What is Density? How to Calculate Density? - [1-1-5]
TLDRThe video script provides an in-depth explanation of the concept of density, emphasizing its importance in understanding the physical properties of materials. It defines density as mass per unit volume and illustrates how to calculate it using various units of measurement. The script also offers examples and problems to solidify the concept, highlighting the intrinsic nature of density as a property that applies to every part of a substance.
Takeaways
- 📚 Density is a fundamental physical property that describes the mass of a substance per unit volume, and it's crucial in understanding the characteristics of materials.
- 🔍 The concept of density bridges everyday language and scientific terminology, often associated with how compact or heavy a material feels.
- 📈 Density is calculated using the formula: Density = Mass / Volume, which provides a measure of how much mass is contained in a given volume.
- 🖥️ Mass and volume are both measurable quantities, with mass typically expressed in grams or kilograms and volume in cubic meters, cubic centimeters, or liters.
- 🔽 Units of density are expressed as mass per unit volume, such as kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) or grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³).
- 💡 Understanding density is essential in chemistry as it helps to characterize and compare different substances, regardless of their size or amount.
- 📊 Density can be used to distinguish between different materials; for example, cotton has a lower density than lead, meaning less mass for the same volume.
- 📝 When calculating density, it's important to ensure that the units of mass and volume are consistent and that the final result includes the correct unit of density.
- 🌟 A substance's density is an intrinsic property, meaning it applies to every part of the substance and is not affected by the quantity or size of the sample.
- 🚀 Practical applications of density include identifying unknown substances, determining the purity of materials, and understanding the behavior of substances under various conditions.
Q & A
What is density and why is it important in the study of chemistry?
-Density is a physical property that represents the mass per unit volume of a substance. It is important in chemistry because it helps to characterize and compare different materials and their mass in relation to their volume, which is crucial for understanding their behavior and properties.
How is the term 'density' used in everyday language?
-In everyday language, 'density' is often used to describe how closely packed or 'heavy' something feels. For example, something described as 'dense' might be hard to understand or difficult to get through, like a dense forest or a dense argument.
What is the formula for calculating density?
-The formula for calculating density is Density = Mass / Volume. By dividing the mass of an object by its volume, you get the density value, which tells you how much mass is contained within a given volume.
What are some units used to measure mass and volume, and how do they relate to density?
-Units for mass include grams (g), kilograms (kg), and units for volume include cubic meters (m³), cubic centimeters (cm³), and milliliters (mL). These units relate to density as you need to measure both mass and volume accurately to calculate the density of a substance. For instance, density can be expressed in units like kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) or grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³).
Why is it necessary to compare mass and volume when determining the properties of a substance?
-Comparing mass and volume is necessary because it allows us to understand how much mass a substance has relative to its size. This is important as two substances can have the same mass but different volumes, or vice versa, leading to different densities. The density can indicate various properties and behaviors of the material, such as compactness, weight, and sometimes even its strength or structural integrity.
What is the significance of understanding density in the context of chemistry?
-Understanding density in chemistry is crucial as it helps in identifying and classifying substances, predicting behavior in various conditions, and in calculations related to reactions and mixtures. It is also an intrinsic property that can be used to distinguish between different materials and to determine purity in substances.
How does the concept of density apply to a substance regardless of its quantity?
-Density is an intrinsic property that applies to a substance no matter the quantity. Whether you have a small amount or a large quantity of a material, the density remains constant because it is a ratio of mass to volume. This means that if you take any volume of a substance, the mass of that volume will always be directly proportional to its density.
What is the relationship between mass, volume, and density for a rectangular block of lead?
-For a rectangular block of lead, the density can be calculated by dividing the total mass of the block by its total volume. The volume is calculated by multiplying the length, width, and height of the block, and the resulting density will be a constant value that represents the mass per unit volume of lead.
How can you determine the mass of a substance if you know its density and volume?
-If you know the density of a substance and the volume it occupies, you can determine the mass by multiplying the density (mass per unit volume) by the volume. The result will give you the total mass of that volume of substance.
What happens to the density of a substance if its mass increases but its volume remains the same?
-If the mass of a substance increases while its volume remains constant, the density of the substance will also increase. This is because density is the ratio of mass to volume, so an increase in mass with no change in volume results in a higher density value.
How can you calculate the volume of a substance with irregular shape?
-Calculating the volume of a substance with an irregular shape can be challenging but can be done using methods like water displacement (for solids) or geometrical approximation (by dividing the object into recognizable shapes and calculating the volume of each shape, then adding them together).
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Density
This paragraph introduces the concept of density as a fundamental physical property of matter. It emphasizes the importance of understanding density when studying different elements and compounds. The tutor, Jason, explains that density is a term used in everyday language and often relates to how heavy or compact something is. He uses examples like lead being dense and feathers being light to illustrate this concept. The tutor then transitions into a more scientific explanation, discussing how mass and volume relate to density. He explains that everything has mass, which can be measured, and everything also has a volume, which can be calculated. The density of a substance is defined as its mass divided by its volume, giving a measure of how much mass is contained within a certain volume. The tutor prepares the audience to delve deeper into the concept by discussing the significance of understanding density beyond just mass.
📈 Calculating Density
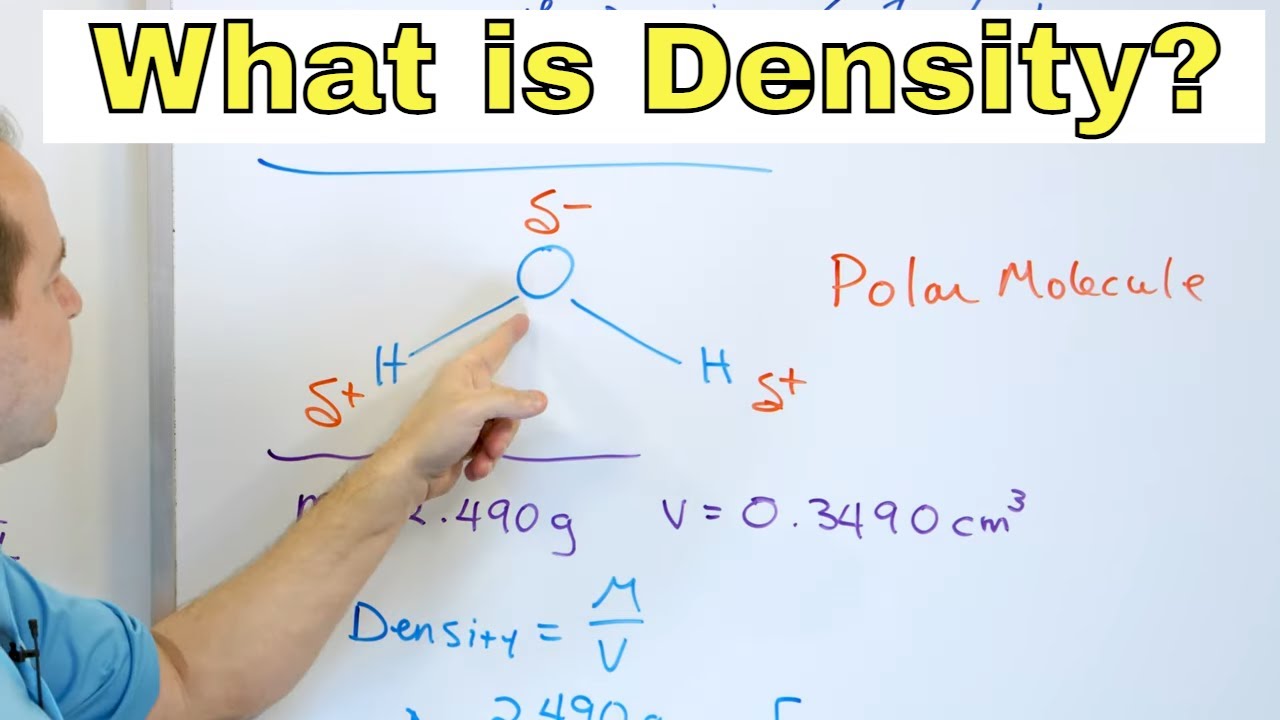
In this paragraph, the tutor explains the process of calculating density by dividing the mass of an object by its volume. He provides various units for measuring mass and volume, such as kilograms, grams, cubic meters, cubic centimeters, and milliliters. The tutor emphasizes the importance of using the correct units when calculating density and understanding the concept of 'per' in unit measurements, such as kilograms per cubic meter. He also explains the concept of cubic measurement, using a cube as a visual aid to demonstrate how volume is calculated. The tutor reinforces the idea that density is a ratio of mass to volume and that it is a useful property for comparing different materials, regardless of their size or quantity.
🔍 Comparing Densities of Different Materials
The tutor uses a comparative approach to illustrate the concept of density further. He contrasts cotton and lead, two materials with vastly different densities, even when comparing equal volumes of each. The tutor explains that despite the same volume, lead will have a greater mass and, consequently, a higher density than cotton. He uses this example to demonstrate that density can be used to differentiate between materials based on their mass-to-volume ratio. The tutor also introduces the concept of density tables and how they can be referenced to understand the densities of various substances. Additionally, he mentions the equivalence of one milliliter to one cubic centimeter, which is a crucial piece of information for understanding and converting volume units.
🧪 Practical Application: Liquid Bromine Density
The tutor presents a practical problem involving the calculation of the density of liquid bromine. Given the mass and volume of the bromine sample, the tutor guides the audience through the process of dividing the mass by the volume to find the density. He emphasizes the importance of including units in the final answer and explains that the calculated density represents a consistent property of the substance. The tutor uses this example to demonstrate how density can be used to identify and compare different chemicals or liquids.
🔩 Metal Chips Density Calculation
This paragraph involves calculating the density of metal chips. The tutor provides the mass of the metal chips along with the mass of a piece of paper they are placed on. He explains how to isolate the mass of the metal chips by subtracting the mass of the paper from the total mass. Once the mass of the metal is determined, the tutor guides the audience through calculating the volume of the metal chips. He uses the given dimensions to calculate the volume and then the density by dividing the mass by the volume. The tutor emphasizes that the calculated density is an intrinsic property of the metal and will be consistent regardless of the amount of metal sampled.
📏 Rectangular Block of Lead Density
The tutor tackles another practical problem involving a rectangular block of lead with given dimensions and mass. He explains how to calculate the volume of the block using its length, width, and height. After determining the volume, the tutor shows how to calculate the density by dividing the mass of the lead block by its volume. The resulting density value represents the mass of lead per cubic centimeter of volume. The tutor reiterates that this value is a characteristic property of the lead and will be the same for any volume of lead measured.
🎓 Conclusion and Importance of Understanding Density
In the concluding paragraph, the tutor summarizes the key points discussed about density. He stresses the importance of understanding the terminology and concepts related to density for success in chemistry. The tutor reflects on the practical applications and examples discussed, reinforcing the idea that density is a fundamental property of materials that can be used for identification and comparison. He encourages the audience to apply the knowledge gained in their studies and daily life, emphasizing that a solid understanding of density will be beneficial for academic success.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Density
💡Mass
💡Volume
💡Physical Property
💡Chemical Substances
💡Cubic Centimeter
💡Measurement
💡Intrinsic Property
💡Comparative Analysis
💡Units of Measurement
Highlights
Density is an important physical property of materials.
Density is a concept that comes up frequently when studying elements and compounds.
In everyday language, something 'dense' is often thought of as being hard to understand or heavy.
Density is defined as mass per unit volume, or mass divided by volume.
Mass and volume are both measurable properties that are essential to calculating density.
Different units of measurement can be used for mass and volume, such as kilograms, grams, cubic meters, cubic centimeters, etc.
Density allows for the comparison of two objects by equalizing the scale and comparing the same physical volume.
The units of density are typically written as mass per unit volume, such as kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³).
One milliliter is exactly equal to one cubic centimeter, a useful equivalence for volume measurements.
The density of a substance is an intrinsic property and is consistent regardless of the amount of the substance.
Calculating density involves dividing the mass of a substance by its volume to find mass per unit volume.
Density can be used to compare the mass of different substances for the same volume.
The density of a substance can be found in reference materials such as chemistry textbooks or tables of densities.
Understanding density is crucial for success in chemistry and related fields.
Practicing problems involving density helps to solidify understanding of the concept and its application.
Density is a fundamental concept that is applicable to a wide range of materials and scientific disciplines.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: