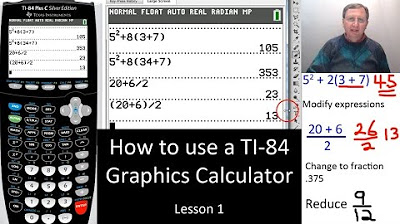
How to Use Your Scientific Calculator
TLDRThe video script provides a comprehensive guide on utilizing a scientific calculator for chemistry, specifically from Texas Instruments. It covers the basics of entering numbers in scientific notation, including coefficients, exponents, and the use of EE or EXP keys. The script explains how to toggle between standard and scientific notation, work with fractions and decimals, and convert percentages to decimals. It also delves into operations involving roots and powers, including squaring, square roots, cubing, and cube roots, as well as raising numbers to any power and finding any root. The importance of using parentheses for accurate calculations in stoichiometry problems is emphasized. The video concludes with tips on avoiding common calculator mistakes and encourages viewers to practice with the provided problems for better understanding and success in chemistry.
Takeaways
- 🧮 Know your calculator: Familiarize yourself with the buttons and functions of your scientific calculator, as they are crucial for chemistry class.
- 🔢 Scientific Notation: Enter numbers in scientific notation by first inputting the coefficient, then pressing EE or EXP, and finally the exponent.
- 🔄 Switch Notations: Use the SCI button (usually on the 5 key) to toggle between scientific and standard notation.
- 📉 Fractions: Input fractions by entering the numerator, pressing the fraction button, and then the denominator.
- 🔁 Convert Fractions: Convert fractions to decimals and vice versa using specific calculator buttons.
- 💯 Subtract Fractions: Perform subtraction with fractions by entering them in sequence and using the minus sign.
- 🔁 Percentage to Decimal: Convert percentages to decimals using the percent symbol on your calculator.
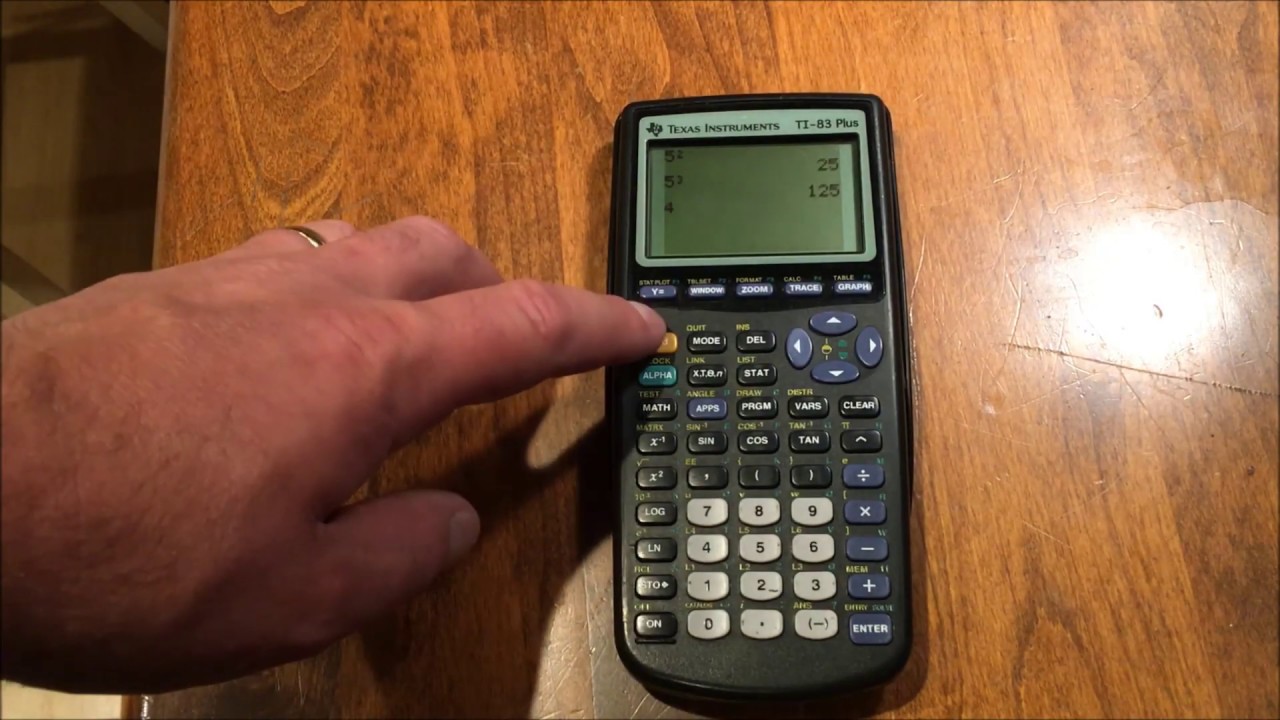
- 📏 Roots and Powers: Calculate squares, square roots, cubes, and cube roots using dedicated buttons on the calculator.
- 🎓 Advanced Powers: For powers other than 2 or 3, use the 'y^x' button to input the base and exponent, then press enter for the result.
- ✅ Roots of Higher Orders: Use the root button in combination with the 2nd function to calculate roots of orders other than square or cube.
- 📐 Logarithms: Use the log button for common logarithms and combine it with the 2nd function for natural logarithms.
- 🛑 Parentheses Matter: Always use parentheses to ensure correct order of operations when performing complex calculations.
Q & A
What is the key to making chemistry easier according to the transcript?
-Knowing how to use the necessary tools for the class, such as a scientific calculator, is key to making chemistry easier.
What is the first step to write a number in scientific notation on a calculator?
-The first step is to plug in the coefficient, for example, if the number is 2.1, you would start by entering 2.1.
How do you account for the 'times 10' portion when entering a number in scientific notation?
-After entering the coefficient, you press the EE or EXP button, which stands for '10 to the power of' on most scientific calculators.
What is the difference between the sign change button and the minus sign on a calculator?
-The sign change button is used to switch the sign from positive to negative, while the minus sign represents subtraction.
How can you switch a number from standard notation to scientific notation on a calculator?
-You would press the 2nd function key followed by the 5 button, which is usually labeled as SCI on the calculator.
How do you convert a fraction to a decimal using a calculator?
-After entering the fraction by inputting the numerator followed by the fraction button and then the denominator, you press the 2nd function key followed by the button that converts to decimal.
What is a quick way to convert a percentage to a decimal on a calculator?
-You enter the percentage number and then press the 2nd function key followed by the percent symbol on the calculator.
How do you calculate the square of a number on a calculator?
-Enter the number, locate the square button (usually marked as 'x²' or '^2'), and press it to get the result.
What is the process to calculate the cube root of a number on a calculator?
-Enter the number, then press the 2nd function key followed by the cube root button (often labeled as '∛' or 'y^x'), and then press the equal sign or enter button.
How do you find the 4th root of a number using a calculator?
-Enter the number, press the 2nd function key, then press the root button, enter the root value which is 4 in this case, and hit the equal sign or enter button.
What is the most common calculator mistake made while solving stoichiometry problems?
-Forgetting to use parentheses to properly group operations, which can lead to incorrect results.
How do you properly calculate a stoichiometry problem on a calculator with multiple operations?
-Use parentheses to group the operations correctly. Press the open parentheses sign, enter the first part of the operation, press the close parentheses sign, then proceed with the rest of the calculation as needed.
What is recommended if you are not comfortable with using parentheses for complex calculations on a calculator?
-Multiply the top and bottom of a fraction separately, then divide the results to avoid the confusion that parentheses might cause.
Outlines
🧮 Scientific Calculator Basics and Scientific Notation
The first paragraph introduces the importance of using a scientific calculator for chemistry and provides a step-by-step guide on how to input numbers in scientific notation. It explains how to enter coefficients, use the EE or EXP button for powers of ten, and input exponents with their respective signs. The paragraph also demonstrates how to toggle between standard and scientific notation using the SCI and FLO buttons. Additionally, it covers how to work with fractions, converting between fraction and decimal forms, and performing basic mathematical operations with fractions. It concludes with a brief mention of converting percentages to decimals and performing operations with roots and powers, including square roots, cubes, and higher order roots and powers.
📚 Stoichiometry Calculations and Common Calculator Mistakes
The second paragraph focuses on solving stoichiometry problems using a calculator, emphasizing the common mistake of omitting parentheses which can lead to incorrect results. It outlines the correct procedure for inputting complex stoichiometric calculations into the calculator, including the use of parentheses to ensure the correct order of operations. An alternative method of multiplying and dividing separately is suggested for those who find the parenthesis method challenging. The paragraph ends with encouragement to practice problems and utilize additional resources to succeed in chemistry.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Scientific Calculator
💡Scientific Notation
💡Fraction
💡Decimal
💡Percentage
💡Roots and Powers
💡Stoichiometry
💡Logarithms and Natural Logs
💡Parentheses
💡Order of Operations
💡Practice Problems
Highlights
Using a scientific calculator can make chemistry much easier
Most scientific calculators have the same buttons and functions
How to write a number in scientific notation on a calculator
Switching between standard and scientific notation
Writing and converting fractions on a calculator
Performing mathematical operations with fractions using a calculator
Converting percentages to decimals on a calculator
Calculating squares, square roots, cubes and cube roots
Raising a number to a power and finding roots of other orders
Using the log and natural log buttons on a calculator
How to properly use parentheses in calculations on a calculator
Multiplying the numerator and denominator separately then dividing as an alternative method
Completing practice problems and utilizing additional resources can help pass chemistry
Calculators from Texas Instruments were used in the demonstration
Different calculators may have buttons arranged differently but functions are the same
The EE button or EXP button is used for 10 to the power in scientific notation
SCI button on the 5 key converts to scientific notation
FLO button on the 4 key converts back to standard notation
Fraction form is indicated by a specific symbol on the calculator
2nd button along with fraction conversion button converts fraction to decimal and vice versa
Percent symbol on the calculator converts a percentage to a decimal
X^2 button calculates the square of a number
X√x button calculates the square root of a number
2nd 1 button calculates the cube of a number
2nd 0 button calculates the cube root of a number
To raise a number to a power other than 2 or 3, use the y^x button
2nd x button calculates the 4th root or other order roots of a number
LOG button calculates the common logarithm of a number
2nd LOG button calculates the logarithm with a specific base
LN button calculates the natural logarithm of a number
2nd LN button calculates the natural logarithm with a specific exponent
Using parentheses correctly in calculations on a calculator is crucial to avoid errors
If uncomfortable with parentheses, multiply the numerator and denominator separately then divide
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: