General Relativity Explained simply & visually
TLDRThe video script narrates the journey of Albert Einstein's groundbreaking work on the theory of relativity. Initially met with skepticism and ridicule, Einstein's theory challenged the long-standing principles of Isaac Newton. Through thought experiments, such as imagining a window washer falling, Einstein conceptualized the equivalence of gravity and acceleration, leading to the insight that gravity could cause space to curve. This idea was mathematically formalized with the help of Marcel Grossman, introducing the world to the concept of space-time curvature as the basis for general relativity. The theory's validity was confirmed through observations of Mercury's orbit and the famous 1919 solar eclipse experiment by Arthur Eddington. General relativity revolutionized our understanding of gravity, space, and time, and while it has profound implications, it also raised new questions that hint at the need for a quantum gravity theory to reconcile it with quantum mechanics.
Takeaways
- 🌌 Albert Einstein's Special Theory of Relativity faced initial ridicule and skepticism when it was first published in 1905.
- 🧐 Einstein was not satisfied with his own theory because it did not account for gravity or accelerating observers.
- 🎢 Einstein's thought experiment involving a falling window washer led to the insight that gravity and acceleration are equivalent experiences.
- 🚀 He imagined scenarios involving a scale in a spaceship and light beams to explore the effects of acceleration and gravity on space.
- 📉 Einstein hypothesized that light must bend in a gravitational field, challenging the notion that light always takes the shortest path.
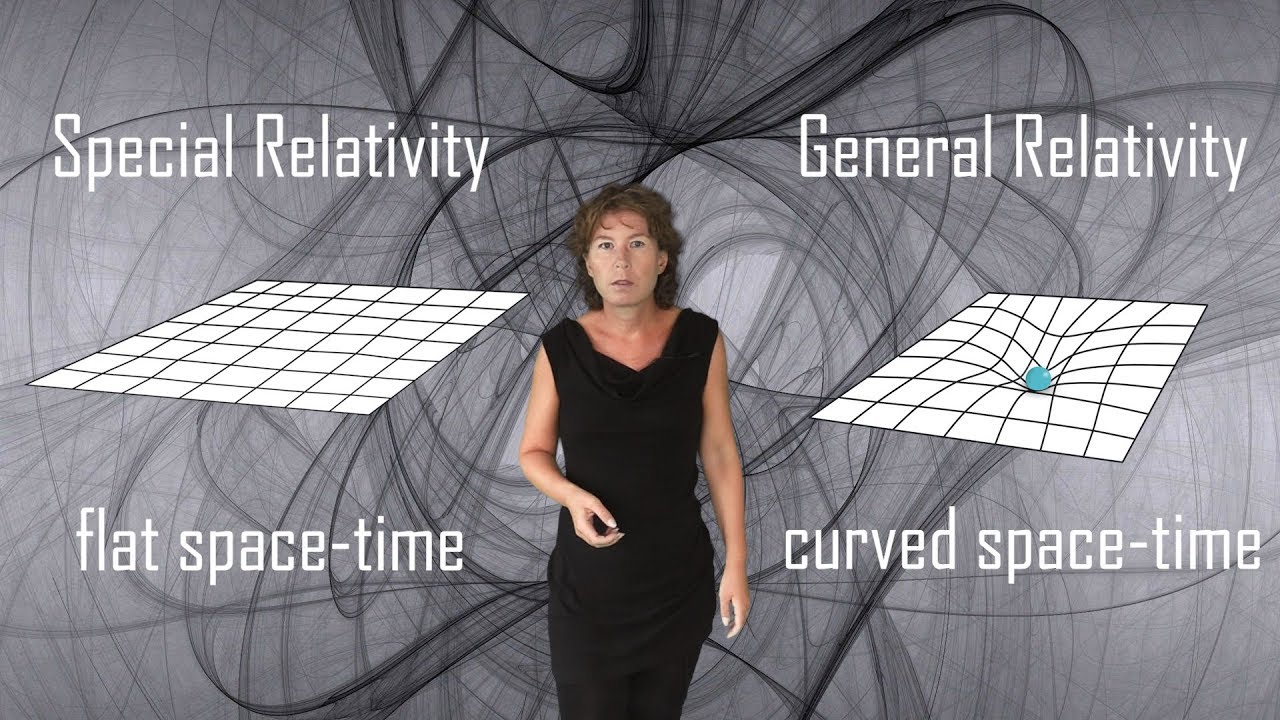
- 🤔 He then theorized that gravity might cause a curvature of space itself, with light taking the shortest curved path in a warped space-time.
- 🤝 Einstein collaborated with mathematician Marcel Grossman to develop the complex mathematics of General Relativity, based on Reimannian Geometry.
- 🌍 General Relativity proposed that gravity is not a force but a curvature of space-time caused by mass and energy.
- 🪐 The theory was confirmed by observations of Mercury's orbit and the bending of starlight during a solar eclipse, turning Einstein into a celebrity.
- ⏱ Special Relativity's principles were integrated into General Relativity, showing that gravity affects time as well as space, leading to time dilation near massive objects.
- 🕳 General Relativity, while groundbreaking, does not fully explain gravity's nature or the physics within black holes, suggesting the need for a quantum gravity theory.
Q & A
What was the initial reaction to Einstein's Special Theory of Relativity when it was first published?
-When Einstein first published the Special Theory of Relativity in 1905, he was either vehemently ridiculed or ignored. People thought the theory was too weird and radical to be real, and some even insulted his religious heritage by calling it 'Jewish science'.
Why was Einstein not satisfied with his own Special Theory of Relativity?
-Einstein was not satisfied with his Special Theory of Relativity because it only applied to observers moving in a straight line at a constant speed and did not account for the presence of gravity or accelerating observers.
What thought experiment led Einstein to develop his theory further?
-Einstein's thought experiment involved imagining what would happen if a window washer on a ladder near his patent office were to fall. He considered the experience of the window washer as he would feel weightless during the fall, which led him to the concept that gravity and acceleration are different ways to describe the same thing.
How did Einstein's thought experiment with a falling window washer lead to his insights on gravity?
-Einstein imagined the experience of the window washer falling and realized that if he was falling, gravity would be the only force acting on him, and he would feel no weight. This led him to the insight that gravity and acceleration are equivalent, which was key to connecting gravity with the theory of relativity.
What did Einstein hypothesize about the nature of space in the presence of mass and energy?
-Einstein hypothesized that in the presence of mass and energy, space itself becomes curved, meaning that the shortest path light can take is not a straight line but a curved path, which is a fundamental concept of General Relativity.
How did Einstein's theory of General Relativity change the understanding of gravity compared to Newtonian physics?
-Einstein's General Relativity proposed that gravity is not a force acting at a distance between massive objects but emerges from the interaction of space and massive objects. This contrasts with Newtonian physics, which considered gravity as a mysterious force acting at a distance and space and time as fixed.
What was the significance of Mercury's orbit in validating Einstein's General Relativity?
-Mercury's orbit had a peculiar precession that could not be explained by Newton's equations. When Einstein applied his General Relativity to Mercury's orbit, it predicted the exact precession observed, providing strong evidence in support of his theory.
How did the 1919 solar eclipse observations confirm Einstein's theory of General Relativity?
-During the 1919 solar eclipse, Arthur Eddington and his team photographed stars near the sun and found that their positions appeared different from where they should be if not for the sun's gravitational influence. This confirmed that light was bent by the sun's gravity, as predicted by General Relativity.
What is the connection between gravity and the distortion of time in Einstein's theories?
-According to Einstein's theories, the speed of light remains constant regardless of the reference frame. In a gravitational field, where the path of light is curved due to space distortion, time must pass slower relative to empty space to maintain the constant speed of light, leading to the concept of time dilation.
Why do scientists believe that a new theory of quantum gravity is needed to fully understand gravity?
-General Relativity and Quantum Mechanics remain incompatible, especially when it comes to understanding gravity at the smallest scales, such as within black holes where a singularity is predicted. A new theory of quantum gravity is needed to reconcile these two frameworks and provide a complete understanding of gravity.
Outlines
🔬 Initial Reception and Einstein's Thought Experiment
The first paragraph introduces the Special Theory of Relativity by Albert Einstein, which was met with skepticism and ridicule upon its publication in 1905. People doubted the theory's validity, questioning Einstein's credentials as a patent clerk rather than a working scientist. The theory was seen as a challenge to Isaac Newton's long-standing and proven theories. Einstein himself was not fully satisfied with his theory as it did not account for gravity or acceleration. The paragraph also describes Einstein's thought experiment involving a window washer, which led to a significant scientific breakthrough. Additionally, the paragraph includes a promotion for Magellan TV, a streaming service for documentaries, and its relevance to the topic of the theory of relativity.
🚀 The Principle of Equivalence and the Curvature of Space
The second paragraph delves into Einstein's insight on the relationship between gravity and acceleration, proposing that they are different expressions of the same phenomenon. Einstein's thought experiment involving a falling window washer led him to conclude that in free fall, one would feel weightless, akin to being in space. He postulated that gravity might cause space to curve, affecting the path light takes, which he initially thought should be straight. This realization was pivotal in developing the General Theory of Relativity. Einstein collaborated with mathematician Marcel Grossman to develop the complex mathematical framework for his theory. The theory redefined gravity not as a force but as a curvature of spacetime caused by mass and energy, a concept later summarized by John Wheeler. The paragraph also discusses the prediction and confirmation of Mercury's unusual orbit as evidence supporting the theory and the famous 1919 solar eclipse experiment that provided further validation.
⏱️ The Distortion of Time and the Quest for Quantum Gravity
The third paragraph explores the integration of time into the concept of space-time as described by General Relativity. It explains how the constant speed of light in all reference frames, as postulated by Special Relativity, implies that time must pass more slowly in a gravitational field. This time dilation effect has practical implications, such as the necessity to adjust GPS satellite clocks to match Earth's time. The paragraph also acknowledges the limitations of General Relativity, particularly its inability to explain the nature of gravity or to function within the context of a black hole's singularity. It suggests that a new theory, quantum gravity, which reconciles quantum mechanics with general relativity, is needed to fully understand gravity at the smallest scales.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Special Theory of Relativity
💡Isaac Newton
💡Thought Experiment
💡Equivalence Principle
💡General Relativity
💡Space-Time
💡Mercury's Orbit
💡Arthur Eddington
💡Time Dilation
💡Quantum Gravity
Highlights
Albert Einstein's Special Theory of Relativity was met with ridicule and skepticism when first published in 1905.
Einstein, a patent clerk at the time, was criticized for challenging the established theories of Isaac Newton.
Einstein was not satisfied with his theory due to its limitations in the presence of gravity or acceleration.
A thought experiment involving a window washer inspired Einstein to connect gravity with the theory of relativity.
Einstein hypothesized that gravity and acceleration are equivalent, leading to the development of General Relativity.
Einstein's thought experiments led him to propose that light bends in the presence of a gravitational field.
Einstein's General Relativity introduced the concept that space is curved due to the presence of mass and energy.
Einstein collaborated with mathematician Marcel Grossman to develop the complex mathematics of General Relativity.
General Relativity redefined gravity as an interaction between space and massive objects, rather than a force acting at a distance.
Einstein's theory explained the precession of Mercury's orbit, a phenomenon that could not be accounted for by Newton's laws.
The 1919 solar eclipse experiment led by Arthur Eddington provided empirical evidence supporting General Relativity.
General Relativity implies that time is affected by gravity, causing it to pass slower in a gravitational field.
The theory of General Relativity has practical applications, such as keeping GPS satellites' clocks in sync with Earth's clocks.
General Relativity does not provide a complete understanding of gravity, and questions about its nature remain.
The search for a theory of quantum gravity aims to reconcile General Relativity with Quantum Mechanics to understand gravity at the smallest scales.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
How we know that Einstein's General Relativity can't be quite right

Warped Spacetime, Gravitational Lensing, and Gravitational Waves (Corroborating General Relativity)
Why Gravity is NOT a Force

Discovery That Changed Physics! Gravity is NOT a Force!

Einstein and the Quantum: Entanglement and Emergence

If light has no mass, why is it affected by gravity? General Relativity Theory
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: