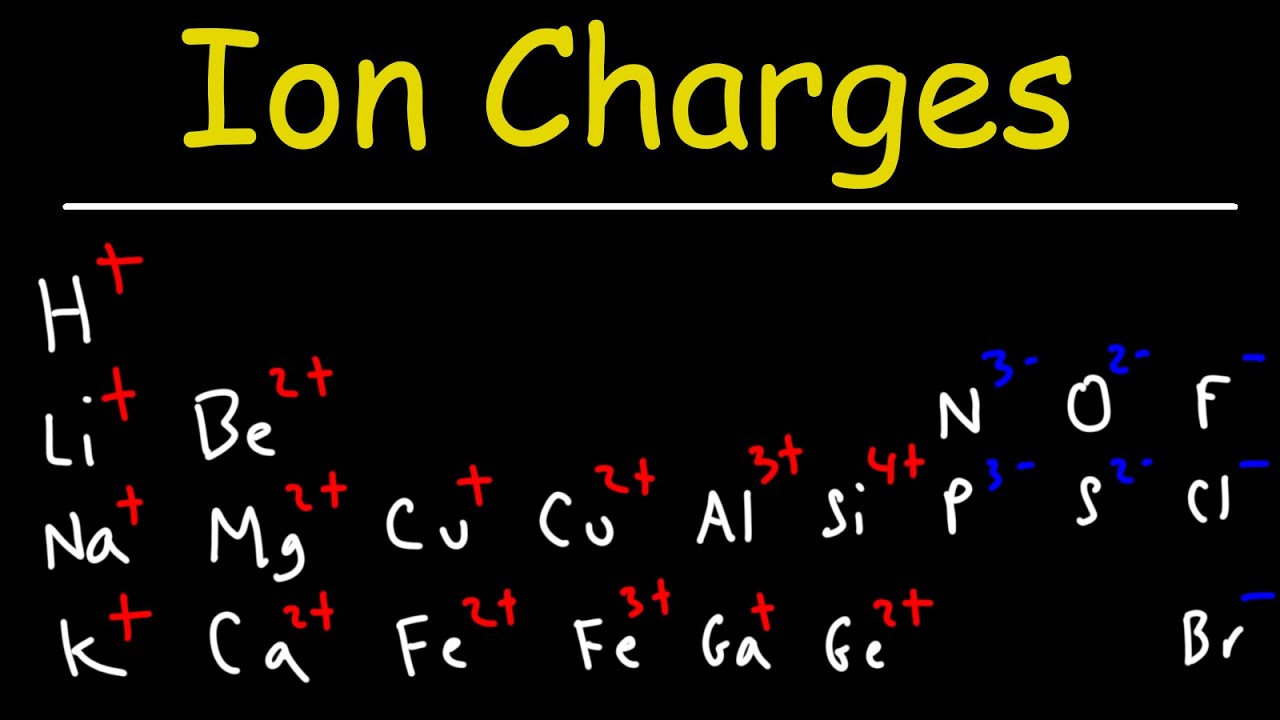What Does OH Stand for in Chemistry for a Formula? : The Marvels of Chemistry
TLDRIn the video, Robin Higgins explains the chemical notation 'OH' as representing a group consisting of one oxygen and one hydrogen, typically with a negative charge, known as a hydroxide ion. This ion tends to bond with positively charged ions, as seen in sodium hydroxide. The 'OH' group is prevalent in chemistry, especially organic, and can be part of alcohols, such as ethanol, which is an ethane group with an alcohol at the end. The versatility of the 'OH' group makes it a common component in various molecules, including sugars.
Takeaways
- 📌 The 'OH' in chemistry signifies a group consisting of one oxygen atom bonded to one hydrogen atom.
- 🔋 When 'OH' stands alone, it carries a negative charge due to the oxygen's three lone pairs and one bond to hydrogen, forming a hydroxide ion.
- 🔄 The hydroxide ion tends to bond with positively charged ions, exemplified by its common pairing with sodium in sodium hydroxide.
- 💥 The combination of sodium hydroxide (a strong base) and hydrochloric acid (an acid) results in an exothermic reaction, producing heat, bubbles, and fizz, ultimately forming water.
- 🧪 The 'OH' group can be part of various compounds, not limited to bases, as seen in organic chemistry with alcohols.
- 🍺 In the case of ethanol (C2H5OH), the 'OH' is part of an alcohol, which is covalently bonded to a carbon chain, differing from ionic bonding.
- 🌿 Alcohols, containing the 'OH' group, are prevalent in organic molecules, including sugars and other natural substances.
- 🧴 'OH' is a common and versatile group found in a multitude of alcohols, which are essential components in many biological and consumer products.
- 🔬 Understanding the 'OH' group is fundamental in chemistry, as it is key to grasping the structure and reactivity of various compounds.
- 👩🏫 Robin Higgins provides valuable insights into the significance and applications of the 'OH' group in chemistry, emphasizing its role in acid-base reactions and organic compounds.
Q & A
What does 'OH' represent in a chemistry formula?
-In a chemistry formula, 'OH' represents a group consisting of one oxygen atom bonded to one hydrogen atom.
What is the charge of the 'OH' group when it stands alone?
-When 'OH' stands alone, it carries a negative charge due to the oxygen's three lone pairs and its bond with the hydrogen.
What is the full name for the 'OH' group with a negative charge?
-The 'OH' group with a negative charge is called a hydroxide ion.
What does the hydroxide ion prefer to bond with?
-The hydroxide ion prefers to bond with positively charged ions due to its negative charge.
Can you provide an example of a compound formed by the attraction between a positively charged ion and a hydroxide ion?
-An example is sodium hydroxide (NaOH), where sodium (Na) has a +1 charge and hydroxide (OH) has a -1 charge, attracting each other to form the compound.
What happens when sodium hydroxide is combined with hydrochloric acid?
-When sodium hydroxide is combined with hydrochloric acid, a reaction occurs that generates a lot of heat, bubbles, and fizzes, resulting in the formation of water and the remaining sodium and chloride ions.
Can the 'OH' group be found in other forms besides a base?
-Yes, the 'OH' group can also be found in other forms, such as in organic molecules like alcohols, and does not always have to be part of a base.
How is the 'OH' group different when it is covalently bonded to carbon, like in the example 'CH3CH2OH'?
-When 'OH' is covalently bonded to carbon, as in 'CH3CH2OH' (ethanol), it is not called a hydroxide because it is not forming an ionic bond; instead, it is part of an alcohol.
What is the significance of the 'OH' group in organic chemistry?
-The 'OH' group is very common in organic chemistry as it forms alcohols, which are found in many different molecules, including sugars and other organic compounds in our body.
How many types of alcohols are there in our body?
-There are hundreds of types of alcohols in our body, playing various roles in biological processes.
What is the relevance of the 'OH' group in the study of sugars?
-In the study of sugars, the 'OH' group is relevant because every type of sugar contains a number of alcohol groups, which are crucial for their structure and function.
Outlines
📚 Understanding the 'OH' Group in Chemistry
In this paragraph, Robin Higgins explains the significance of 'OH' in chemistry, indicating that it represents a group consisting of one oxygen atom bonded to one hydrogen atom, carrying a negative charge. The hydroxide ion's preference to bond with positively charged ions is discussed, using the example of sodium hydroxide, a strong base, and its reaction with hydrochloric acid to produce water and chloride ions. The versatility of the 'OH' group is highlighted, noting its presence in alcohols and sugars within various molecules.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Chemistry formula
💡Oxygen
💡Hydrogen
💡Hydroxide ion
💡Ionic bond
💡Sodium hydroxide
💡Acid-base reaction
💡Alcohol
💡Ethane group
💡Functional group
💡Organic chemistry
Highlights
The 'OH' in chemistry signifies the presence of one oxygen and one hydrogen atom.
The 'OH' group carries a negative charge due to the oxygen's three lone pairs and its bond with hydrogen.
The term 'hydroxide ion' refers to the 'OH' group, indicating its preference to bond with positively charged ions.
Sodium hydroxide is an example of a compound containing the hydroxide ion, with sodium having a +1 charge and hydroxide a -1 charge.
The combination of sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid results in a vigorous reaction, producing heat, bubbles, and eventually water.
The 'OH' group does not always signify a base; its presence depends on the type of bond (ionic or covalent).
In organic chemistry, 'OH' attached to carbon atoms indicates an alcohol group.
Ethanol is an example of an alcohol, with an 'OH' group bonded to an ethane structure.
Alcohols are a common and versatile group found in many molecules, including sugars in our body.
The 'OH' group is a fundamental component in chemistry, particularly in organic chemistry.
Understanding the 'OH' group is essential for studying the properties and reactions of various chemical compounds.
The presence of 'OH' can greatly influence a compound's reactivity and its ability to form certain types of bonds.
The 'OH' group's versatility allows it to be part of many different chemical structures, from simple to complex molecules.
The hydroxide ion's negative charge is a key factor in its reactivity and the types of compounds it forms.
The 'OH' group's role in chemistry extends beyond basic compounds, affecting a wide range of chemical processes.
The distinction between ionic and covalent bonds involving 'OH' is crucial for identifying the nature of a chemical compound.
The 'OH' group's presence in organic molecules like alcohols and sugars highlights its importance in organic chemistry.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: