The Whole of AQA GCSE Physics Paper 1 | 22nd May 2024
TLDRThis script offers a comprehensive overview of essential AQA Physics topics for exams, focusing on energy types, conservation laws, and energy transformations. It covers equations for kinetic, elastic potential, gravitational potential, and thermal energy, alongside power and efficiency calculations. The video also delves into energy efficiency in homes, electricity generation from renewable and finite sources, and the environmental impact. It introduces circuit components, series and parallel circuits, and electrical safety. Additionally, it explains atomic structure, isotopes, radiation types, and their applications, concluding with nuclear fission and fusion processes.
Takeaways
- 🔋 Energy Types: The script introduces various types of energy including gravitational potential, electrical, elastic potential, kinetic, sound, light, nuclear, chemical, and thermal energy, emphasizing their interconvertibility.
- 🚀 Conservation of Energy: It explains the Law of Conservation of Energy, stating that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed, and its implications for the universe.
- ⚡ Kinetic Energy Formula: The formula for kinetic energy is given as \( \frac{1}{2} \times \text{mass} \times \text{velocity}^2 \), highlighting that only velocity is squared.
- 🌐 Potential Energy Formulas: Formulas for elastic potential and gravitational potential energy are provided, with units and variables clearly defined.
- 🔥 Thermal Energy and Power: The script covers the formula for change in thermal energy and defines power in terms of energy transferred over time, with respective units.
- 💡 Energy Efficiency and Waste: It discusses energy efficiency, wasted energy, and how it dissipates into the surroundings, with examples like a light bulb and a house's insulation.
- 🌞 Renewable vs. Finite Energy Sources: The differences between renewable and finite energy sources are outlined, along with their advantages and disadvantages.
- 🔋 Electricity and Circuits: The script provides an overview of electrical circuit components, symbols, and the concepts of series and parallel circuits.
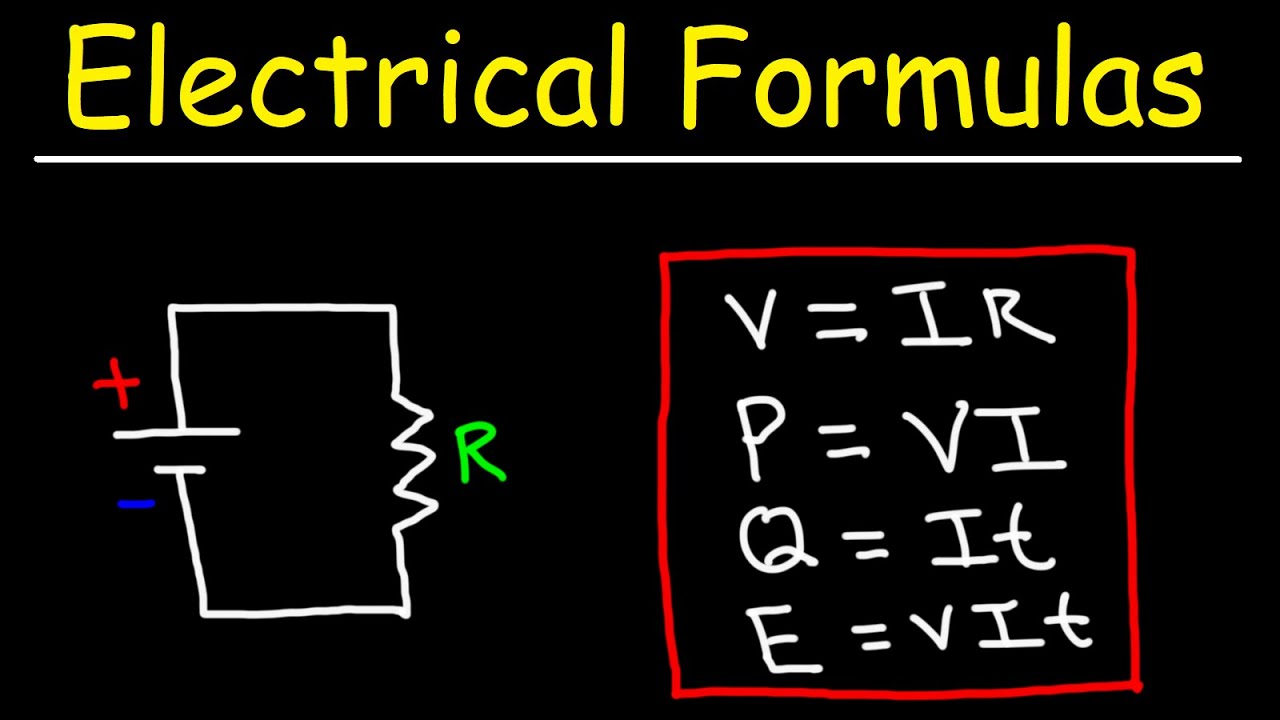
- 🔋 Electrical Measurements: It explains the relationships between charge, current, potential difference, and resistance, including their respective units and formulas.
- 🌐 National Grid and Transformers: The function of the National Grid and the role of step-up and step-down transformers in electricity transmission are described.
- 🔬 Atomic Structure and Isotopes: The script delves into atomic structure, isotopes, and the historical models of the atom, leading to the current nuclear model.
- ⚛️ Radiation Types: It covers the three types of radiation—alpha, beta, and gamma—with their characteristics and applications.
- 📊 Half-Life and Radioactivity: The concept of half-life in radioactivity is explained, along with the use of Geiger-Muller tubes to measure radiation.
- 🌡️ States of Matter and Energy: The behavior of particles in solids, liquids, and gases is discussed, along with energy input and output processes.
- 💼 Static Electricity: The script touches on static electricity, its causes, and the interactions between charged objects.
- 🌟 Nuclear Fission and Fusion: It differentiates between nuclear fission, involving the splitting of heavy atoms, and nuclear fusion, where light nuclei combine, both releasing energy.
Q & A
What is the purpose of the summary video mentioned in the transcript?
-The purpose of the summary video is to provide a quick overview of the first few topics for the first AQA Physics exam, including important equations, units, and concepts that students need to learn.
What is the mnemonic 'Geeks Lunch' used for in the script?
-The mnemonic 'Geeks Lunch' is used to remember the different types of energy: Gravitational potential energy, Electrical energy, Elastic potential energy, Kinetic energy, Sound energy, Light energy, Nuclear energy, Chemical energy, and Heat or thermal energy.
According to the Law of Conservation of Energy mentioned in the script, can energy be created or destroyed?
-No, according to the Law of Conservation of Energy, energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can only be transformed into another type of energy.
What is the formula for kinetic energy as stated in the script?
-The formula for kinetic energy is half times mass (1/2 * m) times velocity squared (v^2), where kinetic energy is measured in joules, mass in kilograms, and velocity in meters per second.
What is the formula for gravitational potential energy?
-The formula for gravitational potential energy is mass times gravity times height (m * g * h), with gravitational potential energy measured in joules, mass in kilograms, gravitational field strength (g) at 9.8 newtons per kilogram, and height in meters.
How is power defined in the context of the script?
-Power is defined as the energy transferred over time, with units measured in watts (W). It can also be defined as work done over time, where power is measured in watts, work done in joules (J), and time in seconds (s).
What is the difference between renewable and finite energy sources as described in the script?
-Renewable energy sources are those that won't run out and can be replenished, such as the sun, wind, water, and geothermal power. Finite energy sources, on the other hand, are those that will eventually run out, like fossil fuels (coal, oil, gas) and nuclear power.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using solar power as mentioned in the script?
-The advantages of solar power include that it doesn't release carbon dioxide and is non-polluting. The disadvantages are that it doesn't work at night or on cloudy/winter days, and it can be expensive to install.
What is the formula for calculating the efficiency of a system?
-Efficiency is calculated as the ratio of useful energy out to the total energy in, and can be expressed as a percentage or decimal. It can also be calculated as the ratio of useful power out to total power in.
What are the three types of radiation described in the script, and how do they differ in terms of size and ionizing capability?
-The three types of radiation are alpha, beta, and gamma. Alpha radiation is the largest and most ionizing but can be stopped by a sheet of paper or skin. Beta radiation is smaller and can be stopped by aluminum foil, while gamma radiation is the smallest, least ionizing, and most penetrating, requiring thick lead to stop it.
Outlines
📚 AQA Physics Exam Summary
This paragraph introduces a summary video for the AQA Physics exam, covering initial topics. It emphasizes the importance of a revision guide for quickfire questions and essential equations and units. The video also mentions a mnemonic 'Geeks Lunch' for remembering different types of energy, such as gravitational, electrical, elastic, kinetic, sound, light, nuclear, chemical, and thermal energy. It explains the Law of Conservation of Energy, stating that energy cannot be created or destroyed but transformed, and provides examples of energy transformation in everyday objects like phones, matches, and fireworks. Key formulas for kinetic, elastic potential, gravitational potential, and thermal energy are detailed, along with the concept of power and its relation to energy and time.
🌡️ Energy Efficiency and Renewables
The second paragraph discusses energy efficiency, focusing on wasted energy as energy that is not utilized as intended. It uses the example of a light bulb to illustrate useful versus wasted energy and explains how wasted energy dissipates into the surroundings. The paragraph further explores energy efficiency measures in buildings, such as insulation and energy-efficient design. It introduces the concept of efficiency as a ratio of useful energy output to total energy input, expressed as a percentage or decimal. The section also contrasts renewable and finite energy sources, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of solar, wind, tidal, wave, hydroelectric, geothermal power, and fossil fuels, including their impact on the environment and climate change.
🔋 Electrical Circuits and Energy Transfer
This paragraph delves into electrical circuits, starting with a review of circuit symbols and components like cells, batteries, ammeters, voltmeters, and various resistors. It differentiates between series and parallel circuits and explains the flow of charge, current, potential difference, and resistance within them. The paragraph also covers the calculation of charge, current, potential difference, and resistance, highlighting their respective units. It discusses Ohm's law and the relationship between current, potential difference, and resistance. Additionally, it introduces the concepts of power, energy, and the National Grid, describing how electricity is transmitted from power stations to homes through a network of transformers and pylons.
🔬 Particle Dynamics and Energy States
The fourth paragraph examines the behavior of particles in different states of matter—solid, liquid, and gas—and their energy requirements for phase transitions. It introduces the concept of density and provides the formula for calculating it. The paragraph also explains specific heat capacity and its role in determining the energy needed to change the temperature of a substance. Furthermore, it discusses specific latent heat, which is the energy required for a phase change at the melting point, and the distribution of molecular energy in systems at different temperatures. It concludes with a simulation demonstrating how gas pressure increases with the addition of more gas.
⚛️ Atomic Structure and Radiation
This paragraph provides an overview of atomic structure, starting with the ancient Greek concept of the atom as uncuttable and moving through historical models, including Dalton's solid sphere, JJ Thompson's plum pudding model, Rutherford's nuclear model, and Bohr's atomic model with electrons orbiting a nucleus. It explains the composition of an atom, including protons, neutrons, and electrons, and how these particles relate to atomic number and mass number. The paragraph also covers isotopes, ions, and the periodic table. It concludes with a discussion of the three types of radiation—alpha, beta, and gamma—detailing their properties, ionizing and penetrating capabilities, and methods for stopping them.
🌟 Nuclear Reactions and Applications
The seventh paragraph explores nuclear reactions, beginning with the concept of half-life and its significance in radioactive decay. It explains the process of alpha and beta decay, using uranium-238 and neptunium as examples. The paragraph then discusses sources of background radiation, including radon gas, medical procedures, ground radiation, food and drink, cosmic radiation, nuclear weapon testing, plane travel, and nuclear power stations. It also covers the uses of radioactivity in various applications, such as gamma radiation in cancer treatment and sterilization, beta radiation in industrial thickness testing, and alpha radiation in smoke detectors. Additionally, it touches on nuclear fission and fusion processes and their roles in energy release.
🎵 Conclusion and Final Thoughts
The final paragraph serves as a conclusion to the video, highlighting the journey through the various topics covered. It provides a brief recap of the key points discussed in the previous paragraphs and offers a musical note with the mention of the song 'Something Elated' by Broke for Free, which has been playing in the background throughout the video. This closing paragraph leaves the viewer with a sense of completion and a reminder of the comprehensive nature of the information presented.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Conservation of Energy
💡Kinetic Energy
💡Gravitational Potential Energy
💡Specific Heat Capacity
💡Power
💡Efficiency
💡Renewable Resources
💡Circuit Symbols
💡Series and Parallel Circuits
💡Transformer
Highlights
Summary video for AQA Physics exam covering fundamental topics.
Availability of a free revision guide with checklist and quickfire questions.
Memory aid 'Geeks Lunch' for different types of energy.
Explanation of energy transformation and conservation.
Formulas for kinetic, elastic potential, and gravitational potential energy.
Calculation of change in thermal energy and power.
Concept of wasted energy and its dissipation.
Importance of energy efficiency in buildings.
Definition and calculation of efficiency.
Comparison of renewable and finite energy sources.
Advantages and disadvantages of solar, wind, tidal, and geothermal power.
Overview of electrical circuit components and symbols.
Differences between series and parallel circuits.
Fundamentals of charge, current, potential difference, and resistance.
Graphs for current-potential difference relationships.
Total resistance calculations in series and parallel circuits.
Safety features of mains electricity and plug sockets.
Explanation of power, energy, and their relationships.
National Grid's function and the role of transformers.
Properties of solids, liquids, and gases in relation to energy.
Concepts of density and specific heat capacity.
Explanation of specific latent heat and phase changes.
Molecular perspective on temperature and energy.
Demonstration of gas pressure in a closed container.
Basic structure and components of an atom.
Atomic number, mass number, and their relationship to protons and neutrons.
Differences between atoms, ions, and isotopes.
Historical models of the atom and their evolution.
Types of radiation: alpha, beta, and gamma.
Practical applications and protection against different types of radiation.
Use of Geiger-Muller tube for measuring radiation.
Concept of half-life and its significance in radioactivity.
Calculating decay of radioactive isotopes through alpha and beta decay.
Sources and percentages of background radiation.
Uses of radioactivity in various fields based on half-life and radiation type.
Processes of nuclear fission and fusion, and their differences.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

GCSE Physics Paper 1 Revision Raps

College Physics 1: Lecture 29 - Forms of Energy

Nuclear Power - IB Physics

Ecosystem & Nature Conservation | How To Save The Planet | The Dr Binocs Show | Peekaboo Kidz
Electrical Formulas - Basic Electricity For Beginners

The whole of EDEXCEL Physics Paper 2 or P2 in only 41 minutes. 9-1 GCSE Science Revision
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: