Molarity , Molality or Mole Fraction || 3D animated explanation || solutions || class12thchemistry
TLDRThis video script delves into the fundamental concept of molarity, a key concept in chemistry that determines the concentration of solutes in a solution. It explains how molarity is calculated through processes like dilution, stoichiometry, and reaction rates. The script also introduces molar mass as an important concept used in various areas of chemistry, such as boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and colligative properties. Molar fraction, a dimensionless quantity used in chemistry to express the moles of a component in a solution relative to the total moles of all components, is also discussed. The video aims to provide a detailed understanding of these concepts to help viewers grasp the calculations and properties related to colligative properties and ideal gas behavior.
Takeaways
- 🧪 The video explains the concept of molarity, which is a fundamental concept in chemistry that determines the concentration of solute in a solution.
- 📚 Molarity is calculated by performing calculations such as dilution, stoichiometry, and determining reaction rates.
- 🔍 The script defines molarity in detail, giving an example of 0.5 moles of sodium chloride dissolved in one liter of water, which is referred to as 0.5 molarity.
- 🌡 Molarity is an important concept in various areas of chemistry, including boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and colligative properties.
- 📉 The script discusses molality, which is defined as moles of solute per kilogram of solvent, and is expressed as molality = moles of solute / mass of solvent.
- 🧊 Molality is used to understand colligative properties and the behavior of ideal gases, and it is calculated by the formula molality of 5 moles of salt to 1 kilogram of solvent.
- 📌 Molality is a dimensionless quantity used in chemistry that expresses the moles of one component in terms of the total moles of all components in a solution.
- 📘 Mole fraction is explained as a dimensionless quantity used in chemistry, which indicates the concentration of a specific component in a mixture.
- 🔢 The mole fraction is important for calculating colligative properties and understanding ideal gas behavior, and it is defined as the total number of moles in the solution.
- 🍬 An example given for mole fraction is the mole fraction of sugar to the total number of moles, which is then multiplied by 5.
- 👍 The video concludes by thanking viewers for watching, encouraging them to like, subscribe, and follow the channel.
Q & A
What is the fundamental concept of Chemistry discussed in the video?
-The fundamental concept discussed in the video is Molarity, which is a measure of the concentration of a solute in a solution.
How is Molarity calculated?
-Molarity is calculated by performing calculations such as dilution, stoichiometry, and determining reaction rates.
What is the definition of Molarity in the context of the video?
-Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. For example, 0.5 moles of sodium chloride dissolved in one liter of water is 0.5 molarity.
What is Molar Mass and how is it expressed in the video?
-Molar Mass is an important concept in various areas of chemistry such as boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and colligative properties. It is expressed as moles per mass in the video.
How is Molar Mass defined in the video?
-Molar Mass is defined as the mass of one mole of a substance, typically expressed in grams per mole.
What is Mole Fraction and how is it used in Chemistry?
-Mole Fraction is a dimensionless quantity used in chemistry to express the amount of a particular component in a solution in terms of moles relative to the total moles of all components.
How is Mole Fraction defined in the video?
-Mole Fraction is defined in the video as the ratio of the moles of a specific component to the total number of moles in the solution.
Why is Mole Fraction important for understanding colligative properties and ideal gas behavior?
-Mole Fraction is important because it helps in the calculation of colligative properties and understanding the behavior of ideal gases, as it provides information about the concentration of a specific component in a mixture.
What is the example given in the video to explain Mole Fraction?
-The example given in the video is 'Mole Fraction of sugar to the total number of moles in a solution by 5', which illustrates how to calculate the Mole Fraction.
What are the processes involved in understanding Molarity, Molar Mass, and Mole Fraction as per the video?
-The processes involved include dilution, stoichiometry, and determining reaction rates for Molarity, and understanding colligative properties and ideal gas behavior for Molar Mass and Mole Fraction.
What does the video suggest for further engagement with the content?
-The video suggests that viewers should like, subscribe, and follow the channel for more such informative videos.
Outlines
🧪 Chemistry of Molarity, Mole Fraction, and Colligative Properties
This paragraph introduces the fundamental concept of molarity in chemistry, which is a measure of the concentration of solute in a solution. It explains how molarity is calculated, for example, with 0.5 moles of sodium chloride in one liter of water being 0.5 molar. The paragraph also touches on colligative properties like boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and the behavior of ideal gases. Molarity is defined as moles of solute per liter of solution, and the importance of mole fraction, which is the ratio of moles of a component to the total moles of all components in a solution, is highlighted. The mole fraction is crucial for understanding collective properties and the behavior of ideal gases.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Molarity
💡Molality
💡Mole Fraction
💡Dilution
💡Stoichiometry
💡Reaction Rates
💡Boiling Point Elevation
💡Freezing Point Depression
💡Colligative Properties
💡Ideal Gas Behavior
Highlights
The video explains the concept of molarity, which is fundamental in chemistry.
Molarity is used to calculate the concentration of solute in a solution.
Methods such as dilution, stoichiometry, and reaction rates are used to determine molarity.
Molarity is defined as moles of solute per liter of solution.
An example of molarity is 0.5 moles of sodium chloride in one liter of water.
Molality is an important concept in various areas of chemistry.
Molality is expressed as moles per mass, and it's used in colligative properties.
Molality is defined as moles of solute per kilogram of solvent.
An example given is 5 moles of salt dissolved in one kilogram of solvent, resulting in a 0.5 molality.
Mole fraction is a dimensionless quantity used in chemistry.
Mole fraction expresses the amount of a component in moles relative to the total moles of all components.
It is important for calculating colligative properties and understanding ideal gas behavior.
Mole fraction is defined as the total number of moles of a component in the solution.
An example of mole fraction is the calculation of sugar in a solution.
The video concludes by thanking viewers for watching and encourages likes, subscriptions, and channel support.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
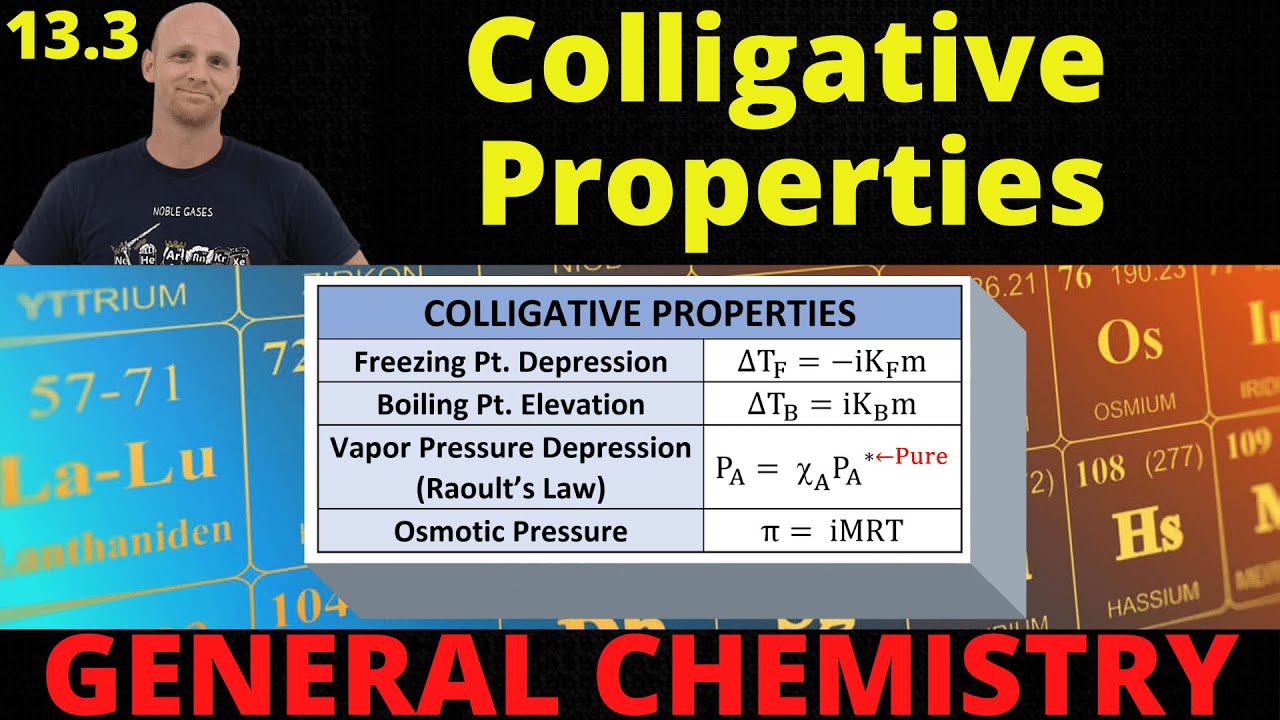
13.3 Colligative Properties | General Chemistry
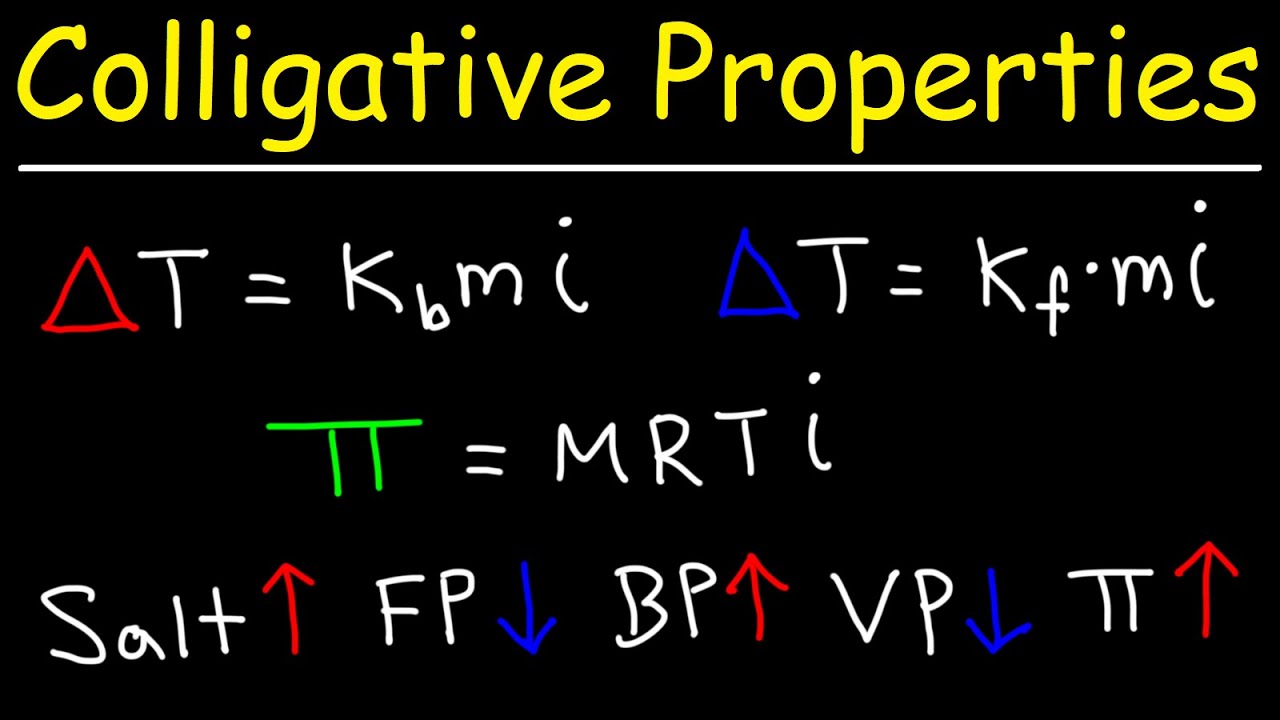
Colligative Properties - Boiling Point Elevation, Freezing Point Depression & Osmotic Pressure
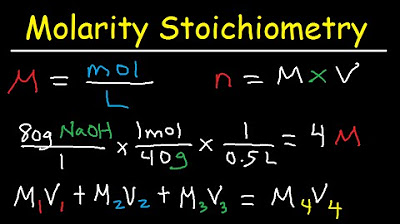
Molarity Dilution Problems Solution Stoichiometry Grams, Moles, Liters Volume Calculations Chemistry

11.3 Colligative Properties | High School Chemistry
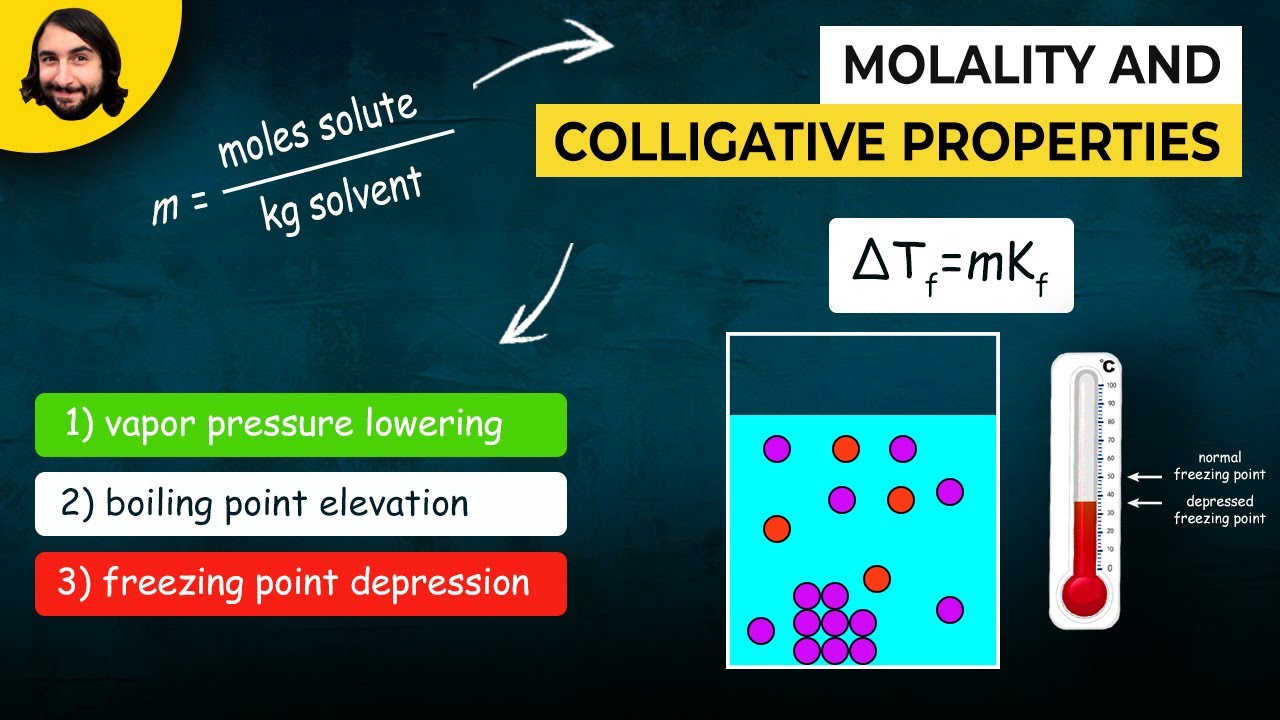
Molality and Colligative Properties

Molarity - Chemistry Tutorial
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: