Medical terms - common prefixes
TLDRThis informative presentation by John Campbell delves into the world of medical terminology, focusing on the significance of prefixes attached to root words. It explains how prefixes such as 'a-', 'an-', 'anti-', 'peri-', and many others can alter the meaning of a word to denote absence, opposition, or relation to a specific body part or condition. The talk covers a wide range of examples, from 'apnea' meaning without breath to 'pyrexia' indicating a high body temperature, offering insights into the building blocks of medical language and its application in understanding various health conditions.
Takeaways
- 📌 Prefixes in medical terminology provide context about the word that follows, often indicating the absence or presence of something.
- 🌬️ Apnea (or apnoea) refers to a temporary cessation of breathing, while achlorhydria indicates a lack of stomach acid.
- 💪 Atony describes a condition where a muscle has lost its tone or strength, affecting various body parts like the gastrointestinal tract or uterus.
- 💧 Anerobic processes occur in the absence of oxygen, leading to the production of lactic acid, as opposed to aerobic processes.
- 🩸 Anemia is characterized by a reduced oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood due to lower concentrations of hemoglobin.
- 🌿 Antibiotics are substances that are 'against life' (anti-biotic), specifically targeting and killing bacteria.
- 🔄 Antiperistalsis refers to the reverse movement of normal peristalsis, which can occur in conditions like vomiting.
- 🛌 Bradycardia is a slow heart rate, technically defined as below 60 beats per minute.
- 🧠 Neurologists and cardiologists specialize in the study and treatment of conditions related to the nervous system and heart, respectively.
- 🌡️ Pyrexia, or fever, is an elevated body temperature as a response to infection or other pyrogenic substances.
Q & A
What does the prefix 'a-' or 'an-' mean in medical terminology?
-The prefix 'a-' or 'an-' in medical terminology means 'without', indicating the absence or lack of the characteristic or function that follows the prefix.
What is the medical term for someone who is not breathing?
-A person who is not breathing is referred to as being 'apneic', derived from 'apnea' which means without breath.
What condition is described by the term 'achlorhydria'?
-Achlorhydria refers to a condition where there is a lack of hydrochloric acid in the stomach, leading to reduced acidity compared to normal levels.
What does 'atony' signify in medical terms?
-Atony refers to a condition where a muscle has lost its tone or strength, resulting in reduced or absent muscle function.
What is the meaning of the prefix 'anemia' in medical terminology?
-Anemia, derived from the prefix 'an-' and the root 'haema-' (blood), technically means 'without blood' but in practice, it refers to a reduced amount of hemoglobin in the blood, leading to a decreased oxygen-carrying capacity.
What does the prefix 'anti-' mean and provide an example of its use?
-The prefix 'anti-' means 'against' or 'opposed to'. An example is 'antibiotic', which refers to a substance that is against or kills bacteria.
What is the medical term for inflammation of the bile ducts?
-The term for inflammation of the bile ducts is 'cholangitis', which can be caused by ascending bacterial infections or other conditions like primary sclerosing cholangitis.
What does the prefix 'col-' refer to in medical terminology?
-The prefix 'col-' refers to the colon, which is the large intestine. Conditions or procedures involving the colon often use this prefix, such as in 'colostomy' or 'colitis'.
What is the significance of the term 'gastroenterologist'?
-A gastroenterologist is a medical specialist who studies and treats diseases of the stomach (gastro-) and intestines (entero-). They are experts in the gastrointestinal tract.
What does the prefix 'hemat-' signify and how is it used in medical terms?
-The prefix 'hemat-' is derived from 'haema-', which means blood. It is used in medical terms to indicate conditions or properties related to blood, such as in 'hematology' (the study of blood) or 'hematoma' (a swelling of blood outside of blood vessels).
What is the term used to describe a high body temperature?
-The term used to describe a high body temperature is 'pyrexia', which is derived from the Greek word 'pyro' meaning fire or heat.
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Medical Prefixes
This paragraph introduces the concept of prefixes in medical terminology, emphasizing their role in providing information about the word that follows. It explains the prefix 'a-' or 'an-' to mean 'without', using examples such as 'apnea' (without breath), 'achlorhydria' (without hydrochloric acid), and 'atony' (loss of muscle tone). The speaker, John Campbell, also clarifies pronunciations and usage in different regions, like the United States, and further explains other prefixes like 'anerobic' (without oxygen) and 'anemic' (reduced blood).
🌡️ Conditions and Treatments
The second paragraph delves into various medical conditions and their corresponding treatments. It discusses terms like 'anti-peristalsis' (opposite of normal digestion), 'anti-inflammatory drugs' (steroids and non-steroidal options), 'antibiotics' (against bacterial life), and 'anesthetic' (without feeling). The prefix 'anti-' is highlighted to mean 'before' or 'against', with examples like 'anti-natal' (before birth) and 'Brady-' (slow). The paragraph also touches on 'cardiology' (study of the heart), 'gastroenterology' (study of stomach and intestine), and conditions like 'gallbladder inflammation' and 'kidney stones'.
🩺 Gastrointestinal and Urinary Health
This paragraph focuses on gastrointestinal and urinary health, explaining terms related to the colon like 'colostomy' (surgical opening of the colon), 'colitis' (inflammation of the colon), and 'cystitis' (inflammation of the bladder). It also covers 'gastroenterologist' (expert in stomach and intestine), 'gastroscopy' (examining the stomach), and conditions like 'gastritis' (stomach inflammation) and 'gastroparesis' (stomach weakness). The paragraph further discusses blood sugar levels, 'glycogen' (storage molecule for glucose), and 'hematology' (study of blood), including conditions like 'hematuria' (blood in urine) and 'hematemesis' (blood in vomit).
🦠 Infections and Liver Diseases
The fourth paragraph discusses various infections and liver diseases. It explains 'hepatitis' (liver inflammation), 'hepatomegaly' (enlarged liver), and 'hepatocellular carcinoma' (primary liver cancer). The prefix 'hepatic' or 'hep-' is associated with the liver, and 'hepatocytes' are identified as liver cells. The paragraph also touches on 'lithiasis' (presence of stones), 'lithotripsy' (crushing of stones), and 'urolithiasis' (stones in the urinary tract). It concludes with 'colithiasis' (stones in the gallbladder or bile ducts) and the historical 'lithotomy position' used in surgery for bladder stone removal.
💊 Medical Conditions and Treatments
This paragraph covers a range of medical conditions and their treatments. It starts with 'lipoma' (fatty lump) and 'lipidemia' (abnormal fat in blood), highlighting 'high-density lipoprotein' (HDL) and 'low-density lipoprotein' (LDL). The prefix 'mal-' signifies abnormality, with examples like 'malabsorption' (improper nutrient absorption) and 'malnutrition' (abnormal nutrition). The paragraph also discusses 'mastectomy' (removal of breast), 'mastitis' (breast inflammation), and 'gynecomastia' (breast development in men). It concludes with 'myocarditis' (heart muscle inflammation) and 'myopathy' (muscle disease).
🩹 Kidney Health and Disorders
The sixth paragraph focuses on kidney health and disorders. It explains 'nephrologist' (kidney specialist), 'nephrotic syndrome' (leaky kidneys), 'nephritis' (kidney inflammation), and 'nephrotoxic' (toxic to kidneys). The prefix 'oligo-' means few or not enough, with examples like 'oligospermia' (low sperm count) and 'oligohydramnios' (deficiency in amniotic fluid). 'Pericarditis' (pericardium inflammation) and 'perinatal' (around birth) are also discussed. The paragraph concludes with 'prostatitis' (prostate inflammation), 'prostatism' (abnormal prostate condition), and 'prostatectomy' (prostate surgical removal).
🌡️ Temperature Regulation and Heart Rate
The final paragraph discusses temperature regulation and heart rate. It explains 'pyrexia' (high body temperature) and 'antipyretic' (fever-reducing drugs), highlighting the role of pyrogens in increasing body temperature. The paragraph also covers 'pyrogen' (substance that increases body temperature) and 'pyrexial' (having a fever). It concludes with conditions related to fast heart and respiratory rates, such as 'tachycardia' and 'tachypnea', and contrasts them with 'Brady-' (slow) conditions.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Medical Terminology
💡Prefixes
💡Apnea
💡Achlorhydria
💡Atony
💡Anemia
💡Anesthesia
💡Antibiotic
💡Anti-inflammatory
💡Bradycardia
💡Cardiology
Highlights
Medical prefixes provide essential information about the nature of medical terms.
The prefix 'a-' or 'an-' indicates the absence of something, such as in 'apnea' meaning without breath.
Chlorhydria refers to the presence of hydrochloric acid in the stomach, with 'achlorhydria' indicating its absence or reduced levels.
The term 'atony' relates to the loss of muscle tone or strength, as seen in postoperative gastrointestinal atony.
Anemia technically means without blood, but in practice, it refers to reduced hemoglobin levels and oxygen-carrying capacity.
Anesthetics are substances that induce a state of 'anesthesia', meaning without feeling or sensation.
Antibiotics are substances that act 'anti' or against bacterial life.
Peristalsis is the normal movement of the gastrointestinal tract; 'anti-peristalsis' refers to the opposite or reversed movement.
Anti-inflammatory drugs work against inflammation, with examples including steroids and nonsteroidal drugs like ibuprofen.
The prefix 'anti-' can also indicate a time before an event, such as in 'anti-natal' referring to the period before birth.
Brady-' means slow, as in 'Bradycardia' which refers to a slow heart rate.
The prefix 'cardio-' relates to the heart, such as in 'cardiac arrest' where the heart stops functioning.
The term 'colitis' refers to inflammation of the colon, which can be caused by various infections or conditions.
The prefix 'endo-' means inside, used in medical terms like 'endoscopy' to describe looking inside a body part.
The prefix 'hepatic-' relates to the liver, such as in 'hepatitis', which is inflammation of the liver.
The term 'nephrology' is the study of the kidneys, with a nephrologist being a specialist in this field.
The prefix 'dis-' indicates an abnormal or painful condition, such as in 'dysuria', which is painful urination.
The term 'gastroenterologist' refers to a specialist in the study of the stomach and intestine, as 'gastro-' means stomach and 'entero-' means intestine.
The prefix 'hyper-' means too high, while 'hypo-' means too low, as in 'hyperglycemia' or 'hypoglycemia' referring to high or low blood sugar levels.
The term 'lithotomy position' refers to a surgical position used historically for the removal of bladder stones, involving the patient's legs being in stirrups.
The prefix 'mal-' indicates abnormal, as in 'malabsorption', which refers to improper nutrient absorption from the gastrointestinal tract.
The term 'myocardium' refers to the muscular part of the heart, with conditions like 'myocarditis' indicating inflammation of this muscle.
The prefix 'peri-' means around, as in 'pericarditis', which is inflammation of the pericardium, the sac surrounding the heart.
The term 'prostatitis' refers to inflammation of the prostate gland, which can cause pain and complications in seminal fluid.
The prefix 'pyro-' relates to fire or heat, as seen in 'pyrexia', which is a medical term for fever or abnormally high body temperature.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
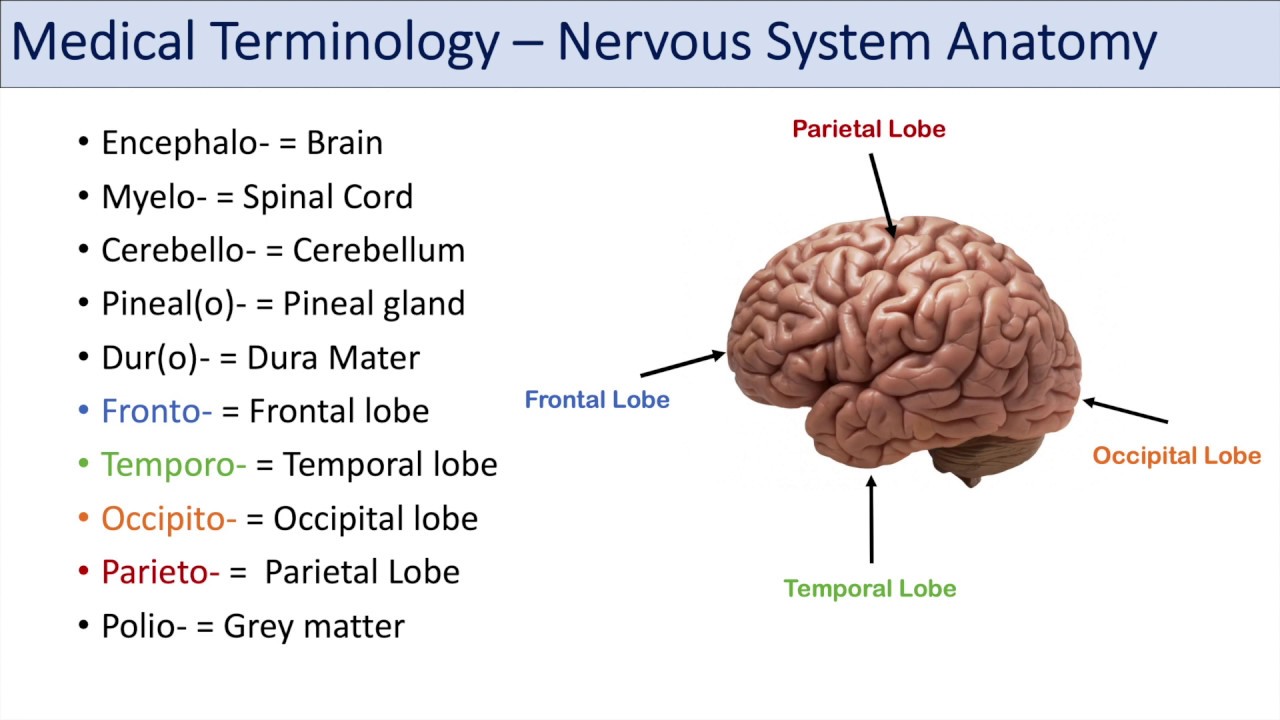
Medical Terminology | Lesson 8 | Nervous System, Cardiorespiratory and Endocrine Anatomy Terms

Affixes - Learn Prefixes and Suffixes in English - prefixes and Suffixes examples

PREFIXES & SUFFIXES | English Lesson

Prefixes for Kids

Prefixes, Suffixes, and Word Roots - Video and Worksheet

English Grammar: Negative Prefixes - "un", "dis", "in", "im", "non"
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: