Torque = Force Times Lever Arm | Physics with Professor Matt Anderson | M12-06
TLDRIn this engaging lecture, the concept of torque is explored through a simple yet effective formula: torque equals force times lever arm. The challenge lies in understanding and determining the lever arm, which is the shortest distance from the line of force to the axis of rotation. The process involves extending the line of force and identifying the perpendicular distance to the axis of rotation as the lever arm. This is then used to calculate torque, with the formula F * r * sin(φ), where F is the force, r is the distance, and φ is the angle between the force and the lever arm. The lecture also touches on the units of torque, mentioning newton meters as the SI unit and foot pounds as the English unit, and explains the practical application of torque through the use of a torque wrench in automotive maintenance.
Takeaways
- 🔧 Torque is a measure of the force that can cause an object to rotate around an axis and can be thought of as force times lever arm.
- 📐 The lever arm is the shortest distance from the line of force to the axis of rotation, which is often found by extending the force line and drawing a perpendicular to the axis of rotation.
- 📏 To calculate the lever arm, you can use the right triangle formed where the sine of the angle (phi) between the force and the lever arm is equal to the lever arm divided by the distance (r).
- 🛠️ The formula for torque is given by the product of the force (in newtons) and the lever arm (in meters), resulting in the unit of newton-meters (Nm).
- 🇺🇸 In the imperial system, torque is measured in foot-pounds, which is the equivalent unit for torque when using feet and pounds.
- 🔩 A torque wrench is a tool used to apply a specific amount of torque to fasten or loosen a bolt, preventing over-tightening which can cause damage.
- 🚗 Torque is a concept that is applicable in various real-world scenarios such as working on a car or bicycle, and even simple tasks like opening a door.
- 📐 The sine function is used to calculate the lever arm when you know the angle and the hypotenuse of the right triangle formed by the force vector and the lever arm.
- 🤔 Understanding torque is important for mechanical applications where precise amounts of force are needed to avoid damage or ensure safety.
- 🛠️ A torque wrench operates by having a release mechanism that prevents further tightening once a set torque value is reached, often indicated by a clicking sound.
- 📐 The concept of torque is closely related to the cross product in physics, which was mentioned earlier in the discussion before introducing the force times lever arm model.
Q & A
What is torque and how does it relate to force and lever arm?
-Torque is a measure of the force that can cause an object to rotate about an axis. It is calculated as the product of the force applied and the lever arm, which is the perpendicular distance from the line of action of the force to the axis of rotation.
How is the lever arm determined when calculating torque?
-The lever arm is determined by extending the line of force and finding the shortest distance from that line to the axis of rotation. This is often the line perpendicular to the force line that passes through the axis of rotation.
What is the formula for calculating torque using the lever arm?
-The formula for calculating torque (τ) using the lever arm (l) is τ = F × l, where F is the magnitude of the force applied.
How does the concept of torque apply to everyday situations like opening a door?
-When opening a door, the force you apply away from the hinge (axis of rotation) creates a torque that tends to rotate the door. The further you apply the force from the hinge (longer lever arm), the less force is needed to achieve the same amount of torque.
What are the units of torque in the International System of Units (SI) and English System?
-In the SI system, torque is measured in newton meters (Nm). In the English system, it is measured in foot pounds (ft-lb).
How does a torque wrench work and what is its purpose?
-A torque wrench is a tool that allows you to apply a specific amount of torque to an object, like a bolt. It has a release mechanism that prevents further tightening once the set torque value is reached. Its purpose is to ensure that fasteners are tightened to the correct specification without over-torquing, which can damage the fastener or the object it is securing.
Why is it important to use the correct amount of torque when working with fasteners?
-Using the correct amount of torque is important to ensure that fasteners are secure without causing damage such as stripping the threads or breaking the fastener. It is crucial for maintaining the integrity and safety of the mechanical assembly.
What is the relationship between the angle of force application and the lever arm?
-The angle of force application in relation to the axis of rotation determines the component of the force that contributes to torque. The lever arm is the perpendicular distance from the line of action of the force to the axis of rotation, and it is maximized when the force is applied at a right angle to the axis.
Can you explain the right triangle concept used to find the lever arm in the script?
-In the script, a right triangle is formed by the force line, the lever arm, and the line connecting the axis of rotation to the point where the force is applied. The lever arm is the opposite side of the angle (phi), the hypotenuse is the distance from the axis to the point of force application (r), and the sine of the angle (phi) gives the ratio of the lever arm to the hypotenuse, which is used to calculate the lever arm as r * sin(phi).
What is the significance of the sine function in calculating the lever arm?
-The sine function is used to calculate the lever arm because it gives the ratio of the opposite side (lever arm) to the hypotenuse (distance r) in a right triangle. This is directly applicable in finding the perpendicular distance from the line of force to the axis of rotation, which is the definition of the lever arm.
How does the method of calculating torque using the lever arm compare to using the cross product?
-Both methods ultimately yield the same result for torque. The cross product method involves calculating the vector product of the force vector and the position vector, which is more suitable for situations involving multiple dimensions or complex geometries. The lever arm method, on the other hand, is a scalar product that simplifies the calculation when the direction of the force is known and the geometry is straightforward.
Why is it necessary to consider the direction of the force when calculating torque?
-The direction of the force is crucial because torque is a vector quantity that depends on the direction of the force relative to the axis of rotation. The torque will have a different magnitude and direction if the force is applied in a different direction, even if the magnitude of the force and the distance to the axis of rotation remain the same.
Outlines
🔧 Understanding Torque and Lever Arm
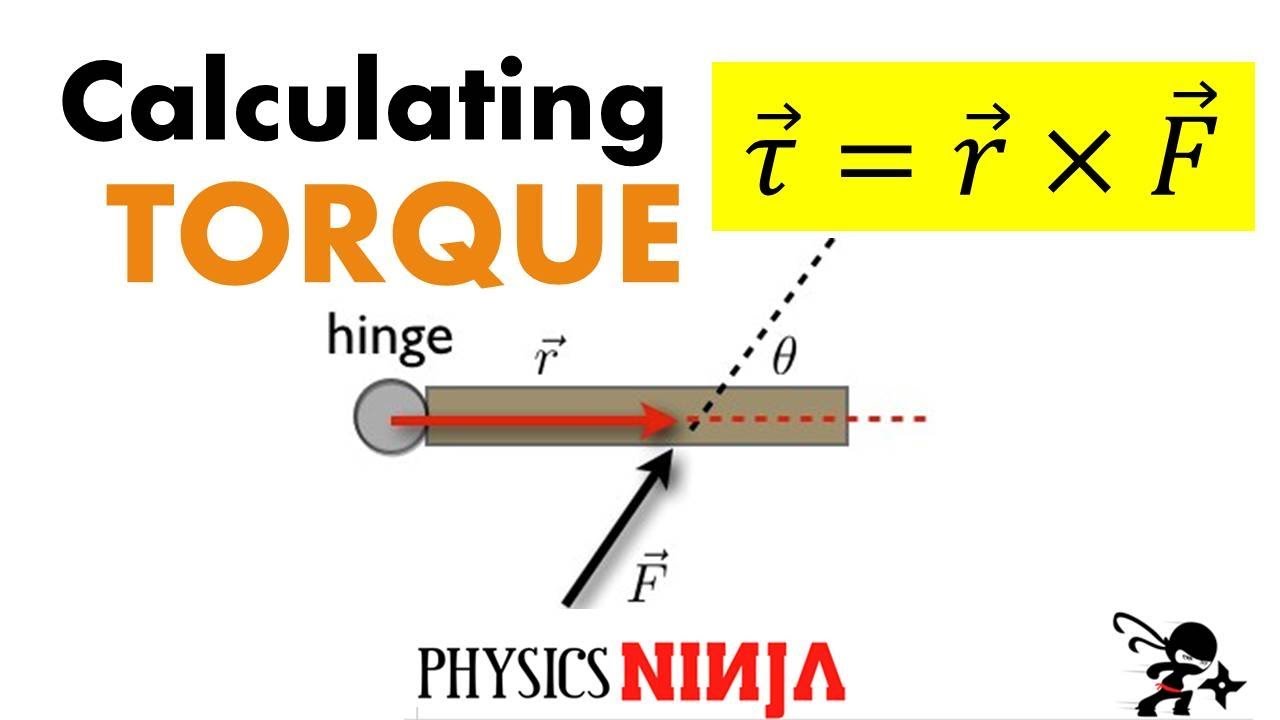
In the first paragraph, the concept of torque is introduced and explained in relation to the cross product. The lecturer emphasizes an alternative way to comprehend torque, which is as the product of force and the lever arm. The challenge lies in identifying the lever arm, which is defined as the shortest distance from the line of force to the axis of rotation. The lecturer uses the example of opening a door to illustrate the process of calculating torque using the lever arm. The line of force is extended, and the shortest distance to the axis of rotation, which is the hinge in this case, is identified as the lever arm. The lever arm is then calculated using trigonometric principles, specifically the sine of the angle formed between the force line and the axis of rotation, resulting in the lever arm being equal to r times the sine of the angle (r * sin(phi)). The torque is finally calculated as the product of the force and the lever arm.
📏 Units of Torque and Practical Applications
The second paragraph delves into the units used to measure torque. The lecturer clarifies that force is measured in newtons, and since the lever arm is a distance, it is measured in meters. Consequently, the unit of torque is the newton meter in SI units, and in the English system, it is measured in foot pounds. The practical application of torque is discussed using the example of a torque wrench, which is used to apply a specific amount of torque when fastening bolts in a car. The torque wrench has a release mechanism that prevents over-tightening, which can lead to damage such as snapped bolt heads or stripped threads. The importance of using the correct amount of torque is emphasized, and the operation of a torque wrench is explained, highlighting its role in ensuring that the applied torque does not exceed the recommended limit.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Torque
💡Cross Product
💡Lever Arm
💡Force
💡Axis of Rotation
💡Line of Action
💡Right Triangle
💡Trigonometric Functions
💡Newton Meter
💡Foot Pounds
💡Torque Wrench
Highlights
Torque can be thought of as force times lever arm, a simple yet effective concept.
Determining the lever arm can be challenging, but there's a prescription for finding it.
The lever arm is the shortest distance from the line of force to the axis of rotation.
Some textbooks refer to the line of force as the line of action, indicating the direction of the force.
To calculate torque, extend the line of force, find the axis of rotation, then draw the lever arm perpendicular to the force line.
The axis of rotation in the door example is the hinge.
The shortest distance from the line of force to the axis of rotation is always a straight line perpendicular to the force line.
The lever arm can be calculated using the right triangle formed, where the sine of the angle is the lever arm divided by the hypotenuse (distance r).
The lever arm is given by r * sine(phi), where phi is the angle between the force and the lever arm.
Torque is calculated as the force (in newtons) times the lever arm (in meters), resulting in newton-meters.
In English units, torque is measured in foot-pounds, commonly used with torque wrenches.
A torque wrench applies a specific amount of torque to avoid over-tightening and potential damage like snapped bolts or stripped threads.
The torque wrench has a release mechanism that clicks once the desired torque is reached.
Understanding torque is important for practical applications like working on a car or bicycle.
The concept of torque as force times lever arm is fundamental and applicable in various real-world scenarios.
The lecture provides a clear, step-by-step approach to visualizing and calculating torque.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: