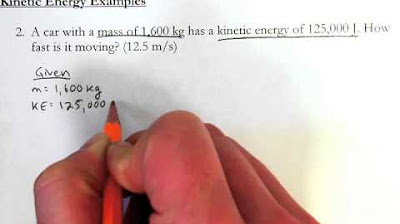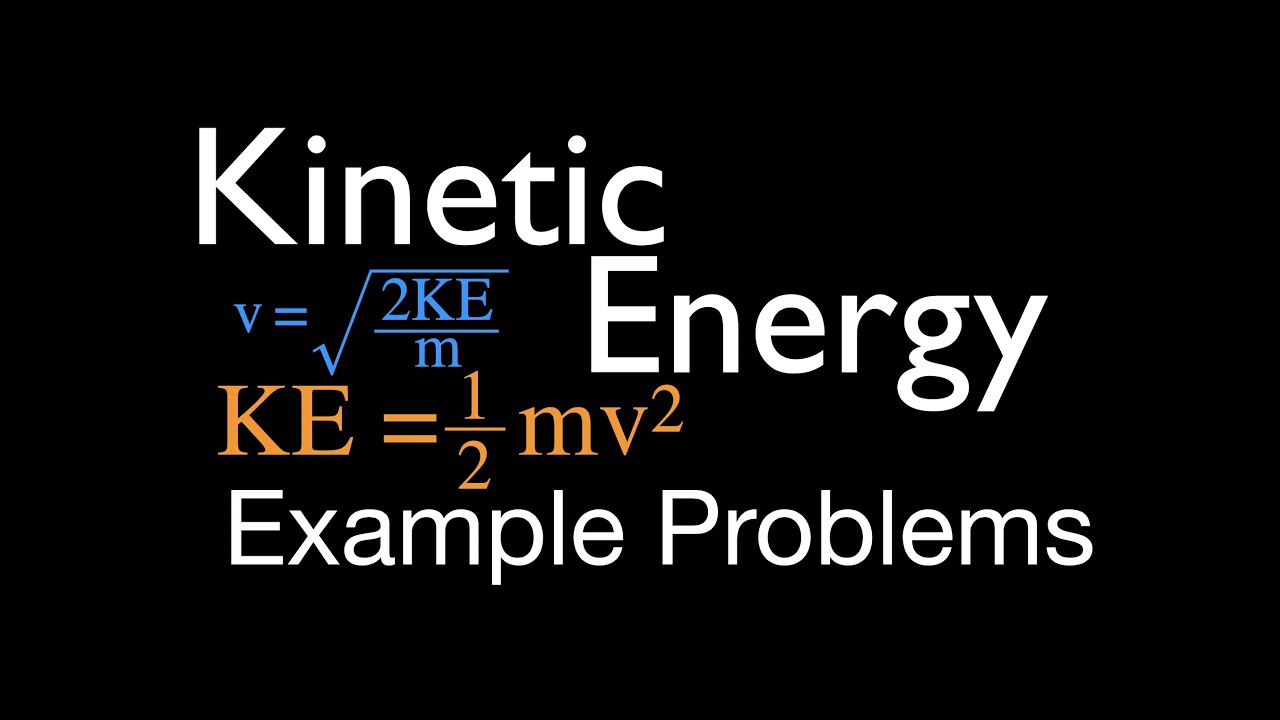Solving Kinetic Energy Sample Problem with Mrs. Aki
TLDRIn this educational video, Mrs. Aki explains the concept of kinetic energy using the equation KE = 1/2 mv^2, where m is mass and v is velocity. She demonstrates how to calculate the kinetic energy of a 45 kg object moving at 13 m/s, emphasizing the importance of unit consistency and the final result in joules. The step-by-step breakdown helps viewers understand the process and the significance of units in physics problems.
Takeaways
- 📚 The kinetic energy (KE) equation is KE = 1/2 * m * v^2, where m is the mass of the object and v is its velocity.
- 🧮 When calculating kinetic energy, it's important to square the velocity (speed without direction) to find v^2.
- 📝 Always read the problem carefully to understand what is given and what is being asked for.
- 🔢 For the given example, the mass (m) is 45 kg and the velocity (v) is 13 m/s.
- 💡 Substitute the given values into the equation to find the kinetic energy.
- 📊 Squaring the velocity (13 m/s) gives 169 m^2/s^2.
- 🧐 Multiply the squared velocity by the mass to get the energy in kilogram meter squared per second squared (kg*m^2/s^2).
- 🔗 The unit kg*m^2/s^2 is equivalent to joules (J), which is the unit of energy.
- 📨 When solving, keep track of units to ensure the final answer is in the correct unit for the quantity being solved.
- 📌 After calculating, divide by 2 to get the final kinetic energy value, as the equation includes a 1/2 factor.
- 🎯 The final answer for the example is 3802.5 joules, which is the kinetic energy of a 45 kg object moving at 13 m/s.
- 📋 Always include the unit in the final answer to clearly indicate the quantity being solved for.
Q & A
What is the kinetic energy equation mentioned in the transcript?
-The kinetic energy equation mentioned is KE = 1/2 mv^2, where KE represents kinetic energy, m is the mass of the object, and v is the velocity of the object.
What does 'm' stand for in the kinetic energy equation?
-In the kinetic energy equation, 'm' stands for the mass of the object.
What does 'v' represent in the kinetic energy equation?
-In the kinetic energy equation, 'v' represents the velocity of the object.
What is the significance of squaring the velocity in the kinetic energy equation?
-Squaring the velocity in the kinetic energy equation means multiplying the velocity by itself, which has the effect of making the kinetic energy dependent on the square of the velocity, thus significantly increasing with greater speeds.
How much is the kinetic energy of a 45 kilogram object moving at 13 meters per second?
-The kinetic energy of a 45 kilogram object moving at 13 meters per second is 3802.5 joules.
What is the importance of reading a problem statement multiple times?
-Reading a problem statement multiple times is important to ensure you understand what information is given and what you are being asked to find or prove.
Why is it necessary to keep track of units when solving physics problems?
-Keeping track of units is necessary in physics problems to ensure the accuracy of the calculations and to provide context for the result. Units also help in verifying that the final answer is dimensionally correct.
What is the unit of energy?
-The unit of energy is the joule (J).
How can you verify the correctness of an answer in a physics problem?
-You can verify the correctness of an answer in a physics problem by checking the calculations, ensuring the units are consistent and correct, and making sure the result makes sense in the context of the problem.
What is the final step in solving the given problem about kinetic energy?
-The final step in solving the given problem is to divide the product of mass (45 kg) and the squared velocity (169 m^2/s^2) by 2, which results in the kinetic energy value of 3802.5 joules.
How does the concept of kinetic energy relate to real-world scenarios?
-The concept of kinetic energy is relevant in real-world scenarios such as calculating the energy needed to move vehicles, understanding the impact of collisions in sports or car accidents, and designing safety features in various applications.
Outlines
📘 Introduction to Kinetic Energy Problem Solving
This paragraph introduces the concept of problem-solving related to kinetic energy. It explains the kinetic energy equation (KE = 1/2 mv^2), where 'm' represents the mass of an object and 'v' is its velocity. The paragraph emphasizes the importance of understanding the given values and the question being asked. It sets the stage for solving the first problem, which involves calculating the kinetic energy of a 45 kg object moving at 13 meters per second.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Kinetic Energy
💡Mass
💡Velocity
💡Equation
💡Substitute
💡Squaring
💡Units
💡Joules
💡Direction
💡Problem Solving
💡Calculator
Highlights
Introduction to kinetic energy and its equation.
Explanation of the kinetic energy equation: KE = (1/2)mv^2.
Identification of 'm' as the mass of the object and 'v' as its velocity.
Clarification on velocity being speed without direction.
The importance of reading and understanding the problem statement.
Given problem: calculating the kinetic energy of a 45 kg object moving at 13 m/s.
Substitution of given values into the kinetic energy equation.
Emphasis on squaring the velocity (13 m/s) to find its square.
Calculation of the squared velocity: 13 * 13 = 169 m^2/s^2.
Use of the equation to find the kinetic energy with given mass and squared velocity.
Result of the calculation: 45 * 169 = 7655 kg m^2/s^2.
Conversion of units from kg m^2/s^2 to joules (J).
Final answer: The kinetic energy is 3802.5 J.
The necessity of including units in the final answer for clarity and correctness.
The practical application of this concept in physics education.
The method's potential for improving problem-solving skills in students.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: