Medical Quiz💊 Can You Pass This Human Body Quiz❓ ⚕️ 2 of 10
TLDRThis script delves into the critical functions of various human organs and systems. It highlights the gallbladder's role in bile storage for digestion, the cornea's part in light focusing for clear vision, and the liver's responsibility in glucose storage and release. The script also covers the respiratory system's gas exchange, the red blood cells' oxygen carriage, the thyroid gland's metabolic and hormonal influence, the trachea's air passage function, the pancreas's insulin production, the UA's role in preventing food from nasal entry, the liver's detoxification capabilities, the bone marrow's white blood cell production, the septum's function in the heart, the larynx's sound production, the adrenal glands' stress hormone release, the iris's pupil size control, the occipital lobe's vision regulation, the hypothalamus's roles in hunger, thirst, and body temperature regulation, the tuary gland's control over other glands, the salivary glands' saliva production, the spinal cord's nerve signal transmission, the kidneys' blood filtering and cleaning, the diaphragm's function in breathing, the amygdala's emotional response regulation, the aorta's oxygenated blood transportation, and the ear's hearing function. It's an educational overview of the body's intricate mechanisms.
Takeaways
- 💡 The gallbladder's primary role is to store and release bile, which aids in digestion.
- 👁️ The cornea in the eye is crucial for focusing light, contributing to clear vision.
- 🍇 The liver is responsible for storing and releasing glucose, providing energy for the body.
- 💨 The alveoli in the respiratory system are essential for gas exchange between the lungs and the bloodstream.
- 🔴 Red blood cells main function is to carry oxygen throughout the body, maintaining vital cellular functions.
- 🥄 The thyroid gland controls metabolism and produces hormones, regulating the body's metabolic rate.
- 🌬️ The trachea's main function is to allow air to pass to and from the lungs, facilitating respiration.
- 🍞 The pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels.
- 🦷 The UA, or uvula, in the mouth prevents food from entering the nasal cavity during swallowing.
- 🥂 The liver is responsible for detoxifying the blood, removing harmful substances from the circulatory system.
- 🧠 The hypothalamus is the part of the brain that regulates hunger and thirst, maintaining homeostasis.
- 🌀 The bone marrow is the organ responsible for producing white blood cells, essential for the immune system.
- 🚦 The septum in the heart separates oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, ensuring efficient circulation.
- 🎤 The larynx is the part of the body responsible for producing sound, enabling speech and vocalization.
- 🥊 The adrenal glands produce stress hormones, helping the body respond to stress and emergencies.
- 👁️ The iris controls the size of the pupil, adjusting the amount of light entering the eye.
- 🧠 The occipital lobe is the part of the brain responsible for vision, processing visual information.
- 🥃 The large intestine's primary function is the absorption of water and electrolytes, as well as the formation and elimination of feces.
- 🌡️ The hypothalamus also regulates body temperature, maintaining a stable internal environment.
- 🧫 The salivary glands are responsible for producing saliva, aiding in digestion and oral health.
- 🧬 The spinal cord's main function is the transmission of nerve signals, connecting the brain with the rest of the body.
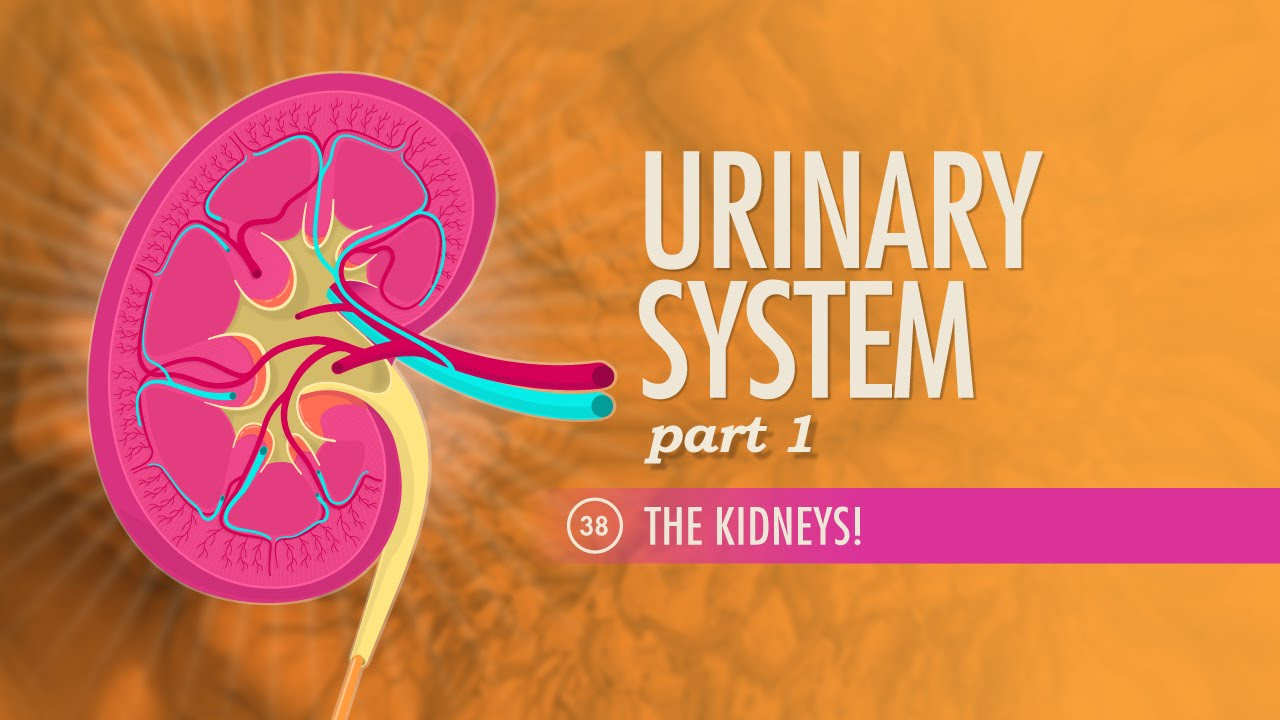
- 💓 The kidneys are responsible for filtering and cleaning the blood, removing waste and excess substances.
- 🎶 The eardrum, or tympanic membrane, vibrates to transmit sound from the outer ear to the middle ear.
- 😢 The amygdala is the part of the brain responsible for emotional responses, particularly related to fear and aggression.
- 💓 The aorta's primary function in the cardiovascular system is to carry oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
Q & A
What role does the gallbladder play in digestion?
-The gallbladder stores bile, which aids in the digestion and absorption of fats.
How does the cornea contribute to vision?
-The cornea helps focus light onto the retina, which is crucial for vision.
Which organ is crucial for regulating blood sugar levels by storing and releasing glucose?
-The liver is responsible for storing and releasing glucose to regulate blood sugar levels.
What is the primary function of alveoli in the respiratory system?
-Alveoli are responsible for gas exchange, allowing oxygen to enter the blood and carbon dioxide to be expelled.
Why are red blood cells essential for the body?
-Red blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body and return carbon dioxide to the lungs for exhalation.
How does the thyroid gland influence metabolism?
-The thyroid gland controls metabolism by producing hormones that regulate energy use and metabolic rate.
What is the function of the trachea in the respiratory system?
-The trachea allows air to pass to and from the lungs, serving as a critical part of the airway.
What role does the pancreas play in insulin production?
-The pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels by facilitating glucose uptake by cells.
What is the purpose of the uvula in the mouth?
-The uvula helps prevent food from entering the nasal cavity during swallowing.
How does the liver function in detoxification?
-The liver detoxifies the blood by metabolizing and removing harmful substances and toxins.
Outlines
📚 Human Anatomy and Physiology Overview
This paragraph delves into the functions of various human organs and systems. It begins with the gallbladder's role in storing bile for digestion, then moves on to the cornea's importance in focusing light for vision. The discussion continues with the liver's responsibility for glucose storage and release, the alveoli's part in gas exchange during respiration, and the red blood cells' task of oxygen transportation. The thyroid gland's control over metabolism and hormone production is also highlighted, as well as the trachea's function in allowing air passage to and from the lungs. The paragraph concludes with the pancreas's insulin production, the UA's role in preventing food from entering the nasal cavity, the liver's detoxification function, the hypothalamus's regulation of hunger and thirst, the pericardium's protective function for the heart, the bone marrow's white blood cell production, the septum's separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, the larynx's sound production, the adrenal glands' stress hormone release, the iris's control over pupil size, the occipital lobe's role in vision, the brain's auditory function via the ear, the large intestine's water absorption, the hypothalamus's temperature regulation, the tuary gland's control over other glands, the salivary glands' saliva production, the spinal cord's nerve signal transmission, the diaphragm's function in breathing, the amygdala's emotional response role, the aorta's oxygenated blood transportation, and ends with a mention of AIDS.
🩸 Cardiovascular System and Its Functions
This paragraph focuses on the cardiovascular system, emphasizing the primary function of carrying oxygenated blood throughout the body. It mentions the aorta's role in the cardiovascular system, which is to transport oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body. This is crucial for delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells and tissues, supporting their survival and function. The paragraph also touches on the importance of maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system for overall well-being.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Gallbladder
💡Cornea
💡Liver
💡Alveoli
💡Red Blood Cells
💡Thyroid Gland
💡Trachea
💡Pancreas
💡Bone Marrow
💡Hypothalamus
Highlights
The gallbladder's role in the digestive system is to store bile.
The cornea in the eye is responsible for helping focus light.
The liver is the organ that stores and releases glucose for energy.
The alveoli are essential for gas exchange in the respiratory system.
Red blood cells carry oxygen throughout the body.
The thyroid gland controls metabolism and produces hormones.
The trachea's primary function is to allow air to pass to and from the lungs.
The uvula in the mouth prevents food from entering the nasal cavity.
The liver is responsible for detoxifying the blood.
The hypothalamus is the part of the brain that regulates hunger and thirst.
The pericardium's main function is to protect the heart.
Bone marrow is the organ responsible for producing white blood cells.
The septum in the heart separates oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
The larynx is the part of the body responsible for producing sound.
The adrenal glands produce stress hormones.
The iris is the part of the eye that controls the size of the pupil.
The occipital lobe is the part of the brain responsible for vision.
The pancreas produces insulin.
The function of the Eustachian tube is hearing.
The large intestine's primary function is the absorption of water.
The hypothalamus regulates body temperature.
The thymus gland controls other glands.
The salivary glands are responsible for producing saliva.
The spinal cord's main function is the transmission of nerve signals.
The kidneys are responsible for filtering and cleaning the blood.
The diaphragm's purpose in the body is for breathing.
The amygdala is the part of the brain responsible for emotional responses.
The aorta's primary function in the cardiovascular system is to carry oxygenated blood.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Endocrine System

Structure of the Human eye | Human eye and the colorful world | Physics | Infinity Learn NEET

Dr Marino - Red blood cells song

Circulatory System for Kids | Learn all about how blood travels through the body

Cirrhosis of the Liver | Signs, Symptoms, Interventions & Nursing Care
Urinary System, Part 1: Crash Course Anatomy & Physiology #38
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: