Aleks Making qualitative estimates of pH change
TLDRThis educational video script focuses on teaching the concept of pH and how to qualitatively estimate changes in it. It explains the neutrality of water with a pH of 7, and how the presence of hydrogen (H) indicates an acid, while hydroxide (OH) suggests a base. The script further clarifies that adding an acid lowers the pH, making the solution more acidic, and adding a base raises the pH, making it more alkaline. It also distinguishes between acids, bases, and salts, noting that salts do not affect pH. The importance of understanding the underlying principles rather than just memorizing facts is emphasized.
Takeaways
- 🧪 The pH scale measures the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, with 7 being neutral, values less than 7 indicating acidity, and values greater than 7 indicating alkalinity.
- 💧 Water (H2O) is neutral with a pH of 7, as it has an equal concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-).
- ⚛️ The presence of an 'H' at the beginning of a chemical formula typically indicates an acid, as it can donate a proton (H+).
- 🔬 If a compound contains 'OH', it is likely a base, as it contains hydroxide ions which can accept protons.
- 🌡 Adding a base to a solution increases the pH, moving it towards the alkaline side of the scale (closer to 14).
- 📉 Adding an acid to a solution decreases the pH, moving it towards the acidic side of the scale (closer to 0).
- 🧂 Salts, such as KClO4 or sodium nitrate, do not change the pH of a solution because they do not contain free hydroxide or hydrogen ions.
- 🌟 The strength of an acid increases as the pH decreases, with very low pH values indicating very strong acids.
- 🌠 The strength of an alkaline solution increases as the pH rises, with very high pH values indicating very strong bases.
- 📚 Recognizing whether a compound is an acid, a base, or neither is crucial for understanding how it will affect the pH of a solution.
- 🔍 The script emphasizes the importance of understanding the concepts rather than just memorizing or looking up information, highlighting the need for comprehension in answering related questions.
Q & A
What is the pH scale and what does it measure?
-The pH scale measures the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral, values less than 7 indicating acidity, and values greater than 7 indicating alkalinity.
How can you determine if a chemical formula represents an acid, a base, or neither?
-A chemical formula can be identified as an acid if it starts with 'H', indicating a proton to give away. If it contains 'OH', it is likely a base. If it does not have these elements, it may be neither an acid nor a base.
What is the pH of water (H2O) and why is it considered neutral?
-The pH of water is 7, which is neutral. This is because water can give away a hydrogen ion (H+), leaving behind a hydroxide ion (OH-), thus maintaining an equal concentration of both ions.
What is nitric acid and how does it affect the pH of a solution?
-Nitric acid is a compound with the formula HNO3. It is an acid because it can donate a proton (H+). When added to water, it will lower the pH, making the solution acidic.
What happens to the pH of a solution when a base is added?
-When a base, which contains hydroxide ions (OH-), is added to a solution, the pH increases, moving towards the alkaline side of the pH scale.
Why does adding potassium chlorate (KClO4) to a solution not change the pH?
-Adding potassium chlorate, a salt, to a solution does not change the pH because it does not introduce additional hydroxide ions (OH-) or protons (H+) into the solution.
What is sodium nitrate and how does it affect the pH of a solution?
-Sodium nitrate is a salt with the formula NaNO3. It does not contain hydroxide ions or protons, so it does not affect the pH of a solution when dissolved.
What is chloric acid or perchloric acid and how does it affect the pH of a solution?
-Chloric acid or perchloric acid is represented by the formula HClO4. It is an acid because it contains a hydrogen that can be donated. Adding it to a solution will lower the pH, making the solution more acidic.
What is the relationship between the concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+) and the pH of a solution?
-The concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+) is inversely related to the pH of a solution. As the concentration of H3O+ increases, the pH decreases, indicating a more acidic solution.
Why is it important to understand the concepts in the script rather than just recalling them?
-Understanding the concepts is crucial because the questions related to pH and acid-base chemistry often require analytical thinking and cannot be simply memorized or looked up. Comprehension allows for problem-solving and application of knowledge in various scenarios.
How does the video script emphasize the importance of understanding over memorization?
-The script emphasizes understanding by stating that the questions have multiple parts and require comprehension to answer correctly. It also mentions that the concepts cannot be googled and must be understood to be applied correctly.
Outlines
🔬 Understanding Acids, Bases, and Neutral Solutions
This paragraph introduces the concept of qualitative estimates of pH change, emphasizing the importance of recognizing whether a chemical formula represents an acid, a base, or neither. It explains that water (H2O) is neutral with a pH of 7, and that the presence of 'H' at the beginning of a formula typically indicates an acid, which will lower the pH when added to water. The paragraph also clarifies that salts, which lack hydroxide ions (OH-) or free hydrogen ions (H+), do not affect the pH of a solution.
📈 The pH Scale and the Effects of Adding Acids and Bases
This paragraph delves deeper into the pH scale, explaining how the concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+) affects the pH level. It states that a lower pH indicates a stronger acid, while a higher pH signifies a more alkaline solution. The paragraph also discusses the impact of adding acids and bases to a solution: acids decrease the pH, making the solution more acidic, whereas bases increase the pH, making it more alkaline. The importance of understanding these concepts is highlighted, as it is necessary to answer related questions correctly.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Qualitative Estimates
💡pH
💡Acid
💡Base
💡Neutral
💡Nitric Acid (HNO3)
💡Salt
💡Chloric Acid (HClO4)
💡Hydronium Ion (H3O+)
💡Alkaline
💡Hydroxide Ion (OH-)
Highlights
The video is a training on making qualitative estimates of pH change.
Understanding the difference between acids, bases, and neither is crucial for the training.
Acidic substances start with 'H' and can donate a proton, while bases contain 'OH'.
Water (H2O) is neutral with a pH of 7, balancing the amount of H and OH.
A pH less than 7 indicates acidity, while a pH greater than 7 indicates alkalinity.
Nitric acid (HNO3) is identified as an acid due to the presence of 'H' at the beginning.
Adding a base to a solution increases the pH towards 14.
Adding a salt, like KClO4, does not change the pH of a solution.
Sodium nitrate is a salt and does not affect the pH when added to water.
Chloric or perchloric acid (HClO4) is an acid and will lower the pH when added.
The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral.
The concentration of H3O+ (hydronium) affects the pH level.
A lower pH indicates a stronger acid, while a higher pH indicates a stronger base.
The video emphasizes the importance of understanding the concepts rather than just recalling them.
The video is designed to test understanding through multiple questions.
The video mentions that the concepts cannot be simply googled and require true understanding.
The instructor offers help in class for those who need it.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
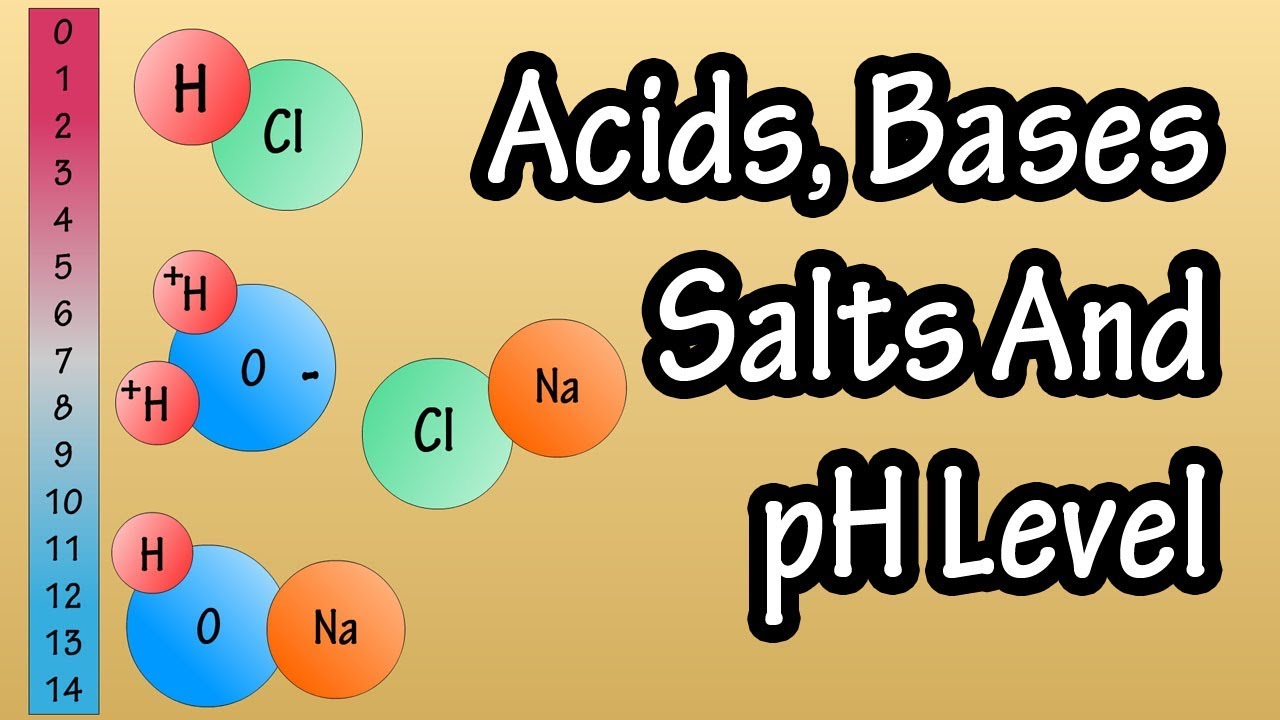
Acids And Bases Salts And pH Level - What Are Acids Bases And Salts - What Is The pH Scale Explained

pH, pOH of strong acids and bases | Chemistry | Khan Academy

Buffers and Henderson-Hasselbalch | Chemistry | Khan Academy

Strong Acid Strong Base Titration Curve - WHY it looks that way

Strong Acid Titration

Buffer Calculations
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: