Simple and fractional distillations | Chemical processes | MCAT | Khan Academy
TLDRThis script delves into the process of distillation, explaining how it's used to purify and concentrate ethanol in alcoholic beverages like vodka. It covers the setup of a distillation apparatus, including a distilling flask, oil bath, thermometer, condenser, and receiving flask, and touches on the use of a vacuum for high-boiling point compounds. The script illustrates the separation of two-component and three-component mixtures, highlighting the challenges of distilling ethanol and water due to their close boiling points. It concludes with an introduction to fractional distillation, which enhances purity by performing multiple vaporizations and condensations through a packed column.
Takeaways
- 🍸 Vodka and other strong alcoholic drinks are made by distillation, a process that increases ethanol concentration through repeated heating and cooling.
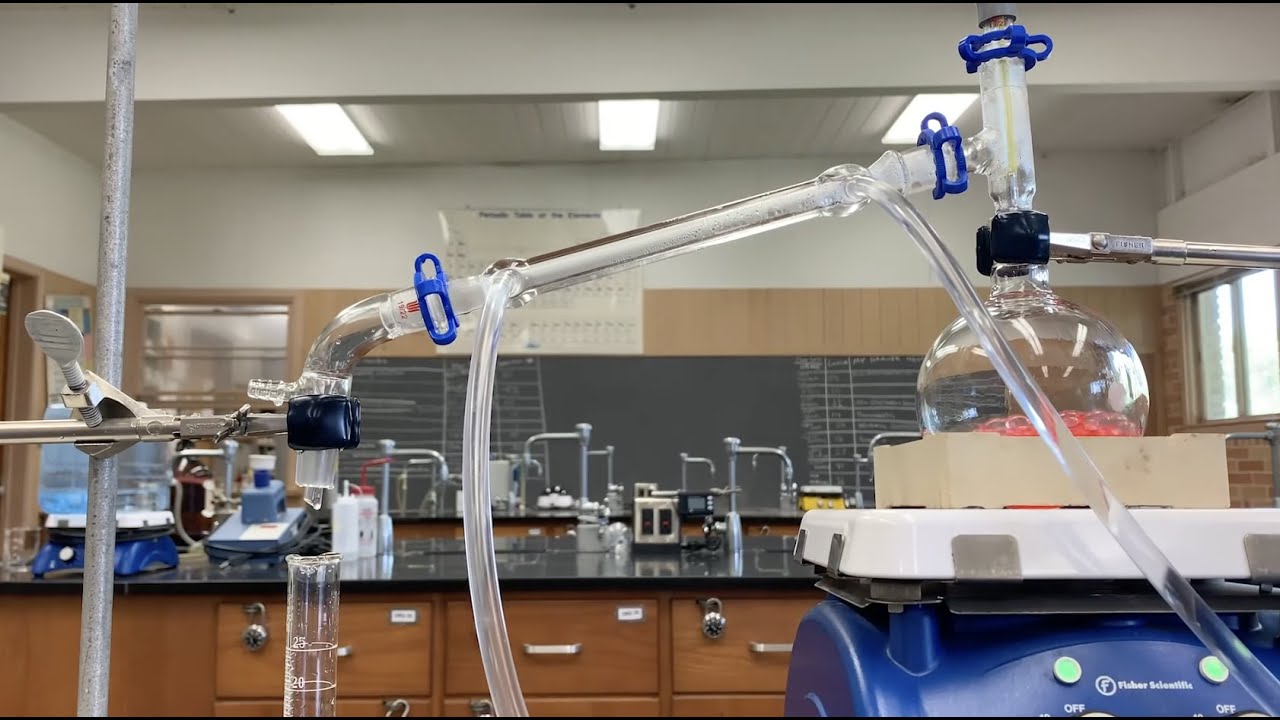
- 🧪 Distillation can be performed in an organic chemistry lab with a setup that includes a distilling flask, oil bath, thermometer, condenser, and receiving flask.
- 🔥 An oil bath is used for heating because it maintains a constant temperature and doesn't evaporate, which is crucial for the distillation process.
- 🌡 A thermometer is essential to measure the boiling points of compounds, which is a key indicator during the distillation process.
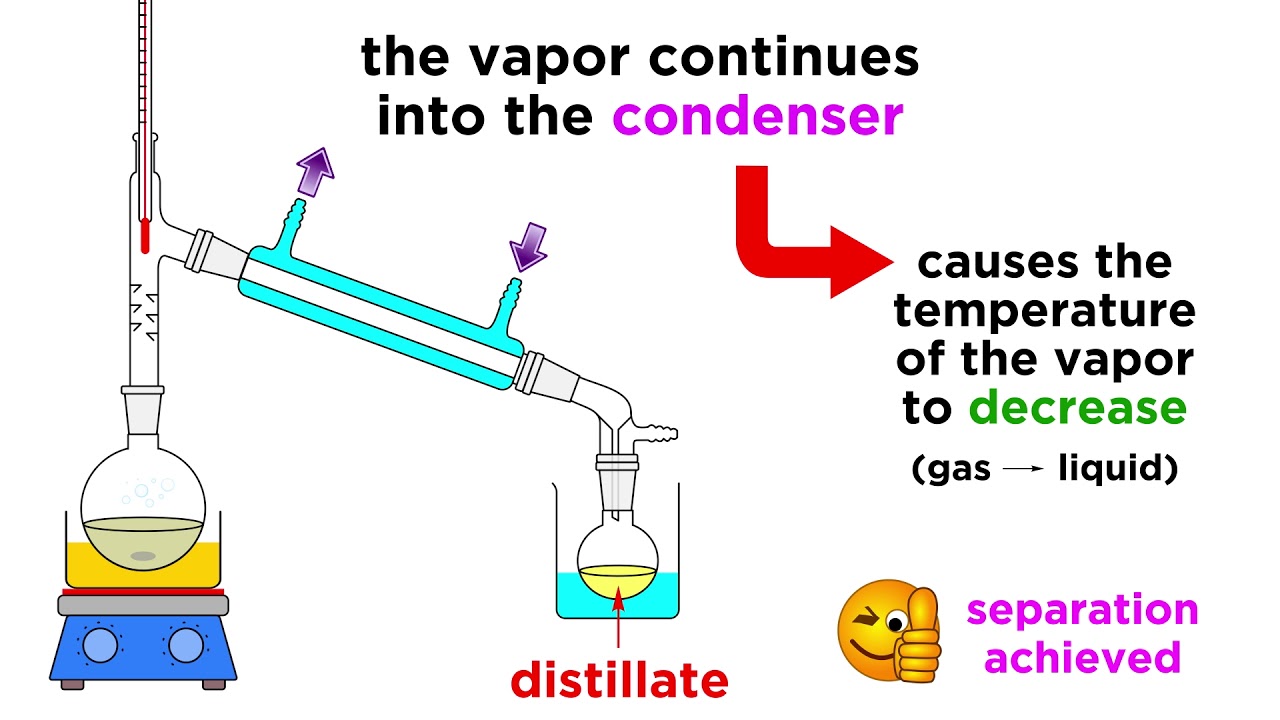
- 💧 The condenser cools the vaporized compounds, facilitating their condensation back into liquid form for collection.
- ❄️ An ice bath is used to keep the receiving flask cold, ensuring efficient condensation of the vaporized compounds.
- 🔭 A vacuum adapter can be used in distillation to lower the pressure and make it easier to vaporize substances with high boiling points.
- 📊 Monitoring distillation involves plotting temperature versus time to identify plateaus that indicate phase changes from liquid to gas and back to liquid.
- 🔄 The process of distillation can be repeated multiple times to achieve a purer separation of compounds, especially when their boiling points are close.
- 🌟 Fractional distillation involves a fractionating column filled with material like beads or stars, which increases the number of vaporizations and condensations, resulting in purer compounds.
- 📉 In cases where compounds have close boiling points, like ethanol and water, simple distillation may result in a mixture rather than pure separation, requiring advanced techniques like fractional distillation for better results.
Q & A
What is the primary reason vodka is a strong alcoholic drink compared to others?
-Vodka is strong because it undergoes a process called distillation, which can be performed once or multiple times to increase the concentration of ethanol in the beverage.
What is the purpose of using a distilling flask in the distillation process?
-The distilling flask is where the mixture of compounds to be separated is placed. It is heated to vaporize the components based on their boiling points.
Why is an oil bath preferred for heating during distillation?
-An oil bath is used because oil does not evaporate when heated, maintaining a constant temperature throughout the distillation process.
What is the role of a thermometer in distillation?
-A thermometer is essential to measure the temperature at which the compounds are boiling and vaporizing during distillation.
Why is a condenser necessary in the distillation setup?
-A condenser is needed to cool the vaporized compounds so they can condense back into a liquid form, which is then collected in the receiving flask.
What is the purpose of keeping the receiving flask cold during distillation?
-Keeping the receiving flask cold ensures that the vaporized compounds condense back into their liquid form efficiently and can be collected for further use.
What is the function of a vacuum adapter in distillation?
-A vacuum adapter is used to lower the pressure of the system, making it easier to vaporize substances with high boiling points by reducing the force pushing back on the liquid.
How does the boiling point of a compound affect its distillation?
-The boiling point determines the temperature at which a compound will vaporize during distillation. Compounds with lower boiling points vaporize first, followed by those with higher boiling points.
What is the significance of plotting temperature versus time during distillation?
-Plotting temperature versus time helps monitor the progress of distillation, indicating when different compounds are vaporizing and condensing, as seen by plateaus in the graph.
How does fractional distillation differ from simple distillation?
-Fractional distillation involves a fractionating column filled with materials like beads or stars, which allows for multiple vaporizations and condensations of the compounds, resulting in a purer separation of components.
Why might simple distillation not be effective for compounds with small boiling point differences?
-Simple distillation may not effectively separate compounds with small boiling point differences because they vaporize and condense at similar temperatures, leading to a mixture rather than a pure separation.
Outlines
🍸 Understanding Distillation in Alcoholic Beverages
This paragraph explains the process of distillation, which is key to creating strong alcoholic drinks like vodka. Distillation increases the ethanol concentration through heating and cooling cycles. The setup includes a distilling flask for the mixture, an oil bath for consistent heating, a thermometer to monitor temperature, a condenser to cool and condense vapors, and a receiving flask kept cold for collecting the purified liquid. A vacuum adapter is also used to lower the pressure and facilitate the vaporization of substances with high boiling points. The paragraph uses a two-component mixture of hexane and toluene to illustrate the process, demonstrating how to monitor the distillation through a temperature versus time graph, resulting in the separation and collection of each component in different flasks.
🧪 Advanced Distillation Techniques for Purity
The second paragraph delves into more complex mixtures and the challenges they present during distillation. It discusses a three-component mixture of acetone, cyclohexane, and acetic acid, highlighting how each component's boiling point affects the distillation process and the resulting graph of temperature versus time. The paragraph addresses the issue of ethanol and water's close boiling points and the difficulty in separating them through simple distillation. It introduces fractional distillation as a solution, which involves a fractionating column filled with materials like beads or stars to increase the number of vaporization and condensation cycles, thus improving purity. The summary concludes with a comparison between simple distillation, suitable for compounds with large boiling point differences, and fractional distillation, ideal for smaller differences.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Distillation
💡Ethanol
💡Boiling Point
💡Condenser
💡Oil Bath
💡Fractional Distillation
💡Vaporization
💡Condensation
💡Vacuum Adapter
💡Phase Change
💡Temperature Plateau
Highlights
Vodka's strength is attributed to the distillation process, which increases ethanol concentration.
Distillation can be performed in an organic chemistry lab using a specific setup.
The distilling flask is used to hold the mixture of compounds for separation.
An oil bath is essential for maintaining a constant temperature during distillation.
A thermometer is necessary to measure the boiling point of compounds.
The condenser plays a crucial role in the vaporization and condensation cycle of distillation.
The receiving flask must be kept cold to facilitate the condensation of vapor back into liquid form.
An ice bath is used to maintain the cold temperature required for efficient condensation.
A vacuum adapter can be used to lower the pressure and ease the vaporization of substances with high boiling points.
Monitoring the distillation process involves plotting temperature against time to identify phase changes.
Hexane and toluene are used as examples of a two-component mixture in distillation.
Acetone, cyclohexane, and acetic acid demonstrate a three-component mixture's distillation process.
Ethanol and water's close boiling points pose a challenge in achieving a strong alcoholic drink through distillation.
Repeated distillation can purify substances but is time-consuming.
Fractional distillation, using a fractionating column, allows for multiple distillations simultaneously, enhancing purity.
The fractionating column filled with packing material like beads or stars facilitates multiple vaporizations and condensations.
Simple distillation is suitable for compounds with large boiling point differences, while fractional distillation is ideal for smaller differences.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: