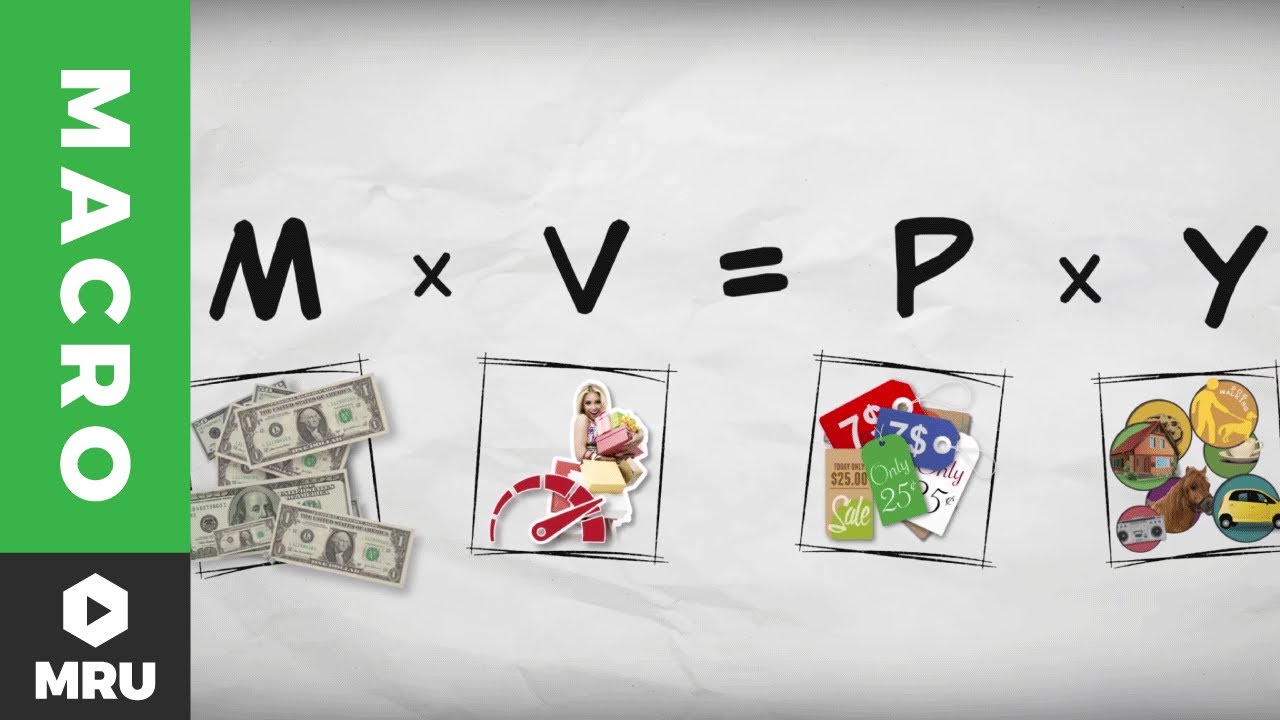Macroeconomics: Crash Course Economics #5
TLDRIn this engaging episode of Crash Course Economics, hosts Adriene Hill and Mr. Clifford delve into the fundamentals of macroeconomics, breaking down its significance in understanding the economy's big picture—such as economic output, unemployment, inflation, and government policies. Through dynamic explanations and playful banter, they illustrate how macroeconomics is vital for making informed decisions, touching upon key concepts like GDP, unemployment rates, and inflation, while using relatable analogies to simplify complex ideas. The video highlights the importance of macroeconomics in navigating economic challenges, offering viewers a foundational grasp on how economies operate and the impact of government policies, ultimately encouraging a deeper interest in economic literacy.
Takeaways
- 😀 Macroeconomics studies the entire economy, including economic output, unemployment, inflation, etc.
- 📈 GDP (Gross Domestic Product) measures a country's total economic output.
- 📉 Recession is defined as two consecutive quarters of declining GDP.
- 🔎 The unemployment rate measures the percentage of people actively looking for work but cannot find jobs.
- ❌ The natural rate of unemployment is between 4-6% in the US due to frictional and structural unemployment.
- 🛒 Inflation reduces purchasing power as prices rise, while deflation discourages spending as prices fall.
- 🚘 The business cycle of economic expansions and contractions is like a car speeding up and slowing down.
- 💶 Consumer spending is the largest component of GDP in most economies.
- 🏦 Fiscal and monetary policies by the government aim to regulate the economy.
- 🎓 Understanding macroeconomics helps individuals make better personal financial decisions.
Q & A
What are the three main economic goals that policy makers aim to achieve?
-The three main economic goals are: 1) Keep the economy growing over time, 2) Limit unemployment, and 3) Keep prices stable.
What is the difference between nominal GDP and real GDP?
-Nominal GDP measures the dollar value of goods and services produced without adjusting for inflation. Real GDP adjusts the value of goods and services produced to account for inflation, giving a more accurate picture of economic growth.
What are the main components that make up a country's GDP?
-The four main components of a country's GDP are: 1) Consumer spending, 2) Business investment spending, 3) Government spending, and 4) Net exports.
What are the three types of unemployment?
-The three types of unemployment are: 1) Frictional unemployment (people between jobs), 2) Structural unemployment (lack of demand for a type of labor), and 3) Cyclical unemployment (due to economic recessions).
What role can government policy play in managing the economy?
-Government policies like increased spending and tax cuts can help speed up the economy during recessions to get back to full employment. However, this also increases government debt.
Why is deflation generally seen as bad by economists?
-Deflation discourages consumer spending as people expect prices to fall further in the future. Less spending slows down the economy, decreasing GDP and increasing unemployment.
What is the difference between a recession and a depression?
-A recession is defined as two consecutive quarters of declining GDP. A depression is a more severe and prolonged recession with very high unemployment and falling prices.
What is the natural rate of unemployment?
-The natural rate of unemployment is the level of unemployment when the economy is at full employment, usually between 4-6% in the United States. This accounts for frictional and structural unemployment.
How does GDP relate to the unemployment rate?
-GDP growth rate and unemployment rate are inversely related. As GDP rises, unemployment falls. As GDP falls, unemployment rises.
What is the business cycle and what drives it?
-The business cycle refers to the cyclical expansions and contractions of economic activity over time. It is driven by factors like consumer and business spending, government policies, and global economic conditions.
Outlines
😀 Introducing Macroeconomics and Economic Measures
Paragraph 1 introduces macroeconomics, which studies the entire economy and economic measures like GDP, unemployment rate, and inflation rate that indicate a country's economic health. It explains why macroeconomics emerged as a field during the Great Depression to guide economic policies. It also notes that economists may disagree on interpretations and predictions.
😟 Greece's Struggling Economy Since 2008
Paragraph 2 analyzes Greece's economic decline using GDP data showing six years of decreasing GDP similar to the Great Depression. It defines technical terms like recession, depression, and problems with GDP as an economic measure.
📈 The Goals of Unemployment and Price Stability Policies
Paragraph 3 explains the economic goals of limiting unemployment, measured by the unemployment rate, and keeping prices stable using the inflation rate. It details different types of unemployment and the natural rate of unemployment when the economy is at full employment.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Macroeconomics
💡GDP
💡Unemployment
💡Inflation
💡Recession
💡Depression
💡Business cycle
💡Fiscal policy
💡Consumer spending
💡Investment
Highlights
First significant research finding
Introduction of new theoretical framework
Proposed innovative methodology for analysis
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: