Average Speed | Forces & Motion | Physics | FuseSchool
TLDRThe video script delves into the concept of speed, distinguishing between average and instantaneous speed, and how it varies throughout a race or journey. It explains that while speed is often calculated by dividing distance by time, this method assumes constant speed. The script uses examples, such as Usain Bolt's race and a dog running across a field, to illustrate the calculation of average speed, which involves total distance and total time taken. It also mentions the use of speed cameras to measure instantaneous speed and average speed cameras that record travel time over a distance. The script concludes with an example of calculating the average speed of a car, emphasizing that for non-uniform motion, the average speed is found by dividing the total distance by the total time.
Takeaways
- 🏃 Calculating speed involves dividing the distance traveled by the time taken.
- 🏃♂️ The assumption of constant speed is rarely accurate for the entire duration of a race.
- 📈 Usain Bolt's graph illustrates the gradual increase to maximum speed and eventual slowing down.
- 🏃♀️ Average speed and instantaneous speed are different; the latter is the speed at a specific moment, while the former is calculated over a period.
- 🚗 Instantaneous speed is like a snapshot taken by a speed camera, whereas average speed is calculated over a longer distance.
- 🚦 Average speed cameras record the time taken to travel a certain distance, influencing driving behavior.
- 🐕 To calculate average speed, sum the total distance and the total time traveled, then divide the former by the latter.
- 🌾 An example of calculating average speed is provided with a dog running across a field at varying speeds.
- 🚗 Another example involves a car that changes speed due to traffic, demonstrating how to calculate average speed in such scenarios.
- 📊 Average speed can also be determined from a distance-time graph by using the total distance and total time from the graph.
- 📐 The formula for average speed in non-uniform motion is total distance divided by total time, regardless of the context.
Q & A
How is speed typically calculated in a race?
-Speed is typically calculated by dividing the distance traveled by the time taken to travel that distance, such as 100 meters in 20 seconds, resulting in a speed of 5 meters per second.
Why can't we assume a runner maintains a constant speed throughout a race?
-A runner's speed is not constant because it takes time to reach maximum speed, and in longer races, they may start quickly and slow down due to fatigue or speed up at the end.
What is the difference between average speed and instantaneous speed?
-Average speed is the total distance traveled divided by the total time taken, while instantaneous speed is the speed of an object at a particular moment in time, such as when a speed camera captures the speed of a car.
How do average speed cameras work?
-Average speed cameras record the time it takes for a vehicle to travel over a certain distance, which helps to calculate the average speed of the vehicle over that distance.
Why would drivers be less likely to speed when average speed cameras are in use?
-Drivers are less likely to speed because they would need to maintain a lower average speed over a distance to avoid fines, which may require them to drive more slowly at times.
What is the formula for calculating average speed?
-The formula for calculating average speed is the total distance traveled divided by the total time taken.
In the example of the dog running across a field, how is the average speed calculated?
-The average speed is calculated by dividing the total distance (100 meters) by the total time (50 seconds), which is the sum of the time for the first 50 meters (20 seconds) and the time for the last 50 meters (30 seconds).
What is the average speed of the car in the second example, and how is it calculated?
-The average speed of the car is 15 meters per second, calculated by dividing the total distance traveled (450 meters + 150 meters = 600 meters) by the total time (20 seconds + 20 seconds = 40 seconds).
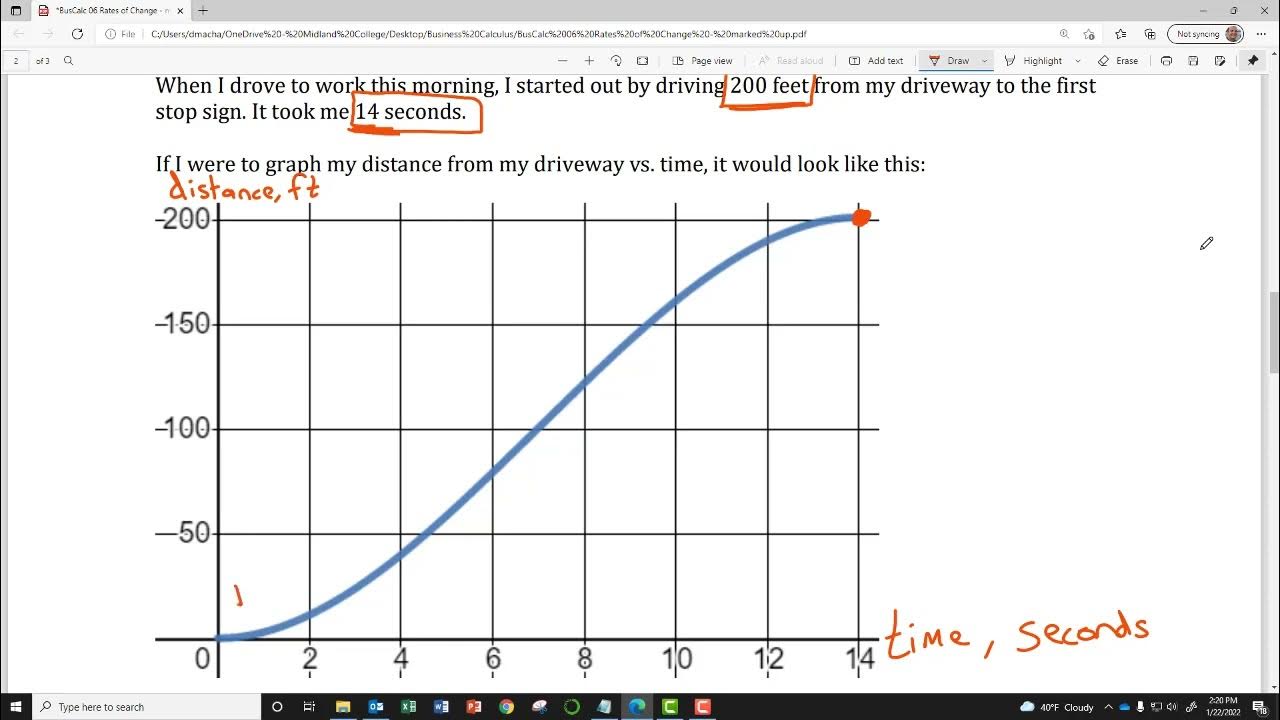
How can you calculate the average speed from a distance-time graph?
-You can calculate the average speed from a distance-time graph by using the total distance and total time represented on the graph, dividing the total distance by the total time.
What is the average speed on the provided distance-time graph?
-The average speed on the provided distance-time graph is 5.7 meters per second, calculated by dividing the total distance (400 meters) by the total time (70 seconds).
Why is it important to understand the concept of average speed for non-uniform motion?
-Understanding the concept of average speed is important for non-uniform motion because it allows us to calculate the overall speed of an object when its speed is changing over time, which is common in real-world scenarios.
How does the concept of average speed apply to different contexts, such as running races or driving cars?
-The concept of average speed applies to different contexts by providing a way to measure the overall speed of an object over a period of time or distance, regardless of variations in speed during that period. This is useful for analyzing performance in races, assessing driving habits, and understanding the motion of objects in various scenarios.
Outlines
🏃 Calculating Speed in a Race
This paragraph explains the concept of speed in the context of a race. It begins with the traditional method of calculating speed by dividing the distance traveled by the time taken, using the example of a person running 100 meters in 20 seconds. However, it points out that this method assumes constant speed, which is rarely the case in reality. It uses Usain Bolt's race as an example to illustrate how runners can accelerate and decelerate during a race. The paragraph then introduces the concepts of average speed and instantaneous speed, using a car as an example to differentiate between the two. Finally, it guides the viewer through calculating the average speed of a dog running across a field with varying speeds, emphasizing that for non-uniform motion, average speed is found by dividing the total distance by the total time.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Speed
💡Distance
💡Time
💡Constant Speed
💡Variable Speed
💡Usain Bolt
💡Average Speed
💡Instantaneous Speed
💡Speed Camera
💡Non-Uniform Motion
💡Distance-Time Graph
Highlights
Calculating speed is achieved by dividing the distance traveled by the time taken.
The assumption of constant speed for an entire race is rarely accurate.
Usain Bolt's graph illustrates that it takes time to reach maximum speed.
In longer races, runners often start fast and slow down due to fatigue.
Runners may speed up at the end of a race.
Average speed and instantaneous speed are different concepts.
Instantaneous speed is the speed at a specific moment, like when a car passes a speed camera.
Average speed cameras measure the time taken to travel a certain distance.
To avoid fines, drivers may need to adjust their driving to lower their average speed.
The average speed is calculated by dividing the total distance by the total time.
An example of calculating a dog's average speed across a field is provided.
A car's average speed is calculated after it travels at different speeds over different time intervals.
The average speed of the car is determined to be 15 meters per second.
Distance-time graphs can also be used to calculate average speed.
On a graph, average speed is found by dividing the total distance by the total time.
The average speed from a graph is illustrated as 5.7 meters per second.
The concept of average speed is applicable in various contexts and situations.
For non-uniform motion, the average speed is found using the total distance and total time traveled.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: