Momentum
TLDRIn this AP Physics essentials video, Mr. Andersen explains the concept of momentum, which is the product of an object's mass and velocity. He uses the historical example of a train in Paris to illustrate the consequences of high momentum and emphasizes the importance of understanding how momentum can be changed by altering mass or velocity. The video demonstrates that applying a net force to an object will eventually change its momentum, showing a direct relationship between net force and momentum. It concludes with a practical example from video games to highlight the real-world application of these principles.
Takeaways
- 📐 **Momentum Definition**: Momentum is the product of an object's mass and its velocity.
- 🚂 **Historical Example**: A train's inability to stop in time due to its high momentum illustrates the concept.
- 🔢 **Calculating Momentum**: To find an object's momentum, multiply its mass by its velocity.
- ↗️ **Increasing Momentum**: Momentum can be increased by adding to the object's mass or velocity.
- 🚀 **Force and Momentum**: Applying a net force to an object changes its momentum over time.
- 🔄 **Direction of Momentum**: The direction of an object's momentum changes to align with the net force applied.
- 🧲 **Net Force Effect**: A greater net force results in a quicker change in momentum.
- 🔄 **Reversing Direction**: If an object is moving in one direction but a net force is applied in the opposite direction, it will eventually reverse and move towards the net force.
- 🎮 **Multidimensional Momentum**: Momentum principles apply in both one-dimensional and multidimensional scenarios, such as in video games.
- 📉 **Deceleration and Acceleration**: Applying a net force opposite to the direction of motion will first slow down the object before changing its direction.
- 🔍 **Data Justification**: It's important to collect data to demonstrate how net force impacts the change in momentum.
Q & A
What is the definition of momentum in physics?
-Momentum in physics is defined as the product of an object's mass and its velocity.
Why did the train in the 1895 Paris incident have too much momentum?
-The train had too much momentum because it was moving at a high velocity and had a large mass, which caused it to continue moving forward even after reaching the train station.
What is the formula to calculate momentum?
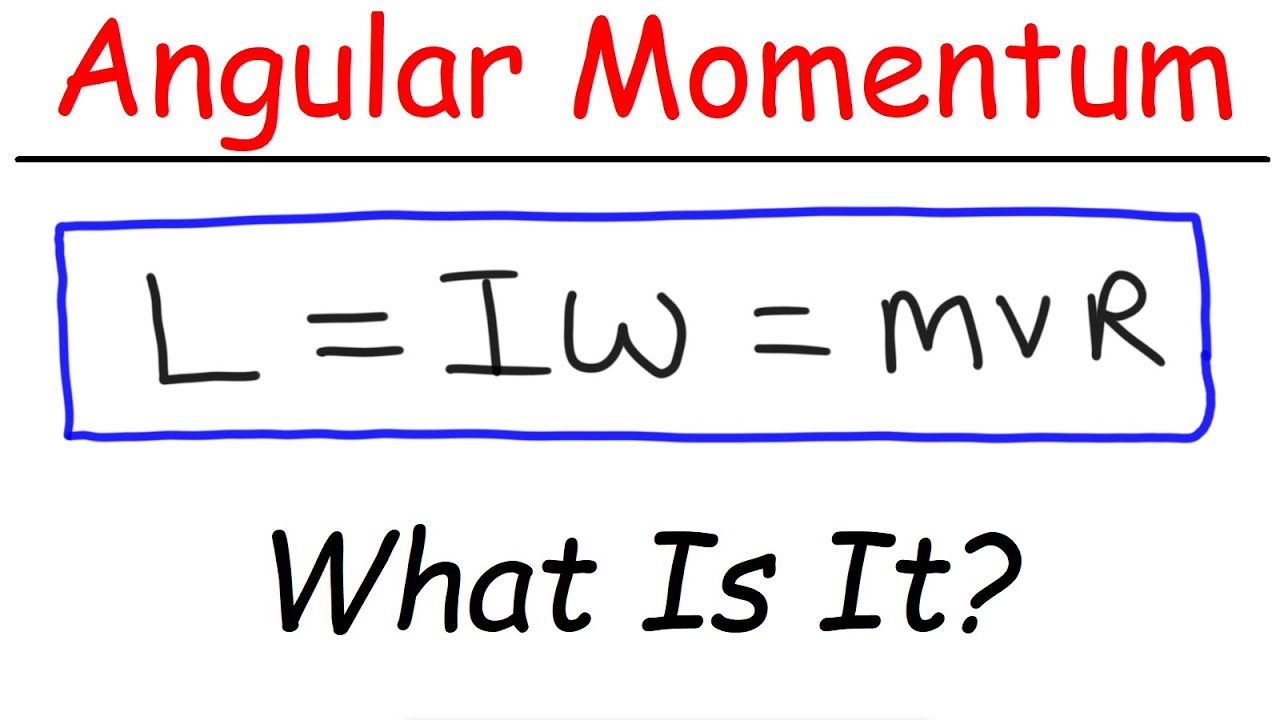
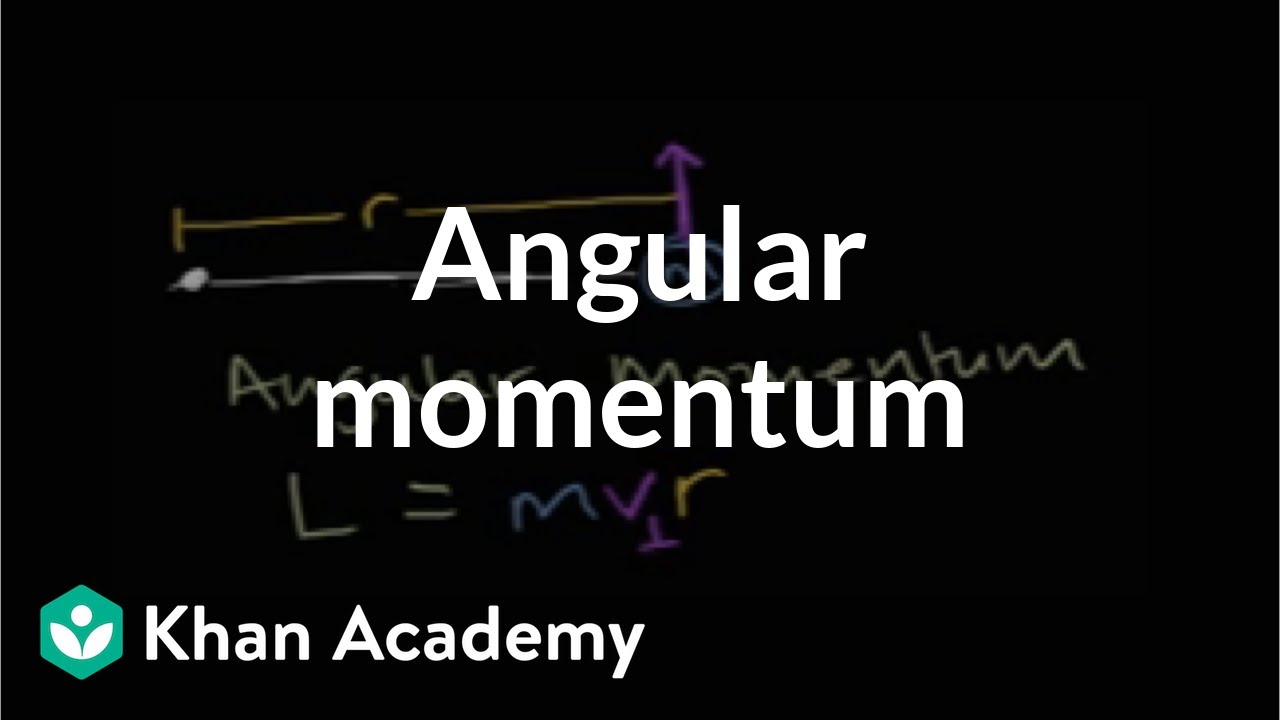
-The formula to calculate momentum is p=mv, where 'p' stands for momentum, 'm' for mass, and 'v' for velocity.
How can the momentum of an object be changed?
-The momentum of an object can be changed by altering its mass, velocity, or by applying a net force to it.
What happens when a net force is applied to an object moving in one direction?
-When a net force is applied to an object, it causes a change in the object's momentum in the direction of the applied force, which may increase, decrease, or change the direction of the object's motion.
How does increasing the net force on an object affect its momentum?
-Increasing the net force on an object results in a more rapid change in momentum, accelerating the object more quickly in the direction of the force.
What is the relationship between the net force applied to an object and its momentum?
-There is a direct relationship between the net force applied to an object and its momentum; the greater the net force, the greater the change in momentum.
If an object is at rest and a net force is applied, what happens to its momentum?
-When a net force is applied to an object at rest, its momentum begins to increase in the direction of the applied force, causing the object to move.
Can an object moving in one direction have its momentum changed to move in a different direction?
-Yes, if a net force is applied in a different direction than the object's motion, the object will eventually slow down, stop, and then start to accelerate in the direction of the net force, changing its momentum.
How does the concept of momentum relate to playing video games, as mentioned in the script?
-In video games, such as the example of playing 'Asteroids', the concept of momentum is evident when the ship's motion (momentum) changes direction or speed due to applied forces, like explosions or thrusters.
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Momentum
Mr. Andersen begins the video by introducing the concept of momentum, which is defined as the product of an object's mass and its velocity. He uses the historical example of a train that couldn't stop in time due to its high momentum to illustrate the principle. The video emphasizes that momentum is a property of moving objects and can be altered by changing either the mass or the velocity of the object. Applying a net force to an object is identified as the primary method to change its velocity and, consequently, its momentum. The formula for momentum, p=mv, is introduced, and a simple example calculation is provided using a 1.0 kg cart moving at 2.0 m/s.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Momentum
💡Mass
💡Velocity
💡Net Force
💡p=mv
💡Train
💡Change in Momentum
💡Physics Lab
💡Weight
💡Direction
💡Video Games
Highlights
Momentum is defined as the product of an object's mass and its velocity.
A historical example of a train with too much momentum causing an accident in Paris in 1895.
Momentum is a fundamental concept in physics that relates to an object's motion.
The formula for calculating momentum is p=mv, where p is momentum, m is mass, and v is velocity.
Increasing mass or velocity results in greater momentum.
Applying a net force to an object can change its velocity and consequently its momentum.
An increase in net force leads to a more rapid increase in momentum.
A demonstration of how applying a net force to a cart at rest results in momentum in the direction of the force.
The relationship between net force and momentum is direct; increasing force increases momentum.
An object moving in one direction but with a net force applied in the opposite direction will eventually change its momentum.
The concept of momentum is applied in real-world scenarios, such as in video games.
In video games, momentum can be influenced by forces applied in different directions.
The importance of collecting data to justify how net force impacts the change in momentum.
The video aims to help viewers understand the concept of momentum and its practical applications.
The video concludes with a hope that viewers have learned about the impact of net force on momentum.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: