Electric Permittivity
TLDRIn this AP Physics essentials video, Mr. Andersen explores the concept of electric permittivity through a homemade capacitor made of Reynolds Wrap and plastic wrap. He demonstrates how permittivity, the ability of a material to resist an electric field, affects capacitance. Using a multimeter, he shows the capacitor charging and discharging. The video explains that permittivity varies with material structure, and adding a dielectric to a capacitor increases its efficiency by resisting the electric field and building up charge. The concept is further illustrated with a PHET simulation, highlighting how different materials with varying permittivity constants can impact a capacitor's performance.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Permittivity is a measure of a material's ability to resist an electric field.
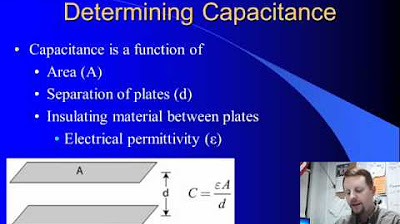
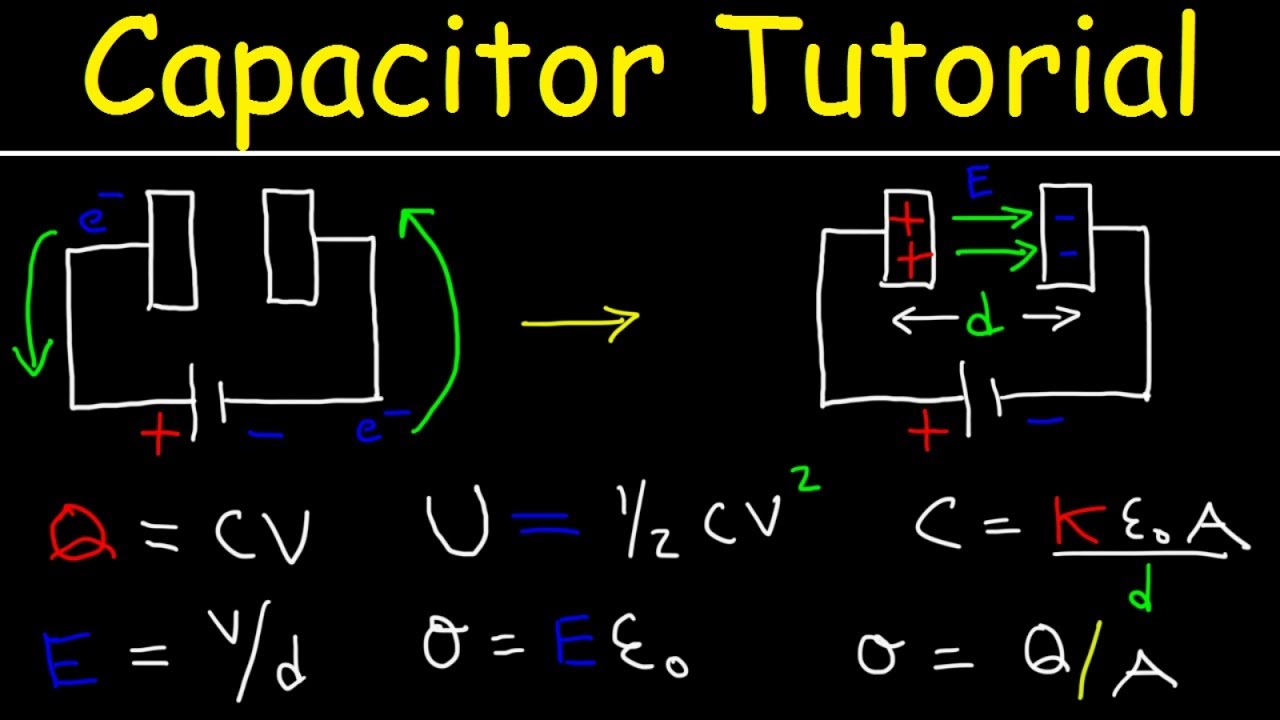
- 🔋 A capacitor is made of two conducting plates with an insulative material, the dielectric, in between.
- 📦 Mr. Andersen demonstrates a homemade capacitor using Reynolds Wrap and plastic wrap, with the plastic wrap serving as the dielectric.
- 🔌 The video shows the process of charging a capacitor by connecting it to a battery and measuring the charge with a multimeter.
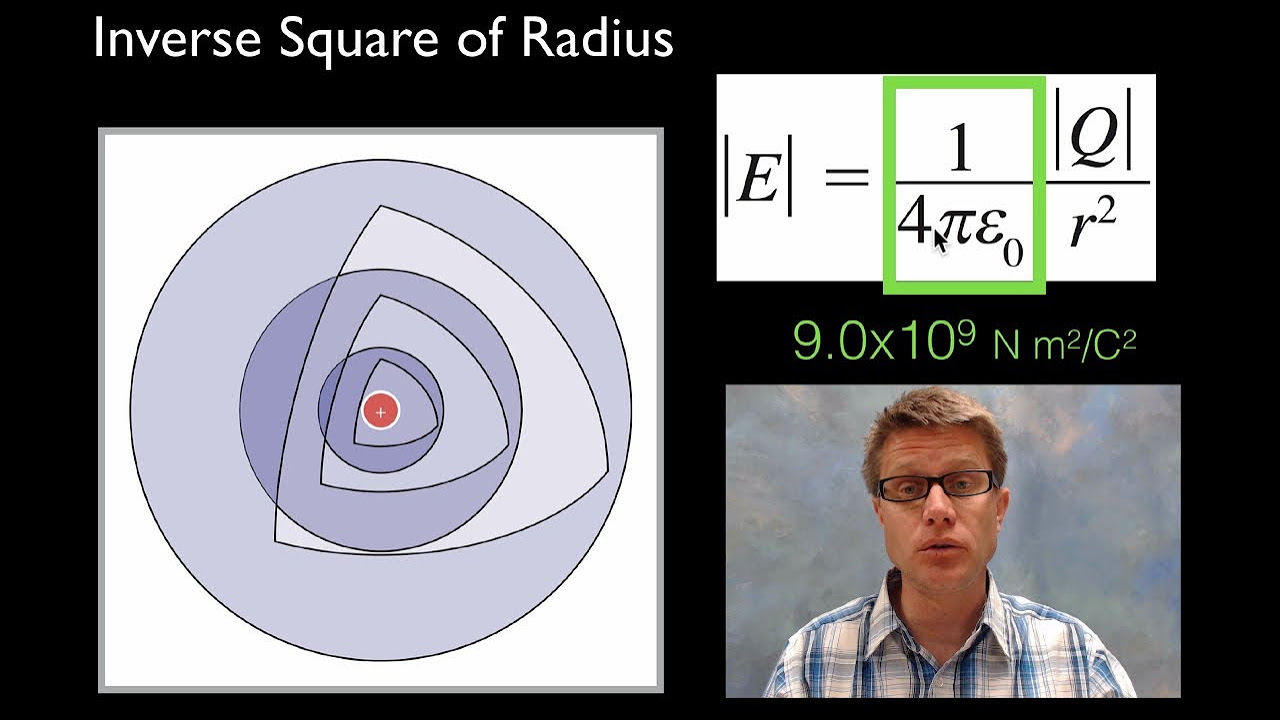
- 🌌 The permittivity of free space, or vacuum, is a constant value and serves as a baseline for comparing the permittivity of other materials.
- 🏗️ The structure of atoms and molecules in a material determines its permittivity, which can vary and affect the efficiency of a capacitor.
- 📈 Adding a dielectric to a capacitor increases its capacitance by resisting the electric field and allowing more charge to build up on the plates.
- 🔬 The dielectric constant is higher than 1 for materials other than a vacuum, with different materials having different constants.
- 🎥 A PHET simulation is used to illustrate how increasing permittivity affects the charge buildup on capacitor plates.
- 📉 Removing the dielectric from a capacitor decreases its capacitance, demonstrating the importance of the dielectric in energy storage.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is electric permittivity and its relation to capacitance.
What is a capacitor made of according to the video?
-A capacitor is made of two conducting plates with an insulative material, known as a dielectric, in the middle.
What materials did Mr. Andersen use to create a simple capacitor in the video?
-Mr. Andersen used two layers of Reynolds Wrap as conductors and one layer of plastic wrap as the dielectric to create a simple capacitor.
How is the homemade capacitor in the video different from a real capacitor?
-The homemade capacitor is essentially the same as a real one, with conductors on either side and an insulative material in the middle, but it is rolled up for portability.
What is permittivity and how is it demonstrated in the video?
-Permittivity is the ability of a material to resist an electric field. In the video, it is demonstrated by showing how the charge on a capacitor increases when connected to a battery.
What is the permittivity of free space?
-The permittivity of free space is the resistance offered by a vacuum between two conducting plates, and it is a constant value used to compare other materials.
How does the atomic or molecular structure of a material affect its permittivity?
-The atomic or molecular structure of a material determines its permittivity, as it influences how the material resists an electric field.
What happens when a dielectric is added to a capacitor?
-When a dielectric is added to a capacitor, it resists the electric field, leading to a build-up of charge on either side of the conducting plates and thus storing energy.
What is the dielectric constant and how does it relate to permittivity?
-The dielectric constant is a measure of a material's ability to store electrical energy in an electric field. It is related to permittivity as it quantifies the material's resistance to the electric field.
How does the permittivity of different materials affect the capacitance of a capacitor?
-Different materials have different permittivities, which means they offer varying levels of resistance to an electric field. A higher permittivity material will increase the capacitance of a capacitor, making it more efficient at storing charge.
What is the purpose of the PHET simulation shown in the video?
-The PHET simulation is used to visually demonstrate how increasing the permittivity of a dielectric material affects the charge build-up on the plates of a capacitor.
Outlines
🔋 Understanding Electric Permittivity and Capacitance
In this educational video, Mr. Andersen introduces the concept of electric permittivity in the context of capacitance. He constructs a homemade capacitor using Reynolds Wrap and plastic wrap, demonstrating how charge can be stored. The video explains that permittivity is the ability of a material to resist an electric field, with free space having a permittivity constant value used as a reference. Different materials have varying permittivities based on their atomic or molecular structure, which affects the efficiency of a capacitor. The video also illustrates how adding a dielectric material to a capacitor increases its capacitance by shifting electrons and creating an opposing electric field, thus enhancing charge storage. The use of a PHET simulation further demonstrates how varying the permittivity of different materials affects the charge buildup on the plates of a capacitor.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Electric Permittivity
💡Capacitance
💡Reynolds Wrap
💡Plastic Wrap
💡Dielectric
💡Conductors
💡Multimeter
💡Electric Field
💡Free Space Permittivity
💡Dielectric Constant
💡Energy Storage
Highlights
Introduction to electric permittivity and its relation to capacitance.
Demonstration of a homemade capacitor using Reynolds Wrap and plastic wrap.
Explanation of how the capacitor is constructed with conductive and insulative layers.
Visual demonstration of charging the capacitor with a multimeter.
Observation of charge increase as the capacitor stores energy.
Definition of permittivity as the resistance to an electric field.
Comparison of permittivity of free space and other materials.
Discussion on how atomic or molecular structure affects permittivity.
Illustration of a basic capacitor with conducting plates and a dielectric.
Explanation of free space permittivity and its role as an electric field resistor.
Impact of adding a dielectric on the electric field and charge buildup.
The concept of dielectric constant and its relation to energy storage.
Use of a PHET simulation to show the effect of permittivity on charge buildup.
Demonstration of how different materials affect the capacitance.
Visual representation of how removing the dielectric reduces capacitance.
Conclusion on the importance of electric permittivity in capacitor design.
Summary of the experiment with Reynolds Wrap and plastic wrap as a simple capacitor.
Final thoughts on the educational value of the video.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: