The World’s Strongest Acid Might be Gentle Enough to Eat
TLDRThis SciShow video script delves into the world of superacids, debunking common misconceptions about hydrofluoric acid and fluoroantimonic acid. It introduces carborane acids as the strongest, highlighting their unique property of being both incredibly potent and unexpectedly gentle. The script explores how these acids are measured using the Hammett acidity function and their potential applications, including a surprising link to vitamin supplements.
Takeaways
- 🧪 The first image that comes to mind for 'the world's strongest acid' is often hydrofluoric acid, known for its ability to dissolve a corpse, bathtub, and even the bathroom floor.
- 🔍 Despite its notoriety, hydrofluoric acid is not the strongest acid; fluoroantimonic acid is often considered stronger but is more of an 'acid cocktail' rather than a singular acid.
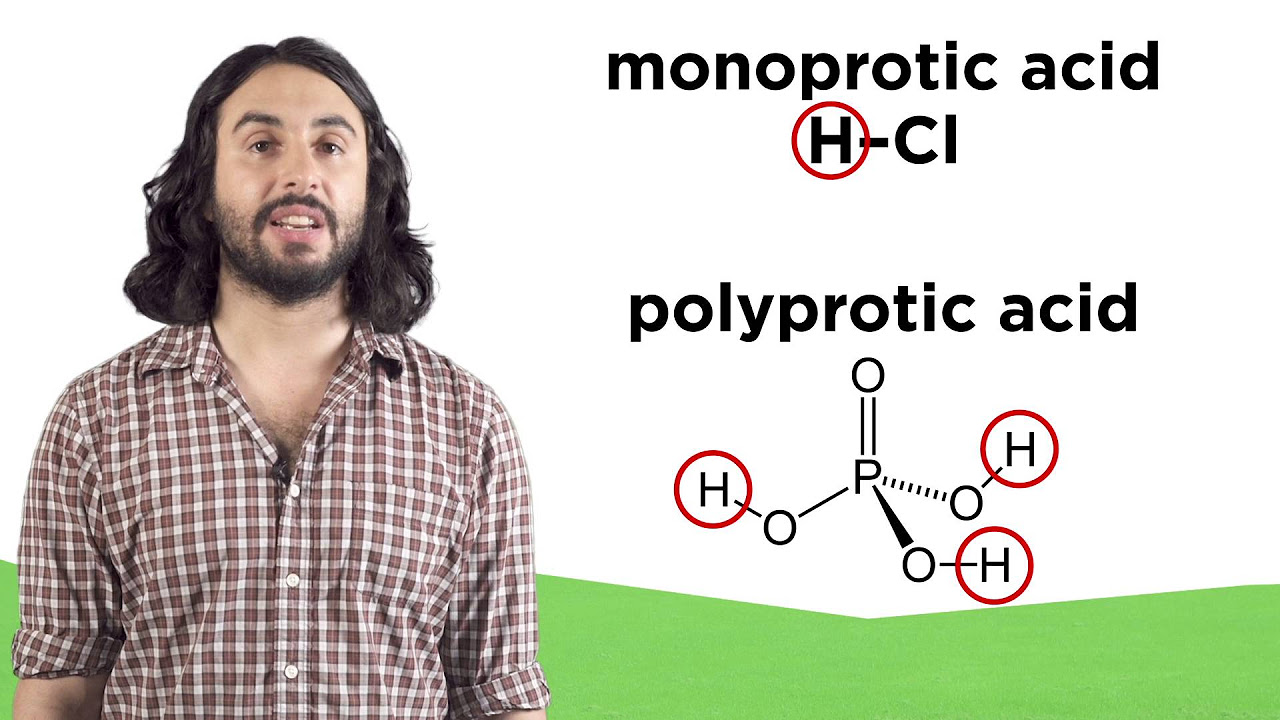
- 📚 The strength of an acid is determined by its ability to donate protons, with the acid dissociation constant (Ka) providing a specific measure of this ability.
- 📉 The pH scale is commonly used to measure acidity but is limited in its ability to accurately describe the strength of very strong acids, known as superacids.
- 🔬 The Hammett acidity function (H0) extends the pH scale and is used to measure the strength of superacids without the need for water dilution.
- 🏆 Carborane acids, specifically chlorinated carborane acid, are recognized as the strongest singular acids across solid, liquid, and gas phases.
- 🌌 The helium hydride ion is another contender for the strongest acid but is only found in interstellar space and has only been tested in the gas phase.
- 🛡️ Unlike other superacids, carborane acids have non-reactive conjugate bases due to their stable cage structure, which makes them surprisingly gentle.
- 💊 The gentle nature of carborane acids has potential applications in modifying molecules for vitamin supplements without causing damage.
- 🔬 Scientists use advanced techniques such as laser spectroscopy and proton affinity measurements to determine the strength of superacids in different states.
- 🍜 The video is sponsored by Immi Ramen, a 100% plant-based alternative to traditional ramen with high protein content and a quick cooking time.
Q & A
What is the first image that comes to mind when discussing the world's strongest acid?
-The script suggests the first image might be a scene from a chemistry-informed show where hydrofluoric acid is used to dissolve a corpse, a bathtub, and the bathroom floor.
Why is hydrofluoric acid not considered the strongest acid despite its ability to dissolve a corpse and other materials?
-Hydrofluoric acid is not the strongest acid because there are other acids that are stronger, and the script implies that the strength of an acid is not solely determined by its ability to dissolve materials but also by its chemical properties and reactivity.
What is fluoroantimonic acid, and why is it disqualified from being the strongest acid?
-Fluoroantimonic acid is an acid cocktail, a mixture of two acids, which makes it a 'cheater' according to the script. It is disqualified because the discussion is about the strongest singular acid.
What is the surprising winner of the strongest singular acid, and how is it different from other superacids?
-The strongest singular acid is a carborane acid, which is different because it is not as destructive as other superacids and has a hypothesized application in making daily vitamin supplements.
What is an acid's strength determined by in terms of its chemical behavior?
-An acid's strength is determined by how readily it donates protons to other atoms, which is not necessarily related to its ability to dissolve materials like bones.
What is the acid dissociation constant (Ka), and how is it used to measure an acid's strength?
-The acid dissociation constant (Ka) is a value calculated by comparing the number of acid molecules that have dissociated against the number that are left intact. A larger Ka value indicates a stronger acid.
Why is the pH scale not sufficient to measure the strength of superacids?
-The pH scale is not sufficient for superacids because it only measures the concentration of hydronium ions and cannot accurately represent the strength of acids stronger than sulfuric acid, which would have a pH lower than the scale's range.
What is the Hammett acidity function, and how does it extend the pH scale for measuring superacids?
-The Hammett acidity function is a method used to measure the strength of superacids by looking at the conjugate base of the acid and determining its weakness, which indicates the strength of the original acid. It extends the pH scale by not requiring the acid to be diluted in water.
How do carborane acids demonstrate their strength across different states of matter?
-Carborane acids have been shown to be the strongest singular acid in solid, liquid, and gas phases through various measurements and experiments, including the Hammett acidity function and proton affinity tests.
Why are carborane acids considered 'gentle' despite being the strongest acids?
-Carborane acids are considered 'gentle' because they leave behind fairly non-reactive conjugate bases due to their stable cage structure, allowing them to modify molecules like buckyballs without causing damage.
What is the potential application of carborane acids in the context of the script?
-The script hypothesizes that carborane acids could potentially be used in the production of vitamin supplements to help acidified molecules accept protons more readily.
Outlines
🧪 The Quest for the World's Strongest Acid
This paragraph introduces the topic of the world's strongest acid, debunking common misconceptions about hydrofluoric acid and fluoroantimonic acid. It sets the stage for an exploration of superacids and introduces the concept of acids as proton donors. The paragraph also outlines the educational journey that will include a review of acids and bases, an introduction to the pH scale, and the revelation of a surprising superacid that is surprisingly gentle in nature.
🔍 Understanding Acid Strength: Ka, pH, and Hammett Scale
This section delves into the scientific measures of acid strength, explaining the acid dissociation constant (Ka) and its limitations when dealing with very strong acids. It introduces the pH scale and its inability to accurately measure superacids due to the equipment's lower limit of zero. The Hammett acidity function is presented as a more suitable method for evaluating superacids, focusing on the strength of the conjugate base rather than the acid itself, and mentioning the challenges of measuring non-liquid superacids.
🏆 Carborane Acids: The Strongest in Solid, Liquid, and Gas
The final paragraph reveals carborane acids, particularly chlorinated carborane acid, as the strongest known superacids across all states of matter. It discusses the unique method of measuring their strength, including the use of lasers to measure bond vibrations and proton affinity tests. The paragraph also highlights the gentle nature of carborane acids, their non-reactive conjugate bases, and their potential applications in modifying molecules like buckyballs without causing damage, hinting at possible uses in vitamin supplements.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Hydrofluoric Acid
💡Superacids
💡Fluoroantimonic Acid
💡Acid Dissociation Constant (Ka)
💡pH Scale
💡Hammett Acidity Function
💡Carborane Acids
💡Conjugate Base
💡Proton Affinity
💡Buckyballs
💡Vitamin Supplements
Highlights
Hydrofluoric acid, despite its ability to dissolve a corpse and a bathtub, is not the strongest acid.
Fluoroantimonic acid, considered by some as the strongest, is actually a mixture of two acids and thus disqualified.
The strongest singular acid is surprisingly gentle and has potential applications in vitamin supplements.
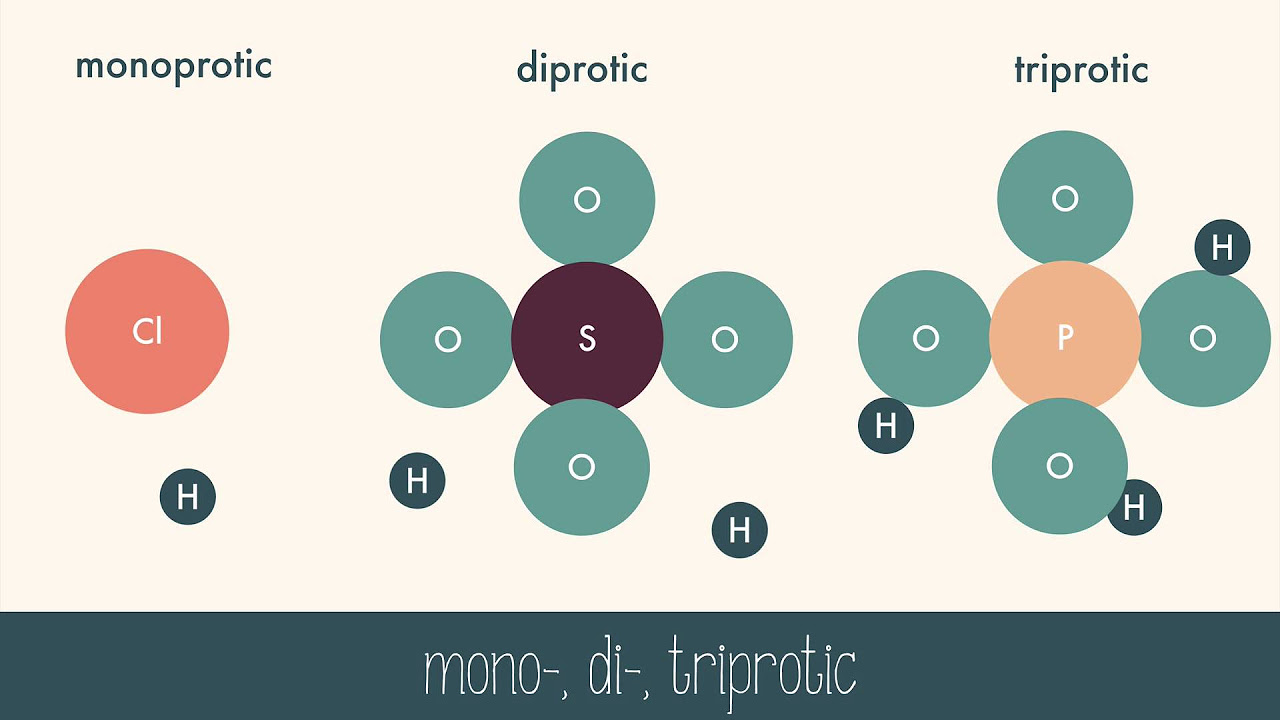
Acids are substances that donate protons to other atoms, with strength determined by how readily they separate from the original molecule.
Weak acids partially release protons, while strong acids readily give them up, like hydrochloric acid.
The acid dissociation constant (Ka) quantifies an acid's strength by comparing the number of dissociated molecules to intact ones.
The pH scale measures the concentration of hydronium ions and is limited in describing the strength of superacids.
Superacids are stronger than sulfuric acid and cannot be accurately measured by traditional pH scales.
The Hammett acidity function extends the pH scale to measure the strength of superacids without the need for water dilution.
Carborane acids are identified as the strongest known acids, even in solid, liquid, and gas phases.
Chlorinated carborane acid has an approximate H0 value of at least -18, indicating its superacid strength.
Researchers used a laser and vibrational measurements to determine the strength of solid superacids.
Carborane acids' conjugate bases are non-reactive due to their stable boron-based cage structure.
Carborane acids can modify buckyballs without causing damage, unlike other superacids.
Chlorinated carborane acid was found to be the strongest measured acid in the gas phase.
In liquid form, carborane acids outperform other strong acids when diluted with sulfur dioxide.
Carborane acids' gentle nature could potentially be used in the production of vitamin supplements.
Immi Ramen supports health goals with 100% plant-based ramen that is high in protein and fiber.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: