SPEED, DISTANCE & TIME | GRADE 6
TLDRIn this educational video, students are introduced to the fundamental concepts of calculating speed, distance, and time. The lesson begins with an example of a family's journey from Quezon City to Batangas City, explaining how to find the distance traveled by multiplying speed (60 km/h) by time (2 hours), resulting in 120 kilometers. Subsequent examples illustrate how to calculate distance given speed and time, as well as how to determine speed when distance and time are known. The video also covers the calculation of time taken for a journey by dividing distance by speed. Each concept is clearly explained with step-by-step calculations, using units of measurement such as kilometers and hours. The lesson concludes with a recap of the key learning points, reinforcing the understanding of these essential principles for students.
Takeaways
- 📏 Distance is the total length between two positions and can be measured in kilometers, centimeters, or millimeters.
- ⏱️ Time is the measurement that tells the duration of an event, and its units can be hours, minutes, or seconds.
- 🚗 Speed is a scalar quantity that refers to how fast an object is moving, with units like kilometers per hour or meters per second.
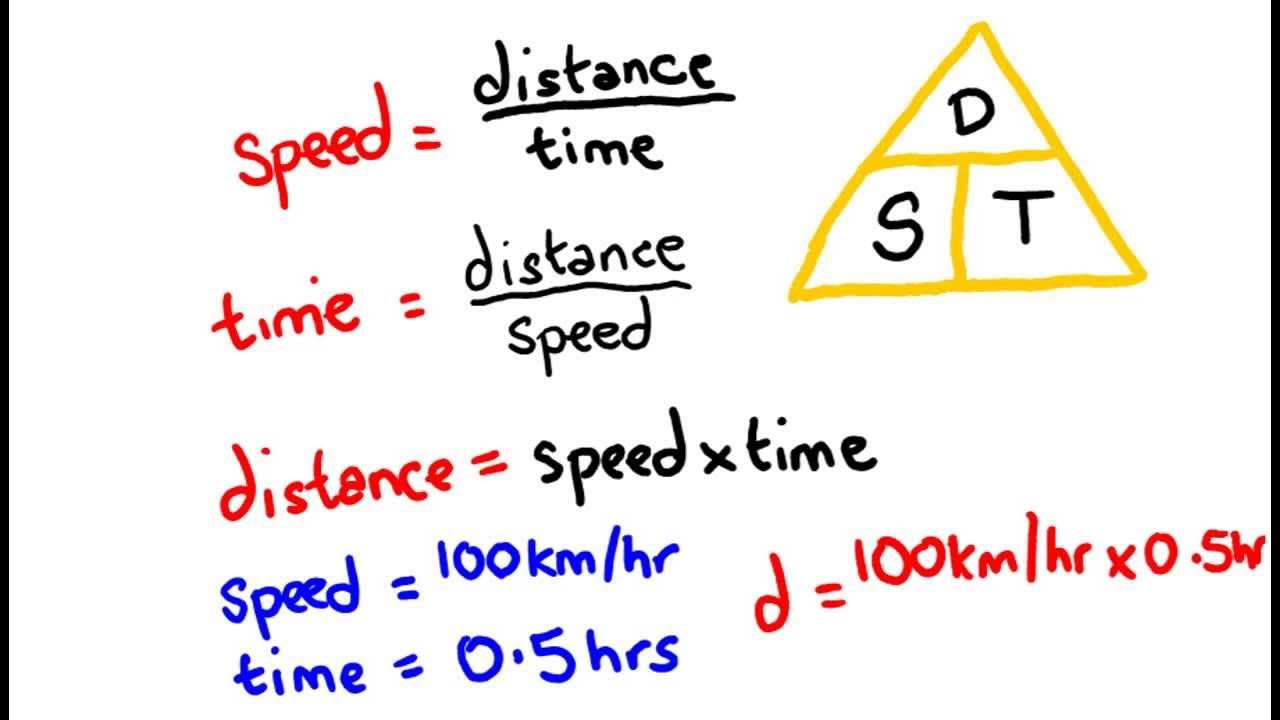
- 🔢 To calculate distance, multiply the speed by the time: Distance = Speed × Time.
- 🔁 To find the speed, divide the distance by the time: Speed = Distance ÷ Time.
- ⏳ To determine the time taken, divide the distance by the speed: Time = Distance ÷ Speed.
- ✖️ When multiplying or dividing units, like kilometers and hours, the units cancel each other out where appropriate, leaving the desired unit.
- 👨👩👧 A family traveled 120 kilometers from Quezon City to Batangas City at an average speed of 60 kilometers per hour for 2 hours.
- 🚘 If you drive for 3 hours at 70 kilometers per hour, you will cover a distance of 210 kilometers.
- 🚗 A car that travels 150 kilometers in three hours has a speed of 50 kilometers per hour.
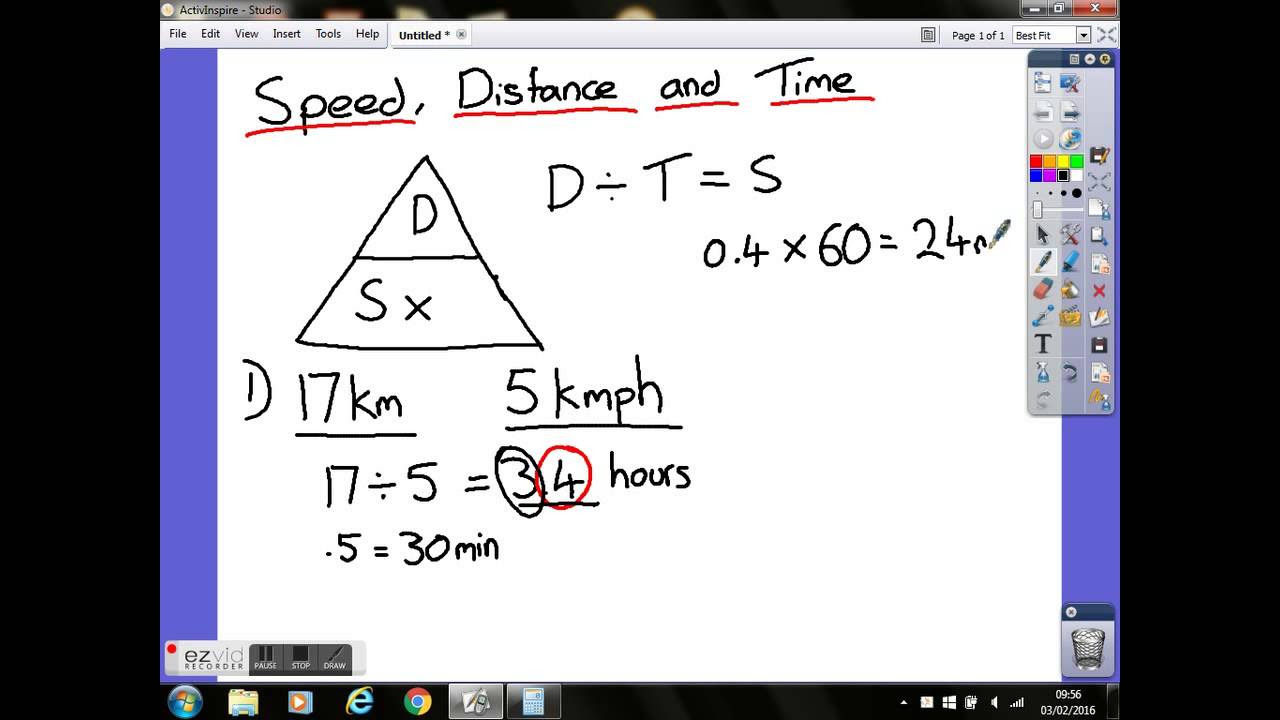
- 🚌 A bus that traveled 252 kilometers at 72 kilometers per hour was on the road for 3.5 hours.
- 🛣️ To travel 180 kilometers at a speed of 45 kilometers per hour, it takes 4 hours.
Q & A
What is the formula to calculate the distance traveled?
-The formula to calculate the distance traveled is Distance = Speed × Time.
How many kilometers did the family travel from Quezon City to Batangas City?
-The family traveled 120 kilometers.
What is the unit of measurement for speed in the given examples?
-The unit of measurement for speed in the given examples is kilometers per hour (km/h).
If a car travels 150 kilometers in three hours, what is the speed of the car?
-The speed of the car is 50 kilometers per hour (km/h).
How do you calculate the speed when given the distance and time?
-To calculate the speed, you divide the distance by the time (Speed = Distance ÷ Time).
What is the time it takes for a bus to travel 252 kilometers at a speed of 72 kilometers per hour?
-The bus traveled for 3.5 hours.
What is the definition of time in the context of motion?
-Time is the measurement that tells the duration of an event or how long it takes for something to occur.
How many hours does it take to travel 180 kilometers at a speed of 45 kilometers per hour?
-It takes 4 hours to travel 180 kilometers at a speed of 45 kilometers per hour.
What is the scalar quantity that refers to how fast an object is moving?
-Speed is the scalar quantity that refers to how fast an object is moving.
What are some common units of measurement for speed?
-Common units of measurement for speed are kilometers per hour (km/h), meters per second (m/s), and centimeters per second (cm/s).
If you are driving for 3 hours at 70 kilometers per hour, how far will you travel?
-You will travel 210 kilometers.
What is the total length between two positions called in the context of motion?
-The total length between two positions is called distance.
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Speed, Distance, and Time Calculations
This paragraph introduces the lesson on calculating speed, distance, and time. The teacher welcomes students to the classroom and explains the concept of distance as the total length between two positions, with units like kilometers, centimeters, or millimeters. The first example involves calculating the distance a family traveled from Quezon City to Batangas City at an average speed of 60 kilometers per hour for two hours. The calculation is done by multiplying speed by time, resulting in a distance of 120 kilometers. The second example asks students to calculate the distance for a 3-hour drive at 70 kilometers per hour, which is 210 kilometers. The paragraph concludes with a problem where a car travels 150 kilometers in three hours, and the students are tasked with finding the car's speed, which is found by dividing distance by time, yielding 50 kilometers per hour.
🚗 Applying Speed, Distance, and Time Formulas
The second paragraph delves deeper into calculating speed, distance, and time with different examples. It begins with a scenario where the speed is given as 70 kilometers per hour, and the students are asked to calculate the distance that would be covered in four hours, which is 280 kilometers. The next problem involves a bus that traveled 252 kilometers at a speed of 72 kilometers per hour, and the students must find out how many hours it traveled. By dividing the distance by the speed, the time is determined to be 3.5 hours. The final example in this paragraph asks for the time it would take to travel 180 kilometers at a speed of 45 kilometers per hour. Again, using the formula for time, which is distance divided by speed, the time is calculated to be four hours. The paragraph concludes with a recap of the concepts learned, emphasizing the importance of understanding speed, distance, and time relationships.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Speed
💡Distance
💡Time
💡Calculation
💡Scalar Quantity
💡Units of Measurement
💡Average Speed
💡Duration
💡Multiplication
💡Division
💡Canceling Units
Highlights
Distance is the total length between two positions, measured in kilometers, centimeters or millimeters.
To calculate distance, multiply speed by time.
A family traveled 120 kilometers from Quezon City to Batangas City at 60 km/h for 2 hours.
Speed is a scalar quantity that indicates how fast an object is moving.
The units of measurement for speed are km/h, m/s, cm/s or mm/s.
To find speed, divide distance by time.
A car travels 50 km/h when covering 150 km in 3 hours.
Time is the measurement of the duration of an event.
The units of measurement for time are hours, minutes or seconds.
To find time, divide distance by speed.
A bus traveled for 3.5 hours when covering 252 km at 72 km/h.
It takes 4 hours to travel 180 km at a speed of 45 km/h.
The formula to calculate distance is speed multiplied by time.
The formula to calculate speed is distance divided by time.
The formula to calculate time is distance divided by speed.
Speed is measured in kilometers per hour (km/h).
Distance can be measured in kilometers (km), centimeters (cm) or millimeters (mm).
Time is measured in hours, minutes or seconds.
The family example demonstrates calculating distance using speed and time.
The car example shows finding speed when distance and time are known.
The bus example illustrates calculating time given distance and speed.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: