fractionating column.
The fractionating column is filled with glass rods to provide a high surface area for condensation.
Temperature gradient in the fractionating column, cooler at the top than at the bottom.
Example of separating methanol, ethanol, and propanol using fractional distillation.
Heating the mixture to 65 degrees to evaporate methanol first.
Ethanol and propanol may also evaporate but will condense back into the flask upon contact with cooler glass rods.
Repeating the process for ethanol by raising the temperature to 78 degrees Celsius.
Assumption that what remains in the flask after evaporating ethanol is pure propanol.
Option to raise the temperature again to ensure all propanol is boiled off for purity.
Conclusion of the video with an invitation for feedback in the comments.
Anticipation of the next video in the series.
Transcripts
in today's video we're going to look at
the two types of distillation that we
can use to separate out mixtures that
contain
liquids let's start with simple
distillation
which is used for separating out a
liquid from a solution
for example we could use simple
distillation to separate pure water from
seawater
before we cover how it works though we
need to be familiar with the equipment
first we have a flask
that contains the solution or the liquid
mixture that we're trying to separate
and the flask is sealed at the top with
a bung so that no gas can escape
we then put a thermometer through the
bung so that we can measure the
temperature inside the flask
next we have our condenser
which consists of a main pipe surrounded
by a water jacket which contains a
stream of continually flowing cold water
with the water being fed into the water
jacket at the bottom
and coming out at the top
then beneath the end of our condenser
we'll have some sort of beaker to
capture our pure liquid
and finally we're going to need some
sort of heating device like a bunsen
burner which we place under the flask
our first step is to heat up the mixture
so that the liquid that we want
evaporates
as it rises to the top of the flask the
pressure will force it down the
condenser
and because we're pumping cold water
through the water jacket
the vapor will cool and condense into
liquid form
which will then run down the pipe and
collect in the beaker
so in our case as we heat the seawater
we'll get more and more pure distilled
water
until eventually all we have left in the
flask is salt
now imagine instead that we were trying
this technique with a different mixture
one containing some different liquids
like methanol ethanol and propanol
because these liquids all have similar
boiling points
when we heat them more than one of them
will evaporate
and so they won't be separated into pure
substances
in this case we'd have to use a
different technique called fractional
distillation
which is the main technique used for
separating mixtures of liquids
the equipment for this is pretty similar
but instead of the gas passing straight
from the flask into the condenser
the vapors have to first pass through a
fractionating column
which has two key features
one is that it's full of little glass
rods which provide a really high surface
area
and the other is that because the colon
is so tall
it's actually cooler at the top than it
is at the bottom
to understand why this is important
let's imagine that we were trying to
separate those three liquids that we
mentioned before
methanol
ethanol and propanol
which all have similar boiling points
although you don't need to remember them
and before we continue just be aware
that in real life these would all be
colorless not green
we're just showing them as green to make
it easier to follow along
now because methanol has the lowest
boiling point we'd heat the mixture to
around 65 degrees first
this would cause the methanol to
evaporate and then rise up the
fractionating column
it would then pass into the condenser
and condense into liquid methanol
which would then collect in our beaker
however just by chance some of the
ethanol and maybe even propanol would
also evaporate
but as they rise up the fractionating
column and come into contact with all of
those glass rods which are much cooler
than their boiling point
they'd condense back into liquid form
and fall back into the flask
this means that the only liquid that
will get out the other side will be pure
methanol
the next step would be to do the same
thing all over again for ethanol by
raising the temperature to around 78
degrees celsius
which will allow us to evaporate off the
ethanol
at this point all that should be left is
the propanol
so we could just assume that what we
have in the flask is pure propanol
or we could raise the temperature again
to boil off the propanol just to make
sure
anyway that's all for today so hope you
enjoyed this video if you did then
please let us know down in the comments
and we'll see you next time
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: