Simple Distillation
TLDRIn this tutorial, we explore distillation, a key separation technique used in chemistry labs and industry. Unlike extraction, distillation separates miscible liquids based on their boiling points. We demonstrate setting up a simple distillation apparatus, including a round bottom flask, condenser, and thermometer, and provide step-by-step instructions. We distill a 50:50 mixture of isopropyl alcohol and water, highlighting the importance of precise temperature control. Key safety tips and data collection for analysis are also covered. The tutorial concludes with an introduction to fractional distillation for mixtures with close boiling points.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Distillation is a common technique used in chemistry labs and industry to separate liquid components of a mixture based on their boiling points.
- 🔑 Unlike extraction, distillation involves miscible liquids with sufficiently different boiling points, allowing one to boil without the other.
- 🌡️ The process requires heating the mixture above the boiling point of the component with the lower boiling point to vaporize it, while the other remains liquid.
- 🧪 A simple distillation setup includes a heat source, round bottom flask, three-way adaptor, thermometer, condenser, vacuum adaptor, and a collection vessel.
- 🔨 Proper sealing is crucial to prevent vapor escape, and joints can be greased for a tight fit.
- 📏 The thermometer should be positioned just below the sidearm to accurately measure the vapor temperature.
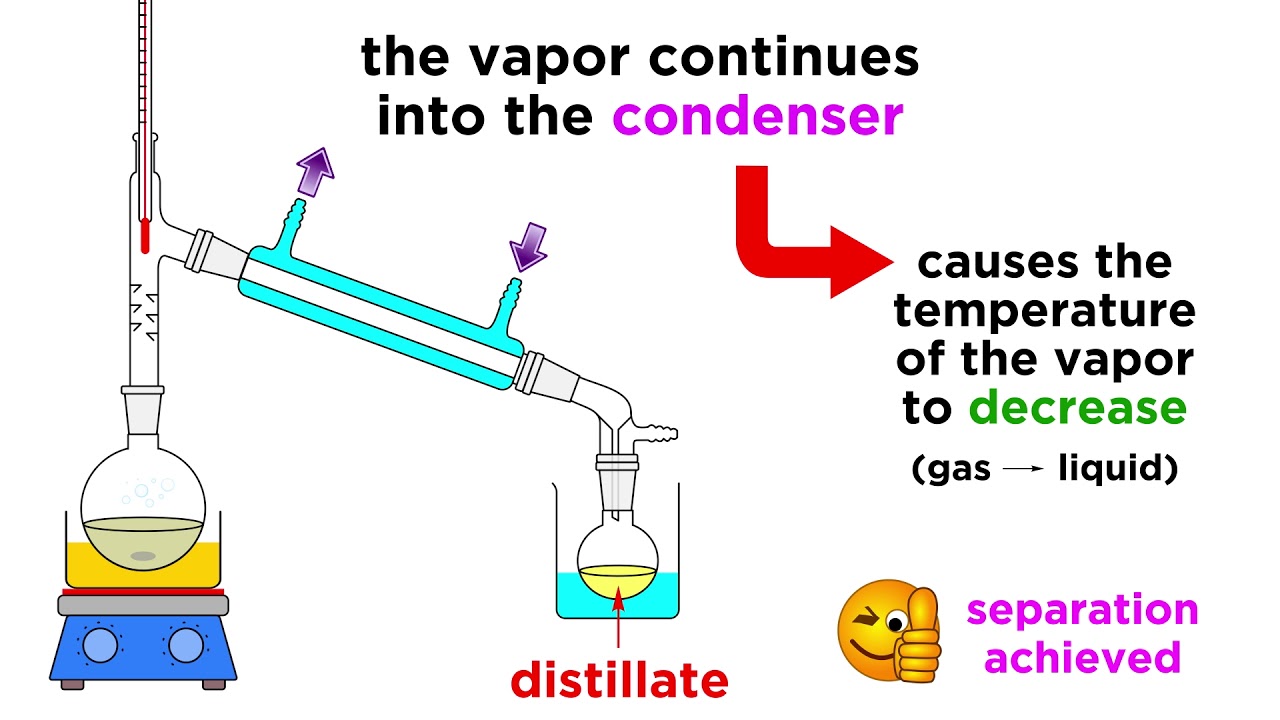
- 💧 Cold water is run through the condenser to cool the vapor and facilitate condensation back into liquid form.
- 🔴 Safety is paramount; wear protective equipment when handling flammable substances like isopropyl alcohol.
- 📝 Data analysis can be incorporated by recording the volume of distillate and vapor temperature for each collection.
- 📈 The temperature should rise as more distillate is collected, leveling off once all the alcohol has been vaporized.
- 🔄 For mixtures with close boiling points, fractional distillation can be used with a column containing glass beads to improve separation.
Q & A
What is distillation and why is it commonly used in chemistry labs and industry?
-Distillation is a technique used to separate liquid components of a mixture based on their boiling points. It is commonly used because it is effective and inexpensive.
How does distillation differ from extraction?
-Distillation separates miscible liquids with different boiling points, while extraction separates immiscible solvents using a separatory funnel.
What is required for successful separation of components using distillation?
-A significant difference in boiling points between the components is required for successful separation, otherwise too much of the other component will vaporize as well.
What equipment is needed for a simple distillation setup?
-A heat source (hot plate or Bunsen burner), round bottom flask, three-way adaptor, thermometer adaptor, thermometer, condenser, vacuum adaptor, collection vessel (e.g., beaker or Erlenmeyer flask), support adaptor, connector clips, ring stands, and clamps.
How is the condenser in a distillation setup kept cool, and why is this important?
-The condenser is kept cool by running cold water through its outer chamber. This is important because it helps the vapor condense back into liquid as it passes through the inner section.
Why is it important to have a tight seal in the distillation apparatus?
-A tight seal ensures that vapor does not escape and that the distillation process proceeds efficiently, preventing loss of the desired components.
What precautions should be taken when distilling isopropyl alcohol?
-Isopropyl alcohol is highly flammable and can cause eye irritation and skin damage. Protective equipment should be worn, and the process should be kept away from fire or sparks.
How should the heating and stirring be set to ensure proper distillation?
-The heating should be set to a medium level to avoid violent boiling, and the stirring function should be adjusted to a moderate speed for even heating. Different instruments may require experimentation to find the right settings.
What happens to the temperature during the distillation process as the volume of distillate increases?
-The temperature rises as more distillate is collected because the composition of the mixture changes with the removal of one component.
When should the collection flask be changed during distillation, and why?
-The collection flask should be changed when the temperature goes much higher than the boiling point of the desired product to avoid collecting impurities with higher boiling points.
Outlines
🔬 Introduction to Distillation Technique
The script introduces distillation as a common and cost-effective method used in labs and industry to separate miscible liquid mixtures based on their boiling points. It distinguishes distillation from extraction, where immiscible solvents are separated using a separatory funnel. The process involves heating the mixture to vaporize the component with the lower boiling point, while the other remains liquid. The vapor is then condensed and collected in a receiving flask. A simple distillation setup is described, including the necessary equipment such as a heat source, round bottom flask, three-way adaptor, thermometer, condenser, vacuum adaptor, and collection vessel. The setup process is detailed, emphasizing the importance of sealing joints, accurate thermometer placement, and securing the apparatus with clamps and clips. The script also explains the importance of running cold water through the condenser and the use of a graduated cylinder for measuring the distillate volume.
🌡️ Distillation Setup and Procedure
This paragraph continues the discussion on distillation, focusing on the setup and procedure for separating a 50:50 mixture of isopropyl alcohol and water with dye. The script advises on the liquid level in the flask, the addition of a stirring bar and boiling chip for even heating, and the importance of stirring speed. It details the steps to ensure all connections are secure and water is flowing through the condenser before starting the distillation. The paragraph also covers safety precautions, such as wearing protective equipment due to the flammable nature of isopropyl alcohol and avoiding fire or sparks. The script introduces the concept of data analysis in distillation by suggesting the recording of vapor temperature and distillate volume. It explains the expected outcome of the distillation process, including the visual confirmation of separation through the clarity of the distillate and the cessation of condensation once all alcohol has been collected. The script concludes with a brief mention of fractional distillation for mixtures with closely related boiling points and the use of a fractional column to improve separation.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Distillation
💡Boiling Point
💡Miscible Liquids
💡Condenser
💡Round Bottom Flask
💡Three-Way Adaptor
💡Thermometer Adaptor
💡Vapor
💡Fractional Distillation
💡Boiling Chip
💡Stirring Bar
Highlights
Introduction to distillation as a separation technique based on boiling points.
Difference between distillation and extraction with immiscible solvents.
Requirement for a significant boiling point difference for effective distillation.
Components needed for a simple distillation setup in a chemistry lab.
Instructions on assembling the distillation apparatus including the round bottom flask and three-way adaptor.
Importance of accurate thermometer placement for vapor temperature measurement.
Securing the flask and condenser to prevent movement during the distillation process.
Setup of the condenser with cold water to cool and condense vapors.
Use of a graduated cylinder to measure and collect distillate volume.
Preparation of the distillation mixture with isopropyl alcohol and water, including safety considerations.
Technique for even heating and stirring of the distillation mixture to prevent violent bubbling.
Observation of vapor condensation and collection in the receiving vessel.
Safety precautions when handling flammable substances like isopropyl alcohol.
Data analysis component involving measurements of distillate volume and vapor temperature.
Graph interpretation of temperature changes during distillation reflecting mixture composition.
Strategy for collecting distillate based on the boiling point of the target compound.
Introduction to fractional distillation for mixtures with close boiling points.
Completion of the distillation process and isolation of isopropyl alcohol.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Simple and fractional distillations | Chemical processes | MCAT | Khan Academy

GCSE Chemistry - Fractional Distillation and Simple Distillation #50
Separating Liquids by Distillation

A Simple Distillation Explained

Separation Techniques in Chemistry - Lesson 3 - Schooling Online

Fractional Distillation | Organic Chemistry | Chemistry | FuseSchool
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: