Electromagnetic Waves
TLDRIn this AP Physics essentials video, Mr. Andersen explains the concept of electromagnetic waves, which are oscillations that generate electromagnetic radiation, including visible light. He clarifies that while electromagnetic waves can travel through the vacuum of space, allowing sunlight to reach Earth, mechanical sound waves cannot. The video covers the electromagnetic spectrum, ranging from high-energy gamma rays to low-energy radio waves, all of which are transverse waves with oscillations perpendicular to their direction of travel. Andersen emphasizes the importance of sunlight for warmth and plant growth, and uses visuals to illustrate the three-dimensional nature of electromagnetic waves, including their electric and magnetic fields. The video concludes with a discussion on energy transfer through particles and waves, highlighting the unique ability of electromagnetic waves to move through both mediums and the vacuum of space.
Takeaways
- 🌌 Electromagnetic waves are oscillations that create electromagnetic radiation, which includes light.
- ☀️ Light, a form of electromagnetic radiation, travels from the sun to the Earth through the vacuum of space.
- 🙉 We cannot hear the sun because mechanical sound waves cannot travel through space, unlike electromagnetic waves.
- 🔊 If audible, the sun's sound would be around 100 decibels, comparable to the noise of a jackhammer.
- 🌱 Electromagnetic waves are essential for life on Earth, providing warmth and enabling plant growth.
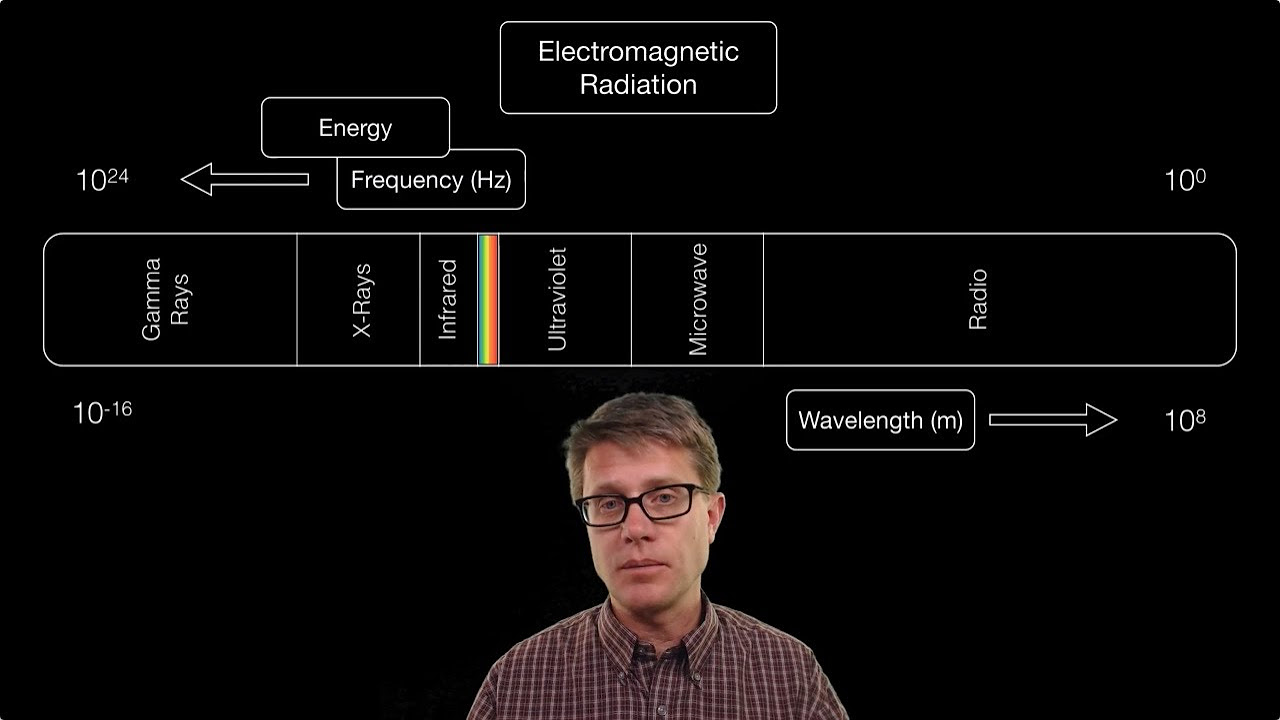
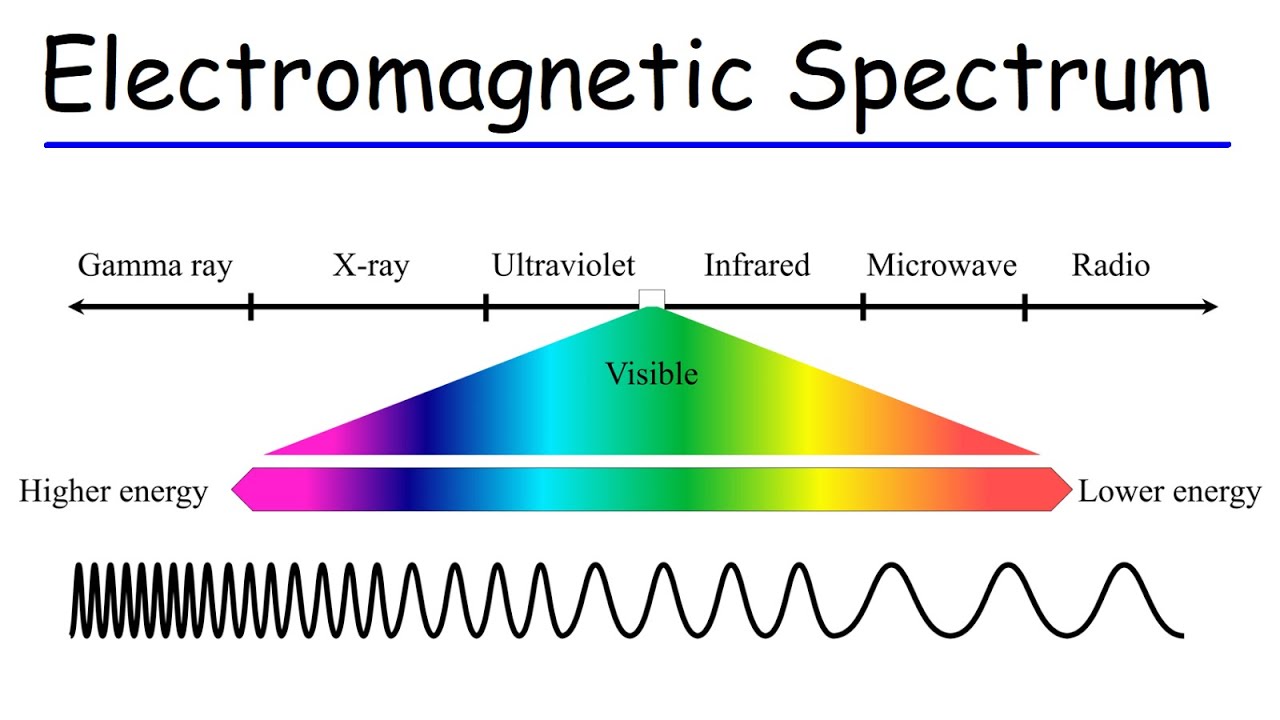
- 📡 The electromagnetic spectrum ranges from high-energy gamma rays with short wavelengths to low-energy radio waves with long wavelengths.
- 🔄 Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves, with oscillations perpendicular to the direction of wave movement.
- 🌀 Both electric and magnetic fields in an electromagnetic wave are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of wave travel.
- 🏠 Electromagnetic waves can travel through various media, including water and the walls of buildings, as well as through the vacuum of space.
- 📈 As energy increases towards gamma rays, wavelength decreases and frequency increases.
- ✋ Energy can be transferred as a particle or through a wave; electromagnetic waves transfer energy without a medium, unlike mechanical waves.
Q & A
What are electromagnetic waves and why are they important?
-Electromagnetic waves are oscillations that create electromagnetic radiation. They are important because they carry light, which is essential for warmth, plant growth, and ultimately, human survival.
Can electromagnetic waves travel through a vacuum?
-Yes, electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum, as evidenced by the fact that light from the sun reaches the earth through the vacuum of space.
Why can't we hear the sun?
-We can't hear the sun because mechanical sound waves cannot travel through the vacuum of space. If they could, the sun's sound would be around 100 decibels, which is as loud as a jackhammer a few meters away.
What is the electromagnetic spectrum and what does it consist of?
-The electromagnetic spectrum consists of electromagnetic waves that range from high-energy, high-frequency, low-wavelength gamma rays to low-energy, long-wavelength radio waves. Humans can only see a small portion of this spectrum.
What is a transverse wave and how does it relate to electromagnetic waves?
-A transverse wave is one where the oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of the wave's movement. Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves, with electric and magnetic fields oscillating at right angles to both the direction of motion and each other.
Can electromagnetic waves travel through different mediums?
-Electromagnetic waves can travel through various mediums, including water and air, and can even pass through solid objects like the walls of a house, allowing us to receive radio signals.
How do electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves?
-Electromagnetic waves are not mechanical, meaning they do not require a medium to transfer energy. They can move through a medium or even through a vacuum, unlike mechanical waves which need a physical medium to propagate.
What is the relationship between the energy of electromagnetic waves and their wavelength and frequency?
-As you move towards higher energy electromagnetic waves, such as gamma rays, the wavelength decreases while the frequency increases. Conversely, lower energy waves like radio waves have longer wavelengths and lower frequencies.
What is the right-hand rule and how does it relate to electromagnetic waves?
-The right-hand rule is a mnemonic for understanding the direction of electric and magnetic fields in electromagnetic waves. It helps visualize the oscillations in two dimensions while the wave moves in the third dimension.
How can energy be transferred from one point to another?
-Energy can be transferred as a particle, where a particle is physically moved from point A to B, or through a wave, where oscillations create waves that transfer energy without the need for a physical medium.
What is the model of an electromagnetic wave described in the script?
-The model of an electromagnetic wave described in the script includes both a transverse wave with perpendicular electric and magnetic fields and the ability of the wave to move through the vacuum of space.
Outlines
🌌 Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance
Mr. Andersen introduces the topic of electromagnetic waves, emphasizing their role in transmitting light, which is a form of electromagnetic radiation. He explains that while light can travel through the vacuum of space, sound cannot, and humorously notes that if we could hear the sun, it would be as loud as a jackhammer. The video underscores the significance of electromagnetic waves for life on Earth, as they provide warmth and enable plant growth. The electromagnetic spectrum is briefly described, ranging from high-energy gamma rays to low-energy radio waves, all of which are transverse waves with oscillations perpendicular to the direction of wave movement. The explanation includes the perpendicular relationship between electric and magnetic fields, and the ability of electromagnetic waves to travel through various mediums and even the vacuum of space.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Electromagnetic Waves
💡Electromagnetic Radiation
💡Vacuum of Space
💡Transverse Waves
💡Electric Fields
💡Magnetic Fields
💡Electromagnetic Spectrum
💡Wavelength
💡Frequency
💡Right-Hand Rule
💡Energy Transfer
Highlights
Electromagnetic waves are oscillations that create electromagnetic radiation.
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation carried by electromagnetic waves.
Electromagnetic waves can travel through the vacuum of space, unlike mechanical sound waves.
The sun emits sound waves at around 100 decibels, comparable to a jackhammer, if they could travel through space.
Electromagnetic waves are essential for warmth and plant growth, enabling our survival.
The electromagnetic spectrum ranges from high-energy gamma rays to low-energy radio waves.
Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves with oscillations perpendicular to the direction of wave movement.
Electric and magnetic fields in electromagnetic waves are perpendicular to each other and the direction of motion.
Electromagnetic waves can travel through various mediums and the vacuum of space.
As energy increases towards gamma rays, wavelength decreases and frequency increases.
Radio waves have wavelengths comparable to building sizes, while gamma rays are atomic in scale.
The right-hand rule is used to understand the relationship between electric and magnetic fields in electromagnetic waves.
Energy can be transferred as a particle or through a wave, such as mechanical waves requiring a medium.
Electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves as they do not require a medium and can move through space.
The model of an electromagnetic wave consists of perpendicular electric and magnetic fields and can move through a vacuum.
The video aims to help viewers understand and describe the characteristics of electromagnetic waves.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: