Light Absorption, Reflection, and Transmission
TLDRIn this AP Physics essentials video, Mr. Andersen explores light absorption, reflection, and transmission using a green laser and gummy bears of different colors. He explains that light can be reflected off surfaces, absorbed and converted into other forms of energy like heat, or transmitted through a medium. The video demonstrates these concepts with the gummy bears, showing how different colors absorb and reflect light differently, affecting the colors we perceive. Reflection is further detailed with the law of reflection, where the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. The video also touches on the absorption spectrum of a leaf, highlighting how chlorophyll absorbs different wavelengths of light for photosynthesis. This engaging lesson provides a clear understanding of how light interacts with different media.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Light can be absorbed, reflected, or transmitted when it interacts with a medium.
- 🍬 Mr. Andersen uses gummy bears of different colors to demonstrate these principles, showing how green light is absorbed by the red gummy bear.
- 💡 Reflection occurs when light bounces off a surface, and the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
- 🌄 The script explains how we see reflections, such as a mountain in a lake, due to light reflecting off the water's surface.
- 🔍 Absorption happens when light is converted into another form of energy, typically heat, and is not reflected back to our eyes.
- 🌿 The example of a leaf is used to illustrate how different wavelengths of light are absorbed by chlorophyll, which is why green light is reflected and makes the leaf appear green.
- 🌱 Leaves can use the absorbed energy for photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy.
- 🌅 Transmission is when light passes through a medium without being absorbed or reflected, as seen when looking at the underside of a leaf.
- 🌈 Some plants have evolved to have a colored barrier on the bottom of leaves to reflect unabsorbed light back up for more efficient energy use.
- 🚀 The gummy bear experiment shows all three behaviors of light: reflection on the surface, absorption as the light enters, and transmission through the gummy bear.
- 📚 The video script concludes by emphasizing the three possible behaviors of light when it travels from one medium to another.
Q & A
What are the three things that can happen when light moves from one medium to another?
-When light moves from one medium to another, it can be reflected, absorbed, or transmitted.
What is the phenomenon where most of the light is transmitted through an object?
-The phenomenon where most of the light is transmitted through an object is known as transmission.
How does the color of an object affect the light it absorbs?
-The color of an object affects the light it absorbs because different wavelengths of light interact differently with the medium, leading to different absorption rates.
What is the process called when light bounces off the surface of an object?
-The process where light bounces off the surface of an object is called reflection.
What is the law that governs the angles of incidence and reflection?
-The law that governs the angles of incidence and reflection is that the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
Can you explain the concept of the normal in the context of reflection?
-In the context of reflection, the normal is an imaginary line that is perpendicular to the surface of an object. The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are measured with respect to this normal line.
What is the primary form of energy that light is converted into during absorption?
-During absorption, light is primarily converted into heat energy.
How does the absorption of light by a leaf contribute to photosynthesis?
-The absorption of light by a leaf, specifically the absorption of red and blue light by chlorophyll A and B, contributes to photosynthesis by providing the energy needed for the process.
What is the purpose of the barrier on the bottom of some leaves?
-The barrier on the bottom of some leaves serves to reflect the transmitted light, such as blue and red light, back up through the leaf, allowing the plant to capture more energy from sunlight.
How can the behavior of light be observed in the gummy bear experiment?
-In the gummy bear experiment, the behavior of light can be observed through the different amounts of reflection, absorption, and transmission as the green laser light interacts with gummy bears of various colors.
What is the significance of the color of a gummy bear in the experiment?
-The color of a gummy bear in the experiment is significant because it determines how much of the incident light is reflected, absorbed, or transmitted, demonstrating the interaction of light with different pigments and chemicals.
Outlines
🌟 Light Interaction with Different Media
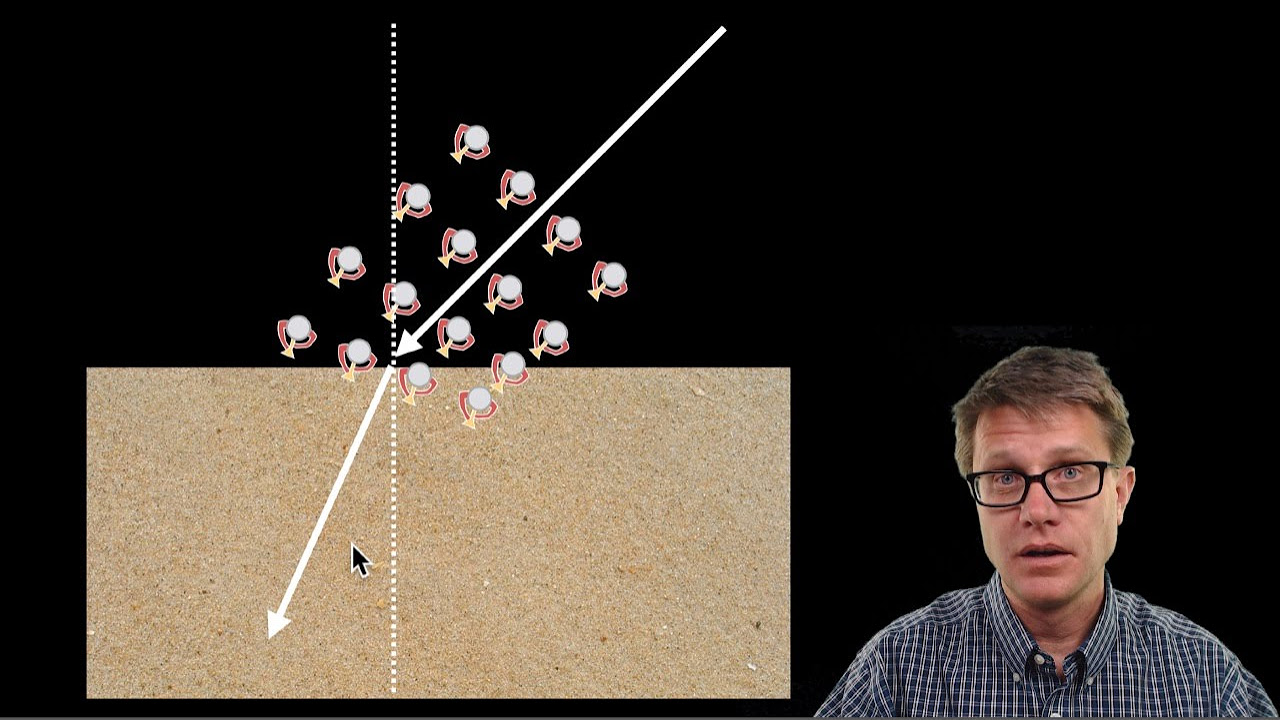
Mr. Andersen introduces the concept of light absorption, reflection, and transmission using a green laser and gummy bears of various colors. He explains that light can be reflected off surfaces, absorbed and converted into other forms of energy, or transmitted through a medium. The video demonstrates these phenomena with the gummy bears, showing how red gummy bears absorb green light and would similarly absorb light if the roles were reversed. The script also touches on the different interactions of light wavelengths with a medium, leading to the colors we perceive in objects.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Light absorption
💡Reflection
💡Transmission
💡Wavelength
💡Color of objects
💡Refraction
💡Pigments
💡Photosynthesis
💡Normal line
💡Angle of incidence
💡Angle of reflection
Highlights
Light absorption, reflection, and transmission are discussed using a green laser and gummy bears of different colors.
Most light is transmitted through gummy bears with some reflection and absorption observed.
The red gummy bear absorbs green light, demonstrating how color affects light interaction.
Light moving from air to a medium like a gummy bear can be reflected, absorbed, or transmitted.
Different wavelengths of light interact differently with a medium, affecting the color of objects.
Reflection is described as the bouncing of light off a surface, with the angle of incidence equaling the angle of reflection.
The color of an object is determined by the light it reflects, exemplified by a green leaf reflecting green light.
Absorption occurs when light hits a surface and is converted into another form of energy, typically heat.
Chlorophyll in leaves absorbs blue, red, and yellow light, while reflecting green light.
Transmitted light passes through a medium, such as light passing through the underside of a leaf.
Some plants have evolved barriers on the bottom of leaves to reflect unused light back for photosynthesis.
The gummy bear experiment illustrates light being transmitted, absorbed, and reflected differently by each color.
The red gummy bear shows significant reflection and absorption with minimal transmission of green light.
The behavior of light is influenced by the pigments and chemicals within a medium.
Understanding light behavior is crucial for explaining how objects appear and interact with their environment.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: