Hydrocarbons | #aumsum #kids #science #education #children
TLDRThis script delves into the world of hydrocarbons, organic compounds composed of hydrogen and carbon. It distinguishes between saturated hydrocarbons, known as alkanes, which feature only single bonds between carbon atoms, and unsaturated hydrocarbons, which include alkenes with at least one double bond and alkynes with at least one triple bond. The script lists examples of each, starting from methane with a single carbon atom up to butyne with four, providing a fundamental understanding of these essential organic molecules.
Takeaways
- 🌐 Hydrocarbons are organic compounds consisting solely of hydrogen and carbon atoms.
- 🔗 Saturated hydrocarbons, known as alkanes, have carbon atoms linked by single bonds only.
- 🔑 The general formula for alkanes is CnH2n+2, where n represents the number of carbon atoms.
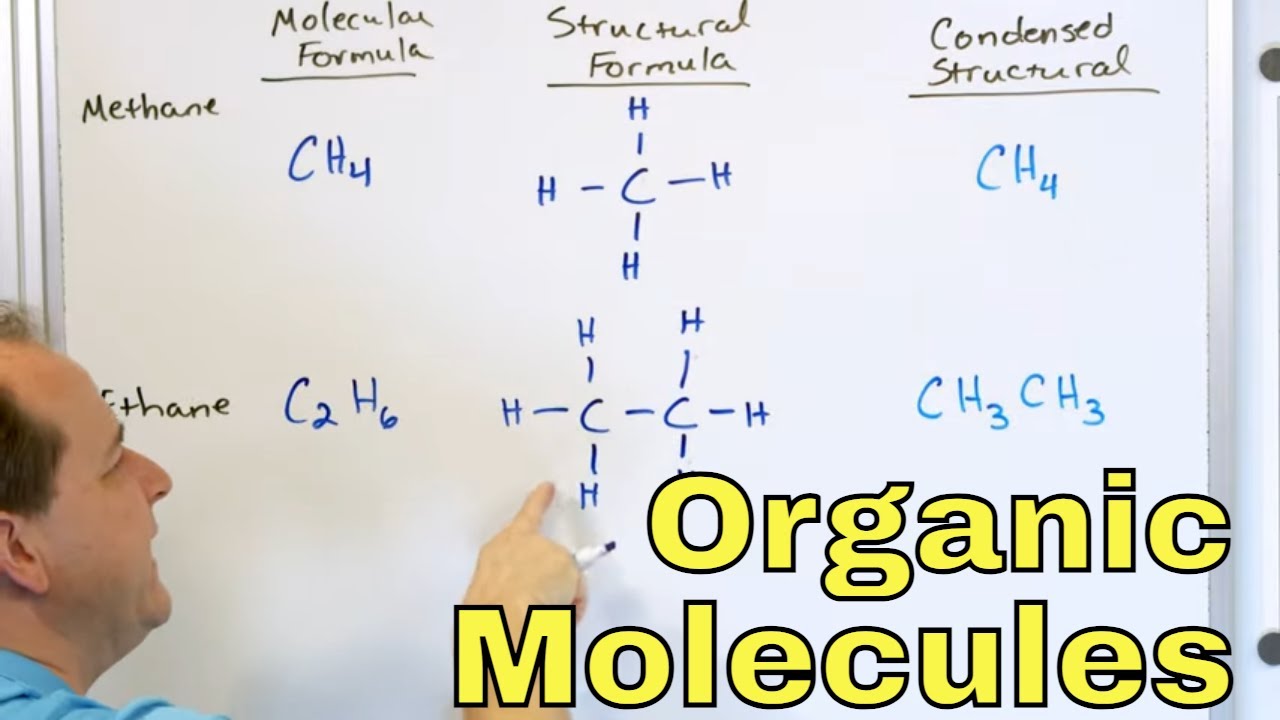
- 🔍 Methane is the simplest alkane with a single carbon atom.
- 🔄 Ethane has two carbon atoms, and propane has three, following the alkane series.
- 🍬 The transcript mentions 'I got some sweets,' which seems unrelated to the main topic.
- 🔗 Unsaturated hydrocarbons contain double or triple bonds between carbon atoms.
- 🔄 Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons with at least one double bond, characterized by the formula CnH2n.
- 🔗 Alkynes, another type of unsaturated hydrocarbons, have at least one triple bond and follow the formula CnH2n-2.
- 🔍 Ethyne, also known as acetylene, is an alkyne with two carbon atoms.
- 🔄 Propyne and butyne are examples of alkynes with three and four carbon atoms, respectively.
Q & A
What are hydrocarbons?
-Hydrocarbons are organic compounds composed exclusively of hydrogen and carbon atoms.
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons?
-Saturated hydrocarbons have only single bonds between carbon atoms, while unsaturated hydrocarbons have one or more double or triple bonds.
What is another name for saturated hydrocarbons?
-Saturated hydrocarbons are also known as alkanes.
What is the general formula for alkanes?
-The general formula for alkanes is CnH2n+2, where n is the number of carbon atoms in the molecule.
What is the name of the alkane with one carbon atom?
-The alkane with one carbon atom is called methane.
How many carbon atoms does ethane have?
-Ethane has two carbon atoms.
What are the two types of unsaturated hydrocarbons?
-The two types of unsaturated hydrocarbons are alkenes and alkynes.
What is the characteristic of alkenes?
-Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond.
What is the general formula for alkenes?
-The general formula for alkenes is CnH2n, where n is the number of carbon atoms in the molecule.
What is the name of the alkyne with two carbon atoms?
-The alkyne with two carbon atoms is called ethyne.
What is the characteristic of alkynes?
-Alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon triple bond.
What is the general formula for alkynes?
-The general formula for alkynes is CnH2n-2, where n is the number of carbon atoms in the molecule.
Outlines
🌿 Hydrocarbons: Saturated and Unsaturated Compounds
This paragraph introduces hydrocarbons, organic compounds consisting of hydrogen and carbon atoms. It distinguishes between two main types: saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Saturated hydrocarbons, also known as alkanes, have single bonds between carbon atoms and are exemplified by methane, ethane, and propane, each with an increasing number of carbon atoms. The paragraph also touches on unsaturated hydrocarbons, which include alkenes and alkynes, characterized by the presence of double or triple bonds, respectively.
🔗 Alkenes and Alkynes: The Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
This section delves deeper into unsaturated hydrocarbons, focusing on alkenes and alkynes. Alkenes are defined by the presence of at least one double bond between carbon atoms, and the paragraph provides a general formula for alkenes, indicating the variable 'n' for the number of carbon atoms. Similarly, alkynes are characterized by at least one triple bond and are also given a general formula with 'n' representing the carbon count. Specific examples of alkynes include ethyne with two carbon atoms, propyne with three, and butyne with four, illustrating the progression in the number of carbon atoms.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Hydrocarbons
💡Saturated Hydrocarbons
💡Alkanes
💡Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
💡Alkenes
💡Alkynes
💡Ethyne
💡Propyne
💡Butyne
💡Double Bonds
💡Triple Bonds
Highlights
Hydrocarbons are compounds composed solely of hydrogen and carbon.
Hydrocarbons are categorized into saturated and unsaturated types.
Saturated hydrocarbons, also known as alkanes, have carbon atoms connected by single bonds only.
Alkanes are named based on the number of carbon atoms present in the molecule.
Methane is the simplest alkane with a single carbon atom.
Ethane contains two carbon atoms, and is the second simplest alkane.
Propane has three carbon atoms, further expanding the alkane series.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons feature carbon atoms connected by double or triple bonds.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons are divided into two subcategories: alkenes and alkynes.
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons with at least one carbon-carbon double bond.
Alkynes are characterized by the presence of at least one carbon-carbon triple bond.
The naming convention for alkenes and alkynes also depends on the number of carbon atoms.
Ethyne, with two carbon atoms, is the simplest alkyne.
Propyne contains three carbon atoms and is an example of an alkyne.
Butyne, with four carbon atoms, is another alkyne in the hydrocarbon series.
The transcript provides a basic understanding of hydrocarbon structures and their classifications.
The naming system for hydrocarbons is based on the number of carbon atoms and the type of bonding.
This transcript serves as an educational resource for understanding the fundamental concepts of organic chemistry.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: