Hess's Law Common Test Question
TLDRIn this educational video, Melissa Maribel, a personal tutor, explains how to apply Hess's law to determine the enthalpy change of a chemical reaction. She guides viewers through the process of manipulating three given reactions to achieve the desired 'goal' reaction. Melissa emphasizes the importance of adjusting the enthalpy change when reactions are multiplied or flipped, and demonstrates how to combine and simplify the reactions to find the final enthalpy change. The video is a helpful resource for students preparing for exams, especially those who have struggled with similar questions.
Takeaways
- 🔍 The video script is a tutorial on applying Hess's Law to calculate the enthalpy change of a chemical reaction.
- 📚 Hess's Law states that the total enthalpy change for a reaction is the same, no matter how many steps or what path the reaction takes.
- 🔢 The process involves manipulating given reactions to match the desired 'goal' reaction by multiplying or reversing them as necessary.
- ⚖️ When a reaction is multiplied by a number, the associated enthalpy change must also be multiplied by that same number.
- 🔄 Multiplying a reaction by a number to match the stoichiometry of the reactants or products in the goal reaction.
- ↔️ Flipping a reaction changes the sign of the enthalpy change, turning a negative value positive or vice versa.
- 🧩 After manipulating the reactions, combining them to form the goal reaction involves canceling out like terms on both sides of the equation.
- 📉 The enthalpy changes from the manipulated reactions must be added together to find the total enthalpy change for the goal reaction.
- 📝 The script provides a step-by-step guide on how to apply Hess's Law, including the mathematical manipulation of enthalpy values.
- 📉 The final step is to sum all the individual enthalpy changes to get the overall enthalpy change for the complete reaction.
- 💡 The tutorial emphasizes the importance of correctly manipulating and combining reactions to solve for the enthalpy change using Hess's Law.
- 🎓 The video also mentions another Hess's Law question that has been a common point of confusion among students, suggesting further resources for learning.
Q & A
What is Hess's law and how is it applied in the context of the given script?
-Hess's law states that the total enthalpy change of a chemical reaction is the same, no matter how the reaction is carried out in steps. In the script, it is applied by manipulating and combining multiple reactions to find the enthalpy change of a target reaction.
Why do we need to multiply the entire reaction by a number when the reactant's amount is not correct?
-Multiplying the entire reaction by a number ensures that the stoichiometry of the reaction matches the target reaction. This also requires multiplying the enthalpy change by the same number to maintain the proportionality of the reaction's energy change.
How does the script handle the situation when a reactant is not present in the correct amount?
-The script demonstrates that if a reactant is not present in the correct amount, the reaction is multiplied by the necessary factor to achieve the correct stoichiometry, and the enthalpy change is also multiplied by this factor.
What is the significance of multiplying the enthalpy change by 5 and 6 in the script?
-The multiplication of the enthalpy change by 5 and 6 corresponds to the stoichiometric coefficients needed to match the reactants in the target reaction. This ensures that the enthalpy changes are correctly scaled to the desired amounts of reactants.
Why is it necessary to flip a reaction when the product is on the wrong side?
-Flipping a reaction changes the direction of the reaction, effectively reversing the process. This is necessary when the product of the target reaction is initially on the reactant side of one of the given reactions. The enthalpy change is multiplied by -1 to reflect this reversal.
What is the purpose of combining and canceling out like terms in the reactions?
-Combining and canceling like terms simplifies the overall reaction and helps to isolate the target reaction. This step removes the common species on both sides of the equation, leaving only the reactants and products of the desired reaction.
How does the script ensure that the final enthalpy change is accurate?
-The script ensures accuracy by adding up all the manipulated enthalpy changes from the individual reactions. This sum gives the total enthalpy change for the target reaction.
What is the role of the personal tutor, Melissa Maribel, in the script?
-Melissa Maribel serves as a guide, explaining the process of using Hess's law to solve a chemistry problem. She breaks down the steps involved in manipulating reactions and calculating the enthalpy change for the target reaction.
Why is it important to check the correct side of the reactants and products in the reactions?
-Checking the correct side is crucial for ensuring that the reactions are manipulated correctly. Reactants must be on the reactant side, and products must be on the product side to accurately represent the target reaction.
What is the final step in the process described in the script?
-The final step is to add all the enthalpy changes from the manipulated reactions together to find the total enthalpy change for the target reaction.
What additional resource is offered by the tutor at the end of the script?
-The tutor offers another Hess's law question that has been a common point of confusion for students, encouraging viewers to check out a related video for further understanding.
Outlines
🔍 Understanding Hess's Law Application
Melissa Maribel introduces a Hess's law problem involving the manipulation of chemical reactions to find the enthalpy change for a target reaction. The process involves identifying reactants and products in given reactions and correctly adjusting their stoichiometry to match the target reaction. This includes multiplying reactions by integers to achieve the desired number of reactant atoms and flipping reactions to correct the side of the reaction where a species appears. Each manipulation of the reaction is accompanied by a corresponding adjustment to the enthalpy change. The goal is to combine all adjusted reactions and their enthalpy changes to derive the overall enthalpy change for the target reaction.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Hess's Law
💡Enthalpy Change
💡Reactant
💡Product
💡Stoichiometry
💡Multiplication
💡Distribute
💡Flip Reaction
💡Combining Reactions
💡Canceling Out
💡Personal Tutor
Highlights
Introduction to Hess's law question on enthalpy change calculation.
Using three given reactions to manipulate and achieve the goal reaction.
Identifying the first reactant, carbon, and its correct placement in the reactions.
Multiplying the entire reaction by 5 to match the required amount of carbons.
Multiplying the enthalpy change by the same factor as the reaction.
Distributing the multiplication factor to all components of the reaction.
Identifying the second reactant, H2, and adjusting its quantity to match the goal.
Multiplying the reaction by 6 to achieve the correct amount of H2's.
Adjusting the enthalpy change to reflect the multiplication by 6.
Flipping a reaction to move a product to the reactant side and vice versa.
Changing the sign of the enthalpy change when flipping a reaction.
Combining all manipulated reactions to form the goal reaction.
Canceling out like terms in the combined reaction.
Achieving the final goal reaction by combining and canceling terms.
Calculating the total enthalpy change by summing all individual changes.
Teasing another Hess's law question that has been a common point of confusion.
Invitation to watch another video for further understanding of Hess's law.
Closing remarks and sign-off from the tutor.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
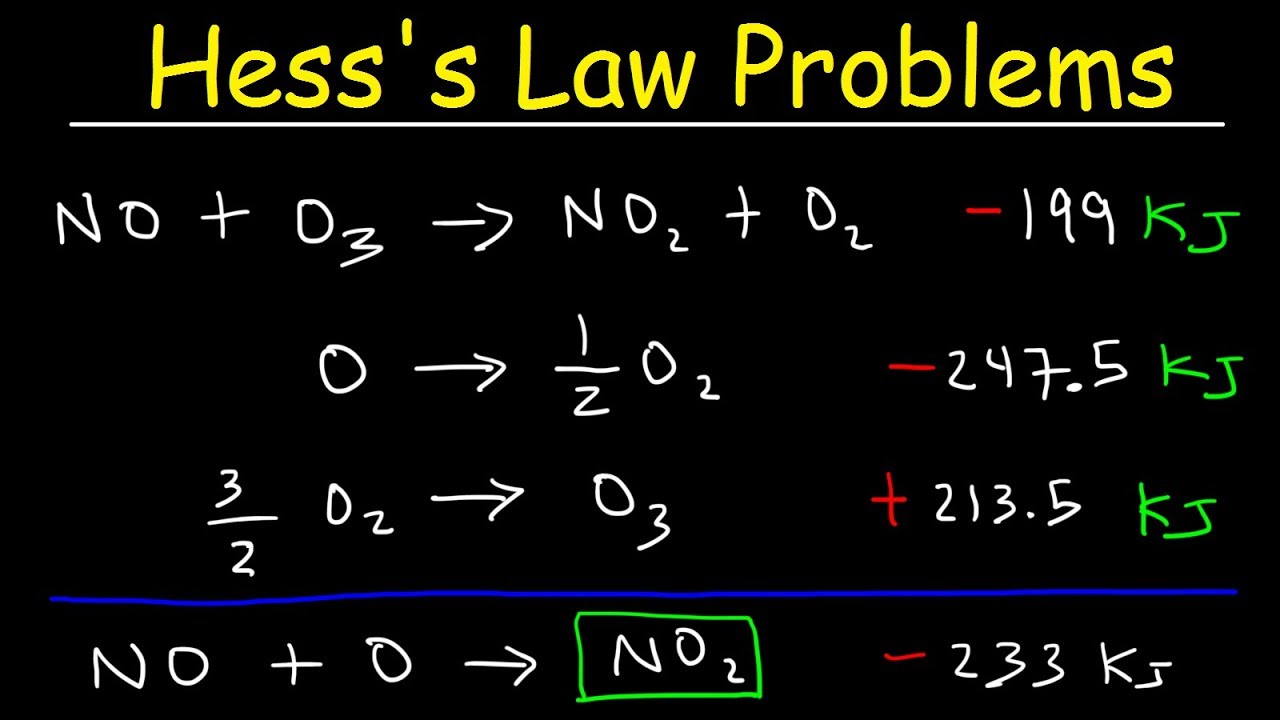
Hess's Law Problems & Enthalpy Change - Chemistry

Hess Law Chemistry Problems - Enthalpy Change - Constant Heat of Summation

Hess's law example | Thermodynamics | Chemistry | Khan Academy

Hess's law and reaction enthalpy change | Chemistry | Khan Academy

Enthalpy Change of Reaction & Formation - Thermochemistry & Calorimetry Practice Problems

Enthalpy: Crash Course Chemistry #18
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: