What is Velocity? Physics
TLDRThe video script explains the concepts of speed and velocity, emphasizing their differences. Speed is a scalar quantity, calculated as the total distance traveled divided by time, indicating the rate of change of distance. Velocity, however, is a vector quantity, which includes both the magnitude and direction of the displacement. The script uses examples of a car traveling different routes between two cities to illustrate how speed and velocity are calculated and how they differ, highlighting that average speed and average velocity are not the same, especially in cases like circular motion where displacement is zero, resulting in zero velocity despite non-zero speed.
Takeaways
- 📏 Speed is calculated by dividing the distance covered by the time taken, expressed as meters per second (m/s).
- 🔄 Distance is a scalar quantity that represents the magnitude of space between two points without considering direction.
- 📍 Displacement, on the other hand, is a vector quantity that accounts for both the magnitude (distance) and direction of movement.
- 🚀 Velocity is the vector equivalent of speed, combining both rate of change of distance with respect to time and direction.
- 🛣️ When a body moves in a specific direction, the distance traveled is referred to as displacement, not just distance.
- 🌐 The SI unit for both speed and velocity is meters per second (m/s), but they are fundamentally different in nature due to scalar vs. vector properties.
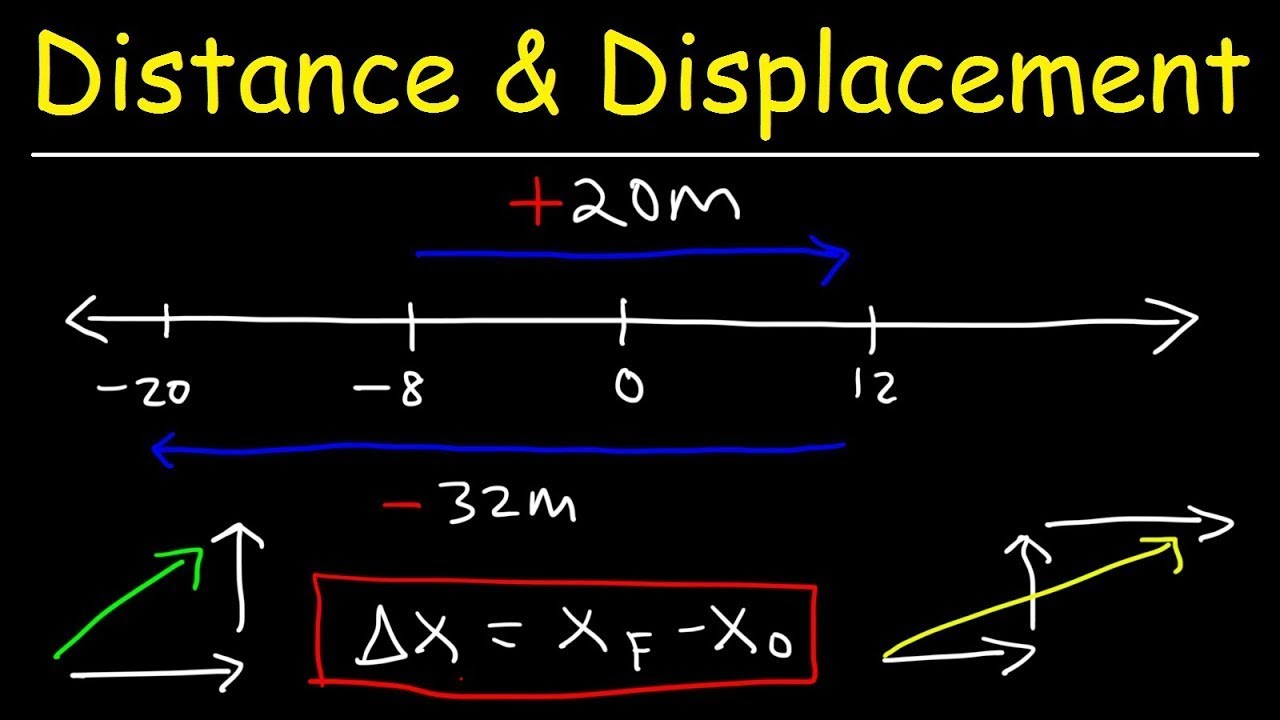
- 🚗 In the context of travel, the total length of the path taken (e.g., 30 km) is the distance, while the straight-line distance between the starting and ending points (e.g., 18 km) is the displacement.
- 🔄 For an object moving in a circular path, the average speed is the total circumference divided by the time taken, but the average velocity is zero since the displacement is zero.
- 📈 Speed can be constant while velocity changes if the direction of motion changes, even if the rate of covering distance remains the same.
- 🚦 It is crucial to distinguish between speed and velocity when analyzing motion, as they provide different insights into an object's movement.
- 📊 Understanding the concepts of speed and velocity is essential for accurately describing and calculating motion in physics.
Q & A
What is the formula to calculate the speed of a body?
-The formula to calculate the speed of a body is the total distance covered divided by the time taken. In symbols, speed (v) equals distance (d) divided by time (t), or v = d / t.
What does 2 meters per second indicate?
-2 meters per second indicates that the body covers a distance of 2 meters in each second of time.
How is distance different from displacement?
-Distance is a scalar quantity that represents the total length of the path traveled by an object without regard to direction. Displacement, on the other hand, is a vector quantity that takes into account both the magnitude and direction of the path traveled from the initial to the final position.
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
-Speed is a scalar quantity that describes how fast an object is moving, calculated as the distance traveled divided by the time taken. Velocity is a vector quantity that includes both the speed and the direction of the object's motion, calculated as displacement divided by time.
What is the SI unit for both speed and velocity?
-The SI unit for both speed and velocity is meters per second (m/s).
How do you calculate the average speed of a body moving in a circle?
-The average speed of a body moving in a circle is calculated by dividing the total circumference of the circle (the distance) by the time taken to complete the circuit.
Why is the average velocity of a body moving in a circle zero?
-The average velocity of a body moving in a circle is zero because the displacement, which is the change in position, is zero since the starting and ending points are the same.
What is the significance of direction in the calculation of displacement?
-Direction is significant in the calculation of displacement because it is a vector quantity. Knowing the direction allows us to specify the path taken by the object, which is essential for determining its displacement from its initial to its final position.
How does the concept of distance apply when a car travels from one city to another?
-The concept of distance applies when calculating the total length of the path a car takes to travel from one city to another. This can be the actual route length, which is the distance the car travels along the roads.
What is the difference in speed and velocity when comparing two cars taking different routes between two cities?
-The speed of the cars can be different based on the length of the route they take, but their velocity will be the same if both cars end up at the same final position, as velocity includes direction and both cars have the same displacement.
Why is it important to distinguish between speed and velocity in physics?
-It is important to distinguish between speed and velocity in physics because speed only considers the magnitude of how fast an object is moving, while velocity accounts for both the magnitude and direction. This distinction is crucial for accurately describing and predicting an object's motion.
Outlines
📐 Understanding Speed and Velocity
This paragraph explains the concepts of speed and velocity in physics. It begins by defining speed as the distance covered per unit of time, using an example of a body moving 10 meters in 5 seconds to illustrate a speed of 2 meters per second. The paragraph then differentiates between distance, which is a scalar quantity, and displacement, which is a vector quantity that includes direction. It further clarifies the concept by explaining that speed does not account for direction, while velocity does. The distinction between average speed and average velocity is also highlighted, with examples of cars traveling different routes between two cities to demonstrate the calculation and understanding of these physical quantities.
🚗 Comparing Speed and Velocity in Real-World Scenarios
The second paragraph delves into practical examples of speed and velocity by considering two routes between two cities. It explains that while both speed and velocity are measured in meters per second, they represent different things. The paragraph clarifies that average speed is the total distance divided by time, while average velocity takes into account both distance and direction, which can result in a velocity of zero if the initial and final positions are the same. This is exemplified by a car traveling in a circular path and returning to its starting point, where the distance traveled is the circumference of the circle, but the displacement and thus the average velocity is zero.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Speed
💡Distance
💡Displacement
💡Velocity
💡Scalar Quantity
💡Vector Quantity
💡Average Speed
💡Average Velocity
💡SI Unit
💡Direction
💡Motion
Highlights
The concept of speed is defined as the distance covered per unit of time.
In the given example, a body covers a distance of 10 meters in 5 seconds, resulting in a speed of 2 meters per second.
The distinction between distance and displacement is clarified, with distance being a scalar quantity and displacement being a vector quantity.
Displacement takes into account both the magnitude and direction of the movement, unlike distance which only considers the magnitude.
Speed is the rate of change of distance with respect to time, whereas velocity is the rate of change of displacement with respect to time.
The formula for speed is correctly expressed as distance divided by time.
Velocity, on the other hand, is the speed in a specific direction, making it a vector quantity.
The difference between average speed and average velocity is explained, with average speed being the total distance divided by time.
For an object moving in a circular path and returning to the starting point, the average speed is the circumference divided by time, but the average velocity is zero due to zero displacement.
The SI unit for both speed and velocity is meters per second.
The example of two cars traveling from city A to city B illustrates the difference between speed and velocity.
Car traveling on route one with a longer distance has a different velocity than the car on route two, despite both covering the same displacement.
The importance of understanding the direction in physics, especially when dealing with vector quantities like displacement and velocity.
The concept of velocity allows for a more precise description of an object's motion compared to speed alone.
The transcript provides a comprehensive explanation of the physical concepts of speed and velocity, suitable for educational purposes.
The use of real-world examples, such as the cities and car routes, helps to contextualize the abstract concepts of speed and velocity.
The transcript emphasizes the need to consider both magnitude and direction when analyzing motion, which is crucial in physics.
The explanation highlights the common misconceptions between speed and velocity and clarifies these concepts for better understanding.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

What is Velocity? - Full Concept of Velocity - Physics | Infinity Learn

Displacement and Velocity - How is it different from Distance and Speed? | Physics

11 - What is Definition of Average Speed & Velocity in Physics? (Speed Formula & Velocity Formula)
Distance, Displacement, Average Speed, Average Velocity - Physics
Velocity and speed: Motion in One Dimension

Distance, Displacement, Speed and Velocity
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: