GCSE Physics Paper 1 Revision Raps
TLDRThis video script delivers an engaging and educational lesson on electricity and energy, using a unique blend of humor and rhyme. It covers the basics of electrical wiring, including fuses, wires, and their respective roles. The script delves into direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC), and explains key physics concepts such as current, voltage, and resistance. It also explores various forms of energy, from kinetic and thermal to potential and nuclear, highlighting both renewable and non-renewable sources. The educational content is creatively presented with a focus on memorization of equations and an overview of energy states and types, making complex topics accessible and entertaining.
Takeaways
- 🔌 Basic Electrical Components: The script introduces electrical components like plugs, fuses, and wires, explaining their roles in a circuit.
- ⚡ Electrical Safety: It emphasizes the importance of not touching live wires, as they carry electricity and can be dangerous.
- 🌐 Circuitry Colors: The script describes the color coding of electrical wires: red for live, blue for neutral, and green and yellow for earth.
- 💡 Current Types: The difference between direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC) is mentioned, with DC being unidirectional.
- 🔋 Basic Physics of Electricity: Key electrical concepts such as current, voltage, and resistance are explained, along with how they relate to each other.
- 📚 Memorable Equations: The script encourages memorizing physics equations like Ohm's law (Power = Voltage x Current) and Power = Resistance x Current^2.
- 💰 Energy and Money: A metaphor is made between energy transfer and money, highlighting that energy cannot be created or destroyed.
- 🔥 Energy Types: Various forms of energy are listed, including kinetic, thermal, potential, elastic, and gravitational.
- ⚡️ Electricity Generation: The script touches on different sources of energy, such as fossil fuels and renewable sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power.
- 🌊 Hydroelectric Power: A detailed explanation is given on how hydroelectric power works, using the gravitational energy of water.
- 🌡️ States of Matter: The script covers the three states of matter—solid, liquid, and gas—and how they are affected by temperature and energy.
- 💿 Radioactivity Basics: An introduction to radioactivity is provided, explaining the types of radiation (alpha, beta, gamma) and the concept of half-life.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of a fuse in an electrical circuit?
-The primary purpose of a fuse is to protect the circuit by breaking the flow of electricity if the current becomes too high, preventing potential damage to the circuit or fire hazards.
What are the three wires mentioned in the script and what do they represent?
-The three wires mentioned are the live wire (often black or red), which carries the current to the device; the neutral wire (usually blue), which brings the current back to the source; and the earth wire (green and yellow), which provides a path for electricity to flow to the ground in case of a fault, enhancing safety.
What does the term 'direct current' (DC) refer to in the context of electricity?
-Direct current (DC) refers to the flow of electric charge in a single direction, typically from a battery or a power supply to a device.
What are the three descriptive words used in the script to describe how electrons move in a wire?
-The three descriptive words are current, voltage, and resistance. Current measures the flow of electrons, voltage is the force that pushes the electrons, and resistance slows down the flow of electrons.
What is the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance in an electrical circuit?
-The relationship between current (I), voltage (V), and resistance (R) is described by Ohm's Law, which states that Voltage equals Current times Resistance (V = IR).
What is the formula for calculating electrical power in a circuit?
-The formula for calculating electrical power (P) in a circuit is Power equals Voltage times Current (P = VI) or Power equals Current squared times Resistance (P = I^2R).
What are the different types of energy mentioned in the script?
-The different types of energy mentioned are kinetic, thermal, potential, elastic, gravitational, magnetic, and electrical.
What is the unit used to measure energy in the script?
-The unit used to measure energy in the script is the joule (J).
What are the two main types of fossil fuels mentioned in the script?
-The two main types of fossil fuels mentioned are coal and oil.
What is hydroelectric power and how does it work?
-Hydroelectric power is a renewable energy source that uses the gravitational energy of water. Water from a high reservoir flows through a turbine, which spins and generates electricity.
What are the three states of matter and what are their characteristics?
-The three states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. Solids have a fixed shape and volume with particles that vibrate but do not flow. Liquids have a fixed volume but take the shape of their container with particles that can slide past each other. Gases have no fixed shape or volume and particles move freely and quickly.
What are the three types of radioactive decay mentioned in the script?
-The three types of radioactive decay mentioned are alpha decay, beta decay, and gamma decay.
What is the purpose of a Geiger counter in the context of radioactive decay?
-A Geiger counter is used to measure the rate of nuclear decay by counting the number of radioactive particles that decay per second.
What is half-life and how is it related to radioactive decay?
-Half-life is the amount of time it takes for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay. It is a measure of the rate at which a radioactive substance decays.
Outlines
🔌 Electrical Safety and Basics
This paragraph introduces the viewer to basic electrical components such as plugs, fuses, and wires, emphasizing the importance of safety when handling electricity. It explains the role of the live wire in carrying electricity to appliances like a dryer and the function of the neutral wire and earth wire in ensuring safety. The live wire is associated with direct current (DC), while the neutral wire completes the circuit. The earth wire is crucial in case of a fault, as it directs the current to the ground, preventing electric shocks. The paragraph also touches on the difference between direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC), highlighting that electrons flow in a single direction in DC, unlike AC.
🔋 Understanding Electrical Concepts
This section delves into the physics behind electricity, focusing on how electrons flow through wires powered by a battery. It introduces key electrical terms such as current, voltage, and resistance, explaining their roles in the flow of electricity. Current is described as the flow of electrons, voltage as the force that pushes them, and resistance as the factor that slows down the flow, likened to walking through a crowd. The paragraph also presents fundamental electrical equations, including the relationship between charge, current, and time, as well as the formulas for calculating power, which is the product of voltage and current or the product of resistance and current squared. These equations are crucial for understanding energy transfer and consumption in electrical circuits.
🌞 Types of Energy and Their Sources
The script moves on to discuss various forms of energy, including kinetic, thermal, potential, elastic, and gravitational energy. It also touches on magnetic and electrical energy, emphasizing their importance and the teacher's enthusiasm for the subject. The paragraph then shifts to energy sources, differentiating between non-renewable fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas, which are burned in power plants to generate energy, and renewable sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. It points out the environmental impact of burning fossil fuels and the benefits of renewable energy sources, which are sustainable and less harmful to the environment.
💧 Hydroelectric Power and States of Matter
This part of the script highlights hydroelectric power as the teacher's favorite form of renewable energy. It describes how hydroelectric power plants use the gravitational potential energy of water stored behind a dam to generate electricity as the water flows through turbines. The teacher uses a casual, humorous tone to engage the audience, comparing the turbines to fans and emphasizing the power and sustainability of hydroelectric energy. The paragraph concludes with a brief mention of the three states of matter—solid, liquid, and gas—explaining that they are all composed of atoms and mass. It outlines the behavior of atoms in each state, from the rigid structure of solids to the free movement of atoms in gases, and the transition between states as a result of energy exchange.
☢️ Radioactivity and Nuclear Decay
The final paragraph of the script addresses the topic of radioactivity, starting with an overview of atomic structure and the process of nuclear decay. It introduces the concepts of alpha, beta, and gamma radiation, explaining their penetration capabilities and ionizing properties. Alpha particles have the weakest penetration and can be stopped by a sheet of paper, while gamma rays are the most penetrating and require denser materials like lead to be stopped. The script also mentions the use of a Geiger counter to measure the rate of nuclear decay, which is the number of radioactive atoms that decay per second. The concept of half-life is introduced as the time it takes for half of a radioactive substance's atoms to decay, emphasizing its importance in understanding the behavior of radioactive materials.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Fuse
💡Wire
💡Live Wire
💡Neutral Wire
💡Earth Wire
💡Direct Current (DC)
💡Alternating Current (AC)
💡Current
💡Voltage
💡Resistance
💡Power
💡Energy Types
💡Renewable Energy
💡Non-renewable Energy
💡Hydroelectric Power
💡States of Matter
💡Radioactivity
Highlights
Introduction to electrical components: plug, fuse, wires, and their functions.
Explanation of the dangers of touching live electrical components.
Description of the roles of the live, neutral, and earth wires.
Overview of fuses and their importance in preventing electrical fires.
Differentiation between direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC).
Fundamental physics concepts: current, voltage, and resistance.
Electrical equations: current times time equals charge, power calculation.
Energy types: kinetic, thermal, potential, elastic, and gravitational.
Discussion on non-renewable and renewable energy sources.
Explanation of hydroelectric power and its generation process.
Introduction to the states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas.
Description of the behavior of atoms in different states of matter.
Radiation types: alpha, beta, and gamma, and their characteristics.
Geiger counter usage for measuring nuclear decay.
Concept of half-life in nuclear decay.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

The Whole of AQA GCSE Physics Paper 1 | 22nd May 2024
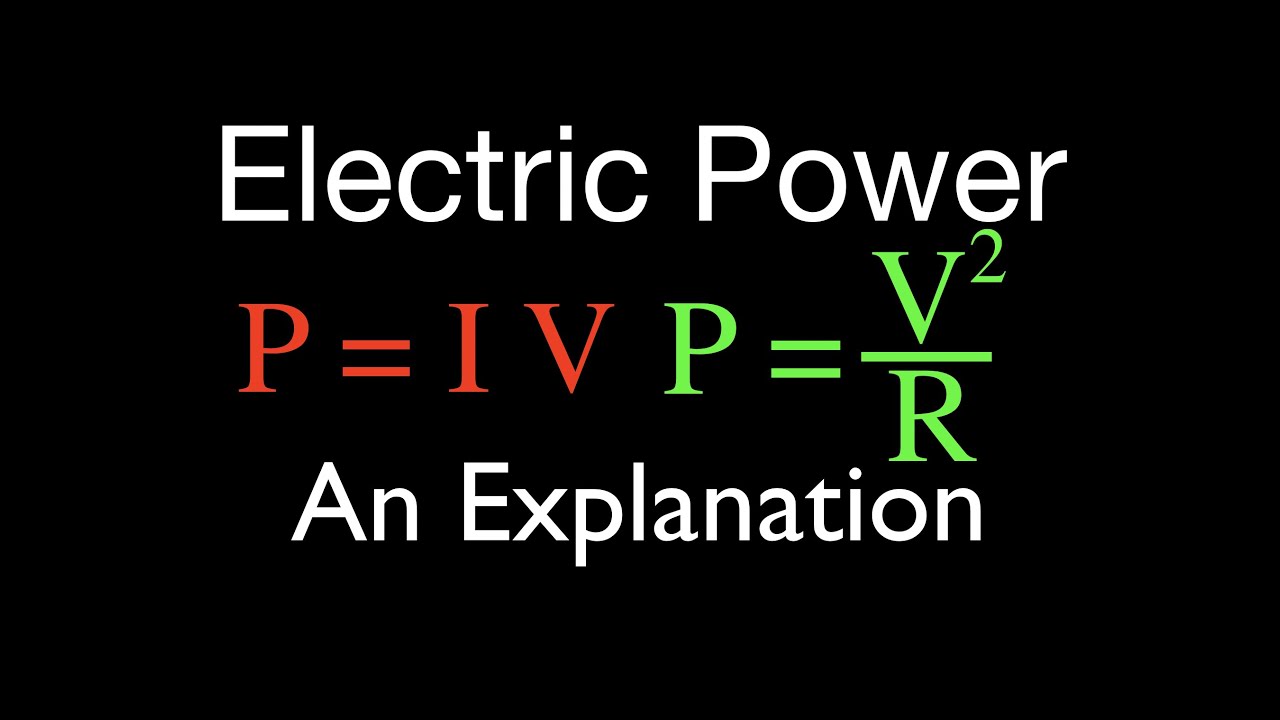
Electric Power (1 of 3) and Watts, An Explanation
Lesson 1 - Voltage, Current, Resistance (Engineering Circuit Analysis)

Electricity for Kids | What is Electricity? Where does Electricity come from?

Circuit symbols (SP10a)
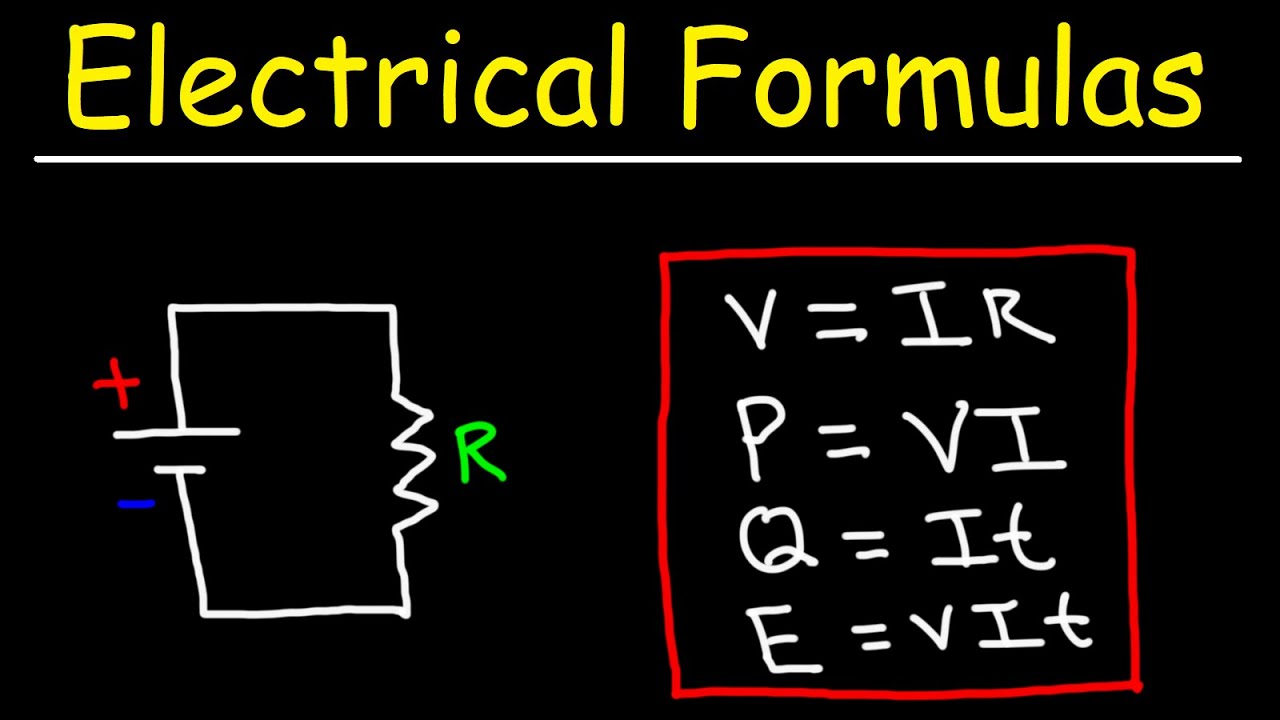
Electrical Formulas - Basic Electricity For Beginners
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: