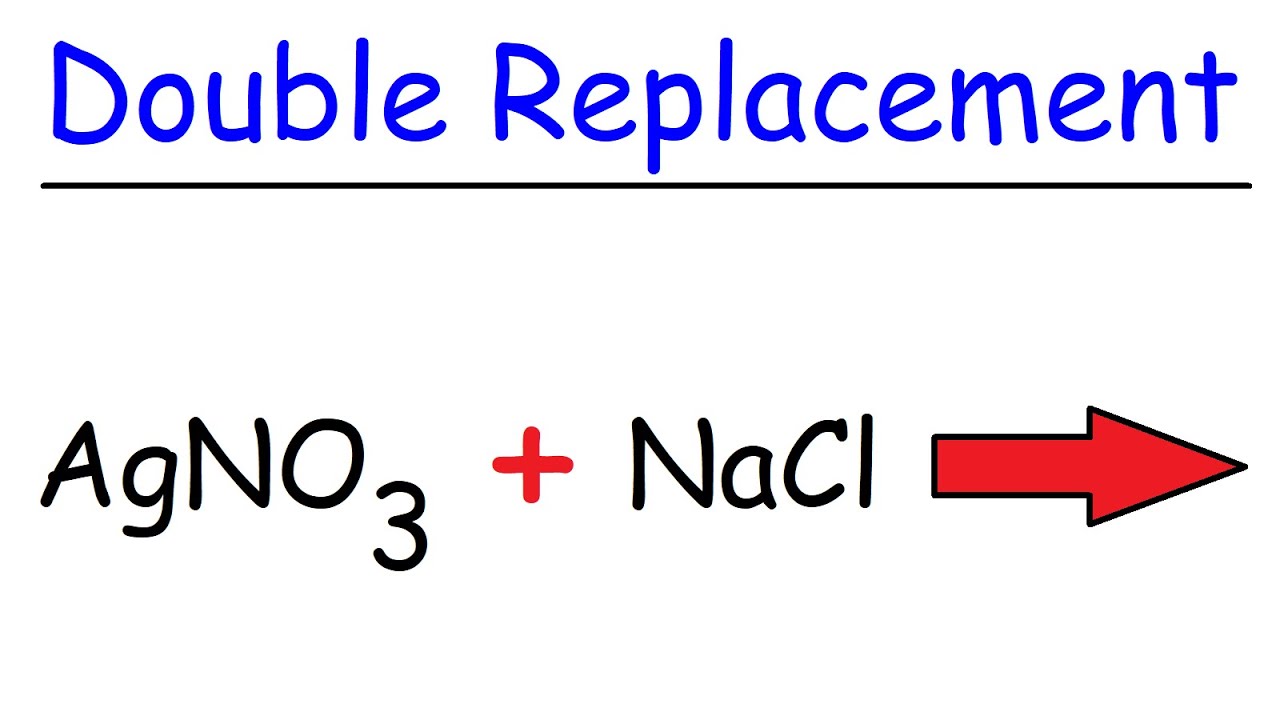
Molecular, complete ionic, and net ionic equations | AP Chemistry | Khan Academy
TLDRThe video script explains a chemical reaction between sodium chloride and silver nitrate when both are dissolved in water. Initially, the molecular equation is presented, showing the formation of sodium nitrate and solid silver chloride. The instructor then delves into the aqueous form, illustrating how the individual ions of each compound dissociate in water due to its polar nature. The sodium and chloride ions are attracted to the partially negative and positive ends of water molecules, respectively, while the silver and nitrate ions behave similarly. To better understand the ion dissociation, a complete ionic equation is introduced, showing all ions involved. The concept of spectator ions, which do not participate in the reaction, is explained, leading to the net ionic equation. This equation omits the spectator ions, providing a more concise view of the actual reaction taking place, focusing on the chloride and silver ions that form the solid silver chloride. The summary emphasizes the importance of understanding the role of each ion in the reaction and how the net ionic equation simplifies the process for a clearer understanding of chemical reactions in aqueous solutions.
Takeaways
- 🧪 The reaction between sodium chloride and silver nitrate in aqueous solution produces sodium nitrate and solid silver chloride.
- 🔄 When dissolved in water, ionic compounds dissociate into their respective ions, with sodium and chloride ions being attracted to the polar water molecules.
- ⚛️ Sodium chloride (NaCl) and silver nitrate (AgNO3) both dissociate into their positive and negative ions when in solution.
- 🧲 Water's polarity as a solvent is key to the dissociation process, attracting cations and anions to its partially charged ends.
- 📜 A molecular equation represents the reaction with the compounds in their molecular form, balanced to show equal numbers of each element on both sides.
- 💧 The aqueous notation in a chemical equation indicates that the substances are dissolved in water.
- 🔍 A complete ionic equation explicitly shows all the ions that are present in the solution, both before and after the reaction.
- 👀 Spectator ions are ions that remain unchanged throughout the reaction and do not participate in the formation of the product.
- ⚖️ The net ionic equation simplifies the reaction by removing the spectator ions, focusing only on the ions that actually react to form the products.
- 📉 The net ionic equation is more compact and makes it easier to identify the actual reactants and products in a chemical reaction.
- 🔬 Understanding the concept of spectator ions and net ionic equations is crucial for predicting the outcome of ionic reactions in solution.
Q & A
What is the reaction between sodium chloride and silver nitrate when dissolved in water?
-When sodium chloride and silver nitrate are both dissolved in water, they react to form sodium nitrate, which remains dissolved in water, and solid silver chloride, which precipitates out of the solution.
Why is water considered a good solvent?
-Water is considered a good solvent because it is a polar molecule, which allows it to attract and dissolve ions due to the partial positive and negative charges on its ends.
What happens to the sodium and chloride ions when sodium chloride is dissolved in water?
-When sodium chloride is dissolved in water, the sodium (a cation) is attracted to the partially negative oxygen end of water molecules, and the chloride (an anion) is attracted to the partially positive hydrogen ends of water molecules, causing them to disassociate.
How does the silver ion behave when silver nitrate is dissolved in water?
-When silver nitrate is dissolved in water, the silver ion disassociates and becomes positive, while the nitrate ion remains negative (an anion).
What is the difference between a molecular equation and a complete ionic equation?
-A molecular equation shows the reaction as if the compounds are still in their molecular form, while a complete ionic equation explicitly shows all the ions that are disassociated in water during the reaction.
Why are sodium and nitrate ions considered spectator ions in the reaction between sodium chloride and silver nitrate?
-Sodium and nitrate ions are considered spectator ions because they are present on both sides of the reaction and do not participate in the formation of the solid silver chloride. They are simply 'watching' the reaction without being consumed or produced.
What is a net ionic equation and how is it derived from a complete ionic equation?
-A net ionic equation is a simplified version of a complete ionic equation that omits the spectator ions, focusing only on the ions that actually participate in the reaction. It is derived by identifying and removing the spectator ions from the complete ionic equation.
Why is the net ionic equation considered more useful than the complete ionic equation in some cases?
-The net ionic equation is more useful because it is more compact and clearly shows which species are actually involved in the reaction, making it easier to predict the products and understand the reaction mechanism.
What would happen if potassium chloride was used instead of sodium chloride in the reaction with silver nitrate?
-If potassium chloride were used instead of sodium chloride, the potassium ions would act as spectator ions, similar to the sodium ions in the original reaction. The net ionic equation would remain the same, as chloride ions would still react with silver ions to form solid silver chloride.
How does the solubility of silver chloride affect its representation in the ionic equation?
-The low solubility of silver chloride means that it does not dissolve in water and instead precipitates out of the solution. In the ionic equation, it is represented in its solid form, distinct from the dissolved ions.
What is the significance of balancing chemical equations?
-Balancing chemical equations is crucial because it ensures that the number of atoms for each element is the same on both sides of the equation, following the law of conservation of mass and reflecting the actual stoichiometry of the reaction.
Can the reaction between sodium chloride and silver nitrate occur without water?
-The reaction as described in the script specifically involves the dissolution of sodium chloride and silver nitrate in water, which allows for the disassociation of ions. Without water, the reaction would not proceed in the same way, as the ions would not be available to interact.
Outlines
🧪 Dissociation of Ions in Aqueous Solutions
This paragraph explains the process of how sodium chloride and silver nitrate, when dissolved in water, react to form sodium nitrate and solid silver chloride. The instructor describes the initial molecular equation and then transitions to a complete ionic equation to illustrate the individual ions that dissociate in water. Sodium and chloride ions are attracted to the polar ends of water molecules, while silver and nitrate ions also dissociate. The paragraph further clarifies the concept of spectator ions, which are ions that are present in the reaction but do not participate in forming the product. The distinction between a complete ionic equation and a net ionic equation is made, with the net ionic equation omitting the spectator ions to focus on the active participants in the reaction.
📐 Net Ionic Equations and Their Significance
The second paragraph delves into the utility of net ionic equations, which are more compact and clearly depict the actual reactants and products in a chemical reaction. The paragraph demonstrates how to derive a net ionic equation by eliminating the spectator ions from the complete ionic equation. The result is a simplified equation that shows only the ions involved in the formation of the solid silver chloride. The paragraph emphasizes the importance of understanding which ions are essential to the reaction, regardless of their source, be it sodium chloride or potassium chloride. The net ionic equation remains the same, highlighting the chloride and silver ions as the key components in the formation of the solid product.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Molecular Equation
💡Aqueous Form
💡Ions
💡Polar Molecule
💡Disassociation
💡Sodium Nitrate
💡Silver Chloride
💡Spectator Ion
💡Net Ionic Equation
💡Complete Ionic Equation
💡Balanced Equation
Highlights
A molecular equation is described for the reaction between sodium chloride and silver nitrate dissolved in water.
The reaction results in the formation of sodium nitrate and solid silver chloride.
Each compound in crystalline form looks distinct, but when dissolved in water, they dissociate into individual ions.
Sodium chloride dissociates into sodium cations and chloride anions, which are attracted to the polar ends of water molecules.
Silver nitrate dissociates into silver cations and nitrate anions when dissolved in water.
A complete ionic equation is written to better convey the dissociation of ions in the reaction.
Sodium and chloride ions are no longer associated after dissociation and dissolve independently in water.
Sodium nitrate remains dissolved in water, while silver chloride precipitates out as a solid.
The solubility of silver chloride is low, so it does not dissolve in water and remains in solid form.
Different forms of the equation are used depending on the level of detail required: molecular, complete ionic, and net ionic equations.
A net ionic equation focuses on the ions that are actually involved in the reaction, excluding the spectator ions.
Sodium and nitrate ions are considered spectator ions as they do not participate in the formation of silver chloride.
The net ionic equation is more compact and clearly shows the reacting species and the product formed.
The concept of spectator ions is introduced, which are ions that are present but do not affect the reaction.
The net ionic equation is useful for understanding which ions react to form the solid product, regardless of their source.
An alternative to sodium chloride could be potassium chloride, with potassium acting as a spectator ion.
The net ionic equation remains the same regardless of the source of chloride and silver ions.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: