UNITS & PHYSICAL QUANTITIES | Physics Animation
TLDRThe video script from 'Easy Engineering' dives into the fundamental concepts of units and physical quantities, which are essential in our daily lives and scientific understanding. It clarifies the distinction between mass, time, and length through common examples, such as weighing 80 kilograms, being 20 minutes early, and measuring a length of 10 meters. The script explains that every physical quantity has a magnitude (numerical value) and a unit, and categorizes physical quantities into base and derived types. Base quantities include length, mass, time, electric current, temperature, amount of substance, and luminous intensity, while derived quantities like area, volume, speed, and acceleration are derived from these base units. The video also highlights the two major unit systems used globally: the metric system (SI units), which is prevalent in the Philippines and many other countries, and the English system, traditionally used in nations that were part of the British Empire. The SI units for the seven base quantities are meter, kilogram, second, ampere, Kelvin, mole, and candela, respectively. The video concludes by encouraging viewers to appreciate the importance of these concepts in their everyday lives.
Takeaways
- 📏 The script discusses units and physical quantities, which are fundamental in engineering and daily life.
- 📊 Physical quantities consist of two parts: magnitude (numerical value) and unit (what the number represents).
- 🌍 Common examples of physical quantities include mass (kilograms), time (minutes), and length (meters).
- 🔍 There are seven base quantities in physics: length, mass, time, electric current, temperature, amount of substance, and luminous intensity.
- 🔑 Derived quantities are calculated from base quantities or their combinations, such as area, volume, speed, and acceleration.
- 🏛️ English units are used in countries that were part of the British Empire, while SI (International System of Units) is used globally, including in the Philippines.
- 📐 The SI units for base quantities are meter (length), kilogram (mass), second (time), ampere (electric current), Kelvin (temperature), mole (amount of substance), and candela (luminous intensity).
- 🌐 Units are essential for standardizing measurements across different countries and facilitating international communication in science and engineering.
- 📈 Understanding the difference between base and derived quantities is crucial for grasping fundamental physical concepts.
- 🕰️ Time is a base quantity that is measured in minutes in the example, highlighting its importance in various contexts.
- 📚 Learning about units and physical quantities helps in developing a deeper appreciation for the role of measurement in science and engineering.
- 🎓 The video is part of an educational series called 'Easy Engineering' aimed at making complex engineering concepts more accessible.
Q & A
What are physical quantities?
-Physical quantities are anything that humans can measure, which have two important parts: their magnitude and unit.
What are the two parts of every physical quantity?
-The two parts of every physical quantity are its magnitude (numerical value) and its unit (measurement standard).
What are the seven base quantities recognized by physics?
-The seven base quantities recognized by physics are length, mass, time, electric current, temperature, amount of substance, and luminous intensity.
How are derived quantities different from base quantities?
-Derived quantities are different from base quantities in that they are derived from base quantities or a combination of base quantities, such as area, volume, speed, acceleration, etc.
What are the two major systems of units used in the world?
-The two major systems of units used in the world are the metric system (SI units) and the English system of units.
Which nations typically use English units?
-English units are typically used in nations that were once part of the British Empire.
What is the SI unit for length?
-The SI unit for length is the metre.
What is the SI unit for mass?
-The SI unit for mass is the kilogram.
What is the SI unit for time?
-The SI unit for time is the second.
What is the SI unit for electric current?
-The SI unit for electric current is the ampere.
What is the SI unit for temperature?
-The SI unit for temperature is the Kelvin.
What is the SI unit for the amount of substance?
-The SI unit for the amount of substance is the mole.
What is the SI unit for luminous intensity?
-The SI unit for luminous intensity is the candela.
Outlines
📏 Understanding Units and Physical Quantities
This paragraph introduces the concept of units and physical quantities, highlighting the importance of both magnitude and unit in measurement. It provides common examples such as weight in kilograms, time in minutes, and length in meters to illustrate these concepts. The paragraph also distinguishes between base quantities, which are fundamental and include length, mass, time, electric current, temperature, amount of substance, and luminous intensity, and derived quantities, which are derived from base quantities. The two major systems of units, SI units and English units, are mentioned, with a note on the Philippines' use of SI units for base quantities.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Units
💡Physical Quantities
💡Magnitude
💡Base Quantities
💡Derived Quantities
💡SI Units
💡English Units
💡Length
💡Mass
💡Time
💡Electric Current
💡Luminous Intensity
Highlights
Units and physical quantities are introduced as key concepts in the field of engineering.
The importance of understanding the difference between mass, time, and length is emphasized.
80 kilograms, 20 minutes, and 10 meters are provided as common examples of physical quantities.
Physical quantities are defined as anything that can be measured by humans.
Every physical quantity consists of a magnitude and a unit.
The distinction between base quantities and derived quantities is explained.
There are seven base quantities recognized in physics: length, mass, time, electric current, temperature, amount of substance, and luminous intensity.
Derived quantities, such as area, volume, speed, and acceleration, are derived from base quantities.
Two major systems of units are used worldwide: the metric system and the English system.
English units are used in nations that were once part of the British Empire.
In the Philippines, the SI (International System of Units) is used.
The SI unit for length is the meter, for mass is the kilogram, and for time is the second.
Electric current is measured in amperes, temperature in Kelvin, amount of substance in moles, and luminous intensity in candelas in the SI system.
The video aims to educate viewers on the fundamental concepts of units and physical quantities.
The presentation is designed to be accessible, using everyday examples to illustrate the concepts.
The educational content is delivered in an engaging manner with the use of music.
Easy Engineering is the source of this informative content on units and physical quantities.
The video concludes with an encouragement for viewers to apply their newfound knowledge.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

SI Base Units and Derived Units - Physics and Chemistry
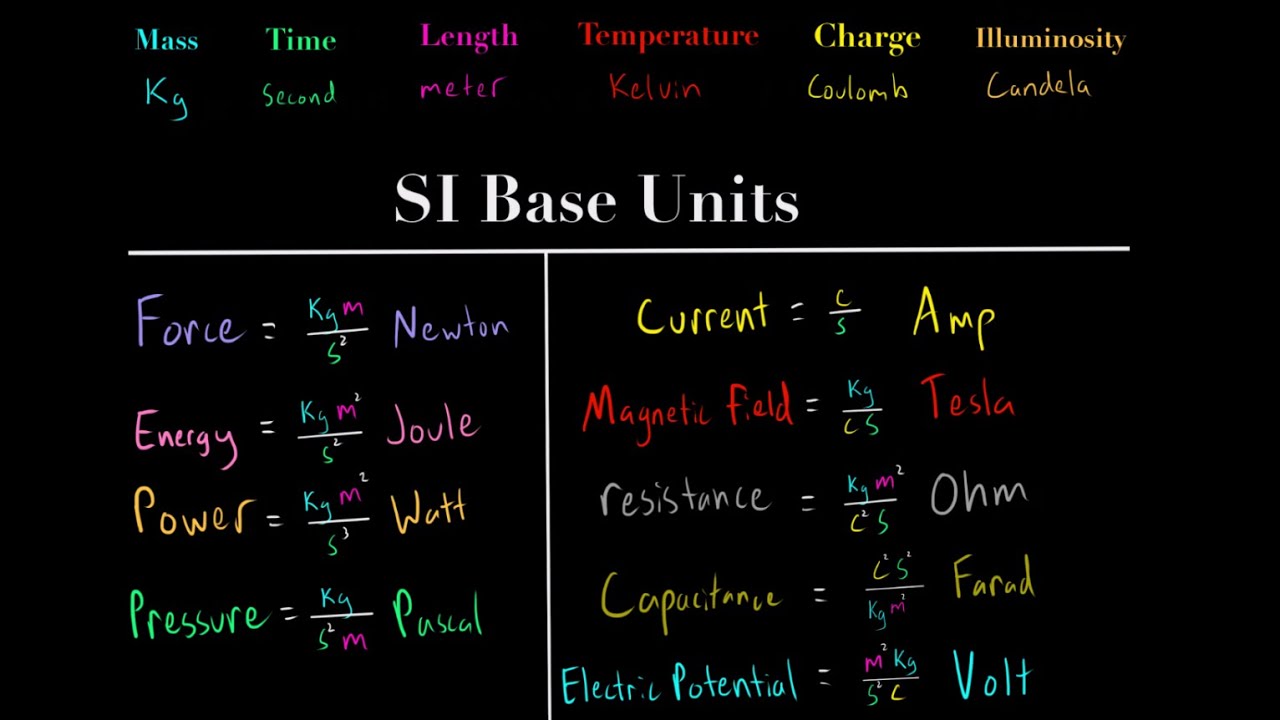
Understanding the SI Units (meters, seconds, kg, kelvin, coulomb, candela) MCAT Physics Chemistry
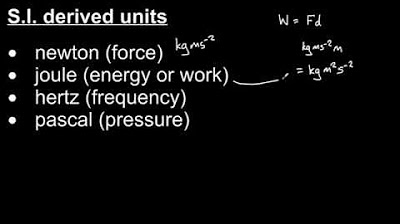
S.I. base units and derived units

How to Find Dimensional Formula ? Dimensional Formula Trick

College Physics 1: Lecture 4 - Units and Unit Conversions
SI Units Quiz | 40 Questions | International System of Units (SI) | Physics Quiz
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: