Types of Sampling Methods (4.1)
TLDRThis video script delves into the concept of sampling within a population, highlighting the importance of unbiased samples for accurate conclusions. It distinguishes between biased samples, such as convenience and voluntary response samples, and unbiased samples, including simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, and multi-stage sampling. The script also introduces the use of a random digits table for selecting samples, emphasizing its utility in ensuring randomness and fairness in the sampling process.
Takeaways
- 🔍 A 'foreign population' refers to the entire group of subjects being studied, while a 'sample' is a subset of this population examined for research purposes.
- 📉 Biased samples occur when some parts of the population are favored over others, leading to unrepresentative results.
- 📌 Two types of biased samples are 'convenience samples', where easily accessible individuals are chosen, and 'voluntary response samples', where only those who choose to participate are included.
- 🌐 A 'good sample' should be representative of the entire population and give each member an equal chance of being selected.
- 🎯 'Simple random sampling' (SRS) is an unbiased method where every individual has an equal chance of being chosen, akin to drawing names from a hat.
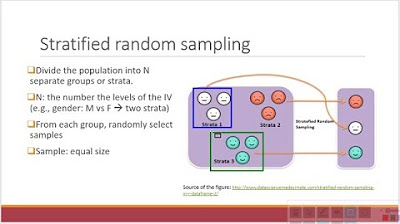
- 🔢 In 'stratified random sampling', the population is divided into 'strata' or groups of similar individuals, and SRS is taken within each stratum to ensure representation.
- 🛤️ 'Multi-stage sampling' involves multiple rounds of simple random sampling to obtain the final sample, going through different stages to reach the sample.
- 📈 The 'random digits table' is a tool that can be used for SRS, consisting of a long string of random numbers to help in random selection.
- 👥 When using the random digits table, each member of the population is labeled with a number to match the two-digit format used for selection.
- 🚫 In multi-stage sampling, numbers outside the population range are ignored, ensuring that only valid members are selected.
- 📋 Proper sampling techniques are crucial for obtaining accurate and reliable data that can be generalized to the larger population.
Q & A
What is the term used to describe a group of things we want information about?
-The term used to describe a group of things we want information about is 'population'.
What is a 'sample' in the context of research and data collection?
-A 'sample' refers to a part of the population that is taken out to examine and draw conclusions from.
What are the two types of biased samples mentioned in the transcript?
-The two types of biased samples mentioned are convenience sample and voluntary response sample.
How is a convenience sample biased?
-A convenience sample is biased because it only includes people who are easy to reach, and not everyone in the population has an equal chance of being part of the sample.
What characterizes a voluntary response sample?
-A voluntary response sample consists of people who have chosen to include themselves in the sample, often leading to overrepresentation of those with a strong interest in the survey topic.
What is an 'unbiased sample' and how is it achieved?
-An 'unbiased sample' is one that is representative of the entire population, giving each member an equal chance of being chosen. This ensures that the sample can accurately represent the population in the study.
What are the three different types of sampling methods discussed in the transcript?
-The three different types of sampling methods discussed are stratified random sampling, multi-stage sampling, and simple random sampling.
How does simple random sampling (SRS) ensure that each individual has an equal chance of being chosen?
-In simple random sampling, each individual has an equal chance of being chosen because the selection process is random, similar to putting names into a hat and selecting from them.
What is stratified random sampling and how is it useful?
-Stratified random sampling involves dividing the population into groups (strata) of similar people and then taking a simple random sample from each stratum. This method is useful for ensuring that each kind of group within the population is represented in the sample.
Explain the process of multi-stage sampling and provide an example.
-Multi-stage sampling involves using a combination of two or more simple random samples. For example, in a two-stage process, the first stage might involve selecting a group using an SRS, and the second stage would involve taking a sample of individuals from that selected group.
How can the random digits table be used to assist in simple random sampling?
-The random digits table, consisting of a long string of random numbers, can be used to assist in simple random sampling by labeling each member of the population with a number and then using the table to randomly select those numbers to determine the sample.
Outlines
🔍 Introduction to Sampling Methods and Bias
This paragraph introduces the concept of a foreign population and a sample, emphasizing the importance of obtaining a representative sample to draw accurate conclusions. It explains the occurrence of biased samples and describes two types of biased sampling methods: convenience sampling and voluntary response sampling. The paragraph highlights how these methods can lead to unrepresentative samples since not all parts of the population have an equal chance of being included. It contrasts these with unbiased samples, setting the stage for the discussion of various sampling techniques to follow in the video.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡foreign, population
💡sample
💡biased samples
💡convenience sample
💡voluntary response sample
💡unbiased sample
💡stratified random sampling
💡multi-stage sampling
💡simple random sample (SRS)
💡random digits table
Highlights
The video discusses various methods of obtaining a sample from a population.
A sample is a part of the population taken to examine and draw conclusions from.
Biased samples occur when some parts of the population are favored over others.
Two types of biased samples are convenience sample and voluntary response sample.
Convenience sampling includes only people who are easy to reach, leading to bias.
Voluntary response sampling consists of people who choose to be part of the sample, which can introduce bias.
A good sample is representative of the entire population and gives each member an equal chance of being chosen.
The video covers three types of sampling: stratified random sampling, multi-stage sampling, and simple random sampling.
Simple random sample (SRS) is the most basic type of sampling where each individual has an equal chance of being surveyed.
Stratified random sample involves dividing the population into groups or strata and taking a sample from each.
Multi-stage sampling uses a combination of two or more simple random samples to find the actual sample.
Random digits table can be used as an alternative to physically drawing names from a hat for simple random sampling.
Each member of the population is labeled with a number to use the random digits table effectively.
The random digits table consists of a long string of random numbers used to select the sample.
The process of selecting a sample using the random digits table is demonstrated with a sample size of four.
Certain numbers are ignored if they exceed the population size or do not fit the sample criteria.
The final selection of individuals for the survey is determined using the random digits table method.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Sampling: Simple Random, Convenience, systematic, cluster, stratified - Statistics Help
Research Methods 1: Sampling Techniques

population sample parameter statistic | Gourav Manjrekar
What Are The Types Of Sampling Techniques In Statistics - Random, Stratified, Cluster, Systematic

Sampling Methods 101: Probability & Non-Probability Sampling Explained Simply

Stratified Sampling Vs Cluster Sampling with Examples | Meaning and Comparison
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: