Learn Metric Units & Unit Conversions (Meters, Liters, Grams, & more) - [5-8-1]
TLDRThis lesson introduces the metric system's unit conversions, focusing on length, mass, and volume. It emphasizes the simplicity of metric units based on powers of ten, which makes calculations easier across various scientific fields. The instructor presents a method for conversions using a chart and explains how to handle prefixes like kilo, centi, and milli, providing examples for converting grams to milligrams, liters to kiloliters, and centimeters to millimeters. The lesson stresses the importance of understanding unit conversions for future studies in math, science, and engineering.
Takeaways
- 📏 The metric system is fundamental for various fields such as physics, chemistry, math, and engineering due to its simplicity and ease of use in unit conversions.
- 🔢 The metric system is based on powers of ten, making conversions straightforward and involving nice round numbers, unlike the US or British systems which have less intuitive values.
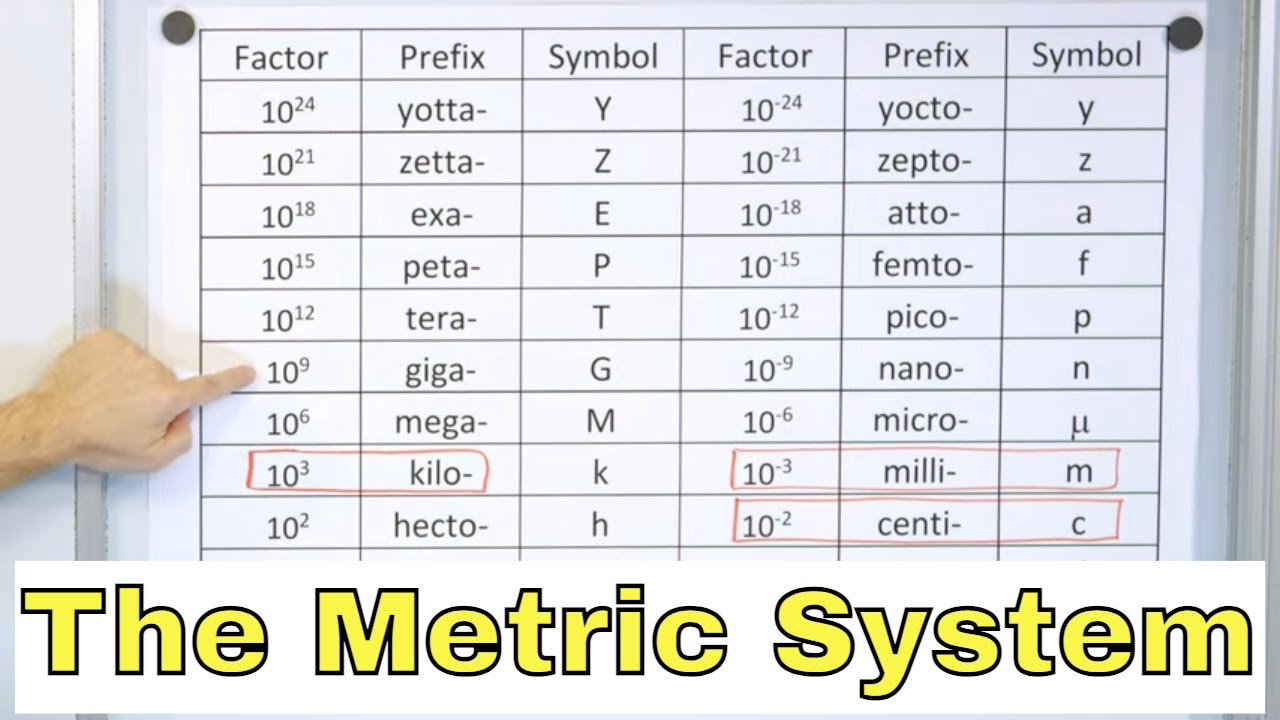
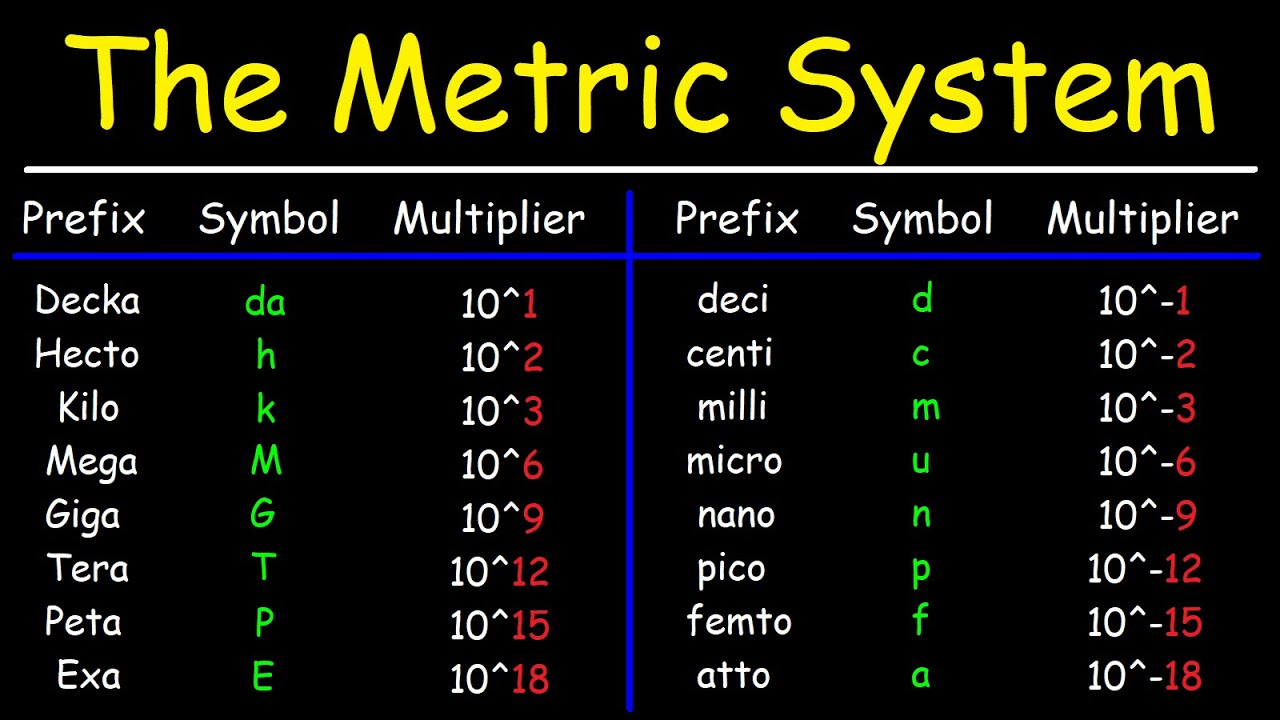
- 📐 The basic unit of length in the metric system is the meter, with common prefixes like kilo (1000x), centi (1/100), and milli (1/1000) to denote larger or smaller units.
- 📈 The basic unit of mass is the gram, and mass is different from weight, remaining constant regardless of the gravitational force on different celestial bodies.
- 📊 The basic unit of volume is the liter, with subunits like milliliter and kiloliter following the same power of ten convention as other metric units.
- 🔄 Unit conversions in the metric system involve using conversion factors, which are ratios of the units, such as 1 gram being equivalent to 1000 milligrams.
- ✍️ When converting units, set up a conversion factor by placing the known unit on top and the desired unit on the bottom, ensuring they cancel each other out, leaving the target unit.
- 📝 Multiply the given value by the conversion factor to find the equivalent in the target unit, and remember to add trailing zeros when dealing with powers of ten.
- 💡 It's crucial to practice unit conversions as they are widely used in scientific calculations and problem-solving.
- 🌐 The metric system's universal acceptance in scientific communities makes it an essential tool for clear and consistent communication of measurements and data.
- 📚 Understanding and mastering the metric system's unit conversions is a foundational skill that supports learning and application in advanced scientific and technical subjects.
Q & A
What is the basic unit of length in the metric system?
-The basic unit of length in the metric system is the meter.
What does the prefix 'kilo' represent in the metric system?
-The prefix 'kilo' in the metric system represents 1,000 times larger than the base unit.
What is the basic unit of mass in the metric system?
-The basic unit of mass in the metric system is the gram.
How many milligrams are there in 5 grams?
-There are 5,000 milligrams in 5 grams.
What is the relationship between a kilogram and a gram?
-One kilogram is equal to 1,000 grams.
How many liters are there in 6,000 kiloliters?
-There are 6,000,000 liters in 6,000 kiloliters.
What is the basic unit of volume in the metric system?
-The basic unit of volume in the metric system is the liter.
How many milliliters are there in one centimeter?
-There are 10 milliliters in one centimeter.
What is the conversion factor between centigrams and grams?
-One gram is equal to 100 centigrams.
How many milliliters are there in 51,000 milliliters?
-51,000 milliliters is equal to 51 liters.
How many centigrams are there in 19 kilograms?
-There are 1,900,000 centigrams in 19 kilograms.
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Metric Unit Conversions
The paragraph introduces the concept of metric unit conversions, emphasizing the importance of understanding the metric system for various scientific and engineering fields. It outlines the plan to review the metric system, focusing on units of length, mass, and volume, and to teach a method for conversions using a unit conversion table. The paragraph also highlights the simplicity of metric units due to their base-10 nature, contrasting with other measurement systems.
📏 Understanding Length Units and Prefixes
This section delves into the specifics of length units within the metric system, starting with the meter as the base unit. It explains the use of prefixes such as 'kilo' for kilometers and 'centi' for centimeters, illustrating how they relate to the base unit through powers of ten. The paragraph clarifies the difference between mass and weight, using the example of a paper clip's mass remaining constant across different gravitational environments.
📐 Converting Mass Units and Problem Solving
The paragraph focuses on mass units in the metric system, defining the gram as the base unit and explaining the conversion between grams and milligrams. It introduces a method for solving unit conversion problems through the use of conversion factors and demonstrates how to convert 5 grams to milligrams, emphasizing the role of multiplication and division by powers of ten in simplifying the process.
📏 Advanced Length Unit Conversions
This part continues the discussion on length units, specifically addressing the conversion between centimeters and millimeters. It reinforces the concept of using conversion factors and demonstrates how to perform multi-step conversions when a direct conversion is not available. The example given shows how to convert one centimeter to millimeters, explaining the process of canceling out units and simplifying the calculation.
📏 Further Exploration of Length Unit Conversions
The paragraph expands on the method of converting between different length units, particularly focusing on the conversion from milliliters to liters and then to kiloliters. It provides a step-by-step guide on how to use the conversion factor chart effectively and emphasizes the ease of canceling zeros in calculations involving powers of ten. The explanation includes an example of converting 6,000 liters to kiloliters.
📏 Complex Conversions and Zero Cancellation
This section discusses the technique of canceling zeros in unit conversions, especially when dealing with large numbers. It explains how to simplify the process by canceling zeros during division and provides an example of converting 42,000 millimeters to meters. The paragraph also touches on the concept of converting units in multiple steps, as seen in the example of converting 800 centigrams to milligrams.
📏 Final Conversion Examples and Practice
The paragraph concludes the lesson with additional examples of unit conversions, including converting 51,000 milliliters to liters and 19 kilograms to centigrams. It reiterates the importance of using the correct conversion factors and the method of canceling units to arrive at the correct answer. The section emphasizes the convenience of the metric system for scientific calculations and encourages practice to solidify understanding of the concepts taught.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Metric System
💡Unit Conversion
💡Powers of Ten
💡Meter
💡Gram
💡Liter
💡Kilo-
💡Centi-
💡Milli-
💡Conversion Factor
💡Unit Conversion Table
Highlights
Introduction to metric unit conversions and its importance in various fields like physics, chemistry, math, and engineering.
Explanation of the metric system's base units: meter for length, gram for mass, and liter for volume.
Understanding the concept of powers of ten and how they relate to metric unit conversions.
Use of a unit conversion table to facilitate easy conversion between metric units.
Conversion process from grams to milligrams using the method of multiplying and dividing by powers of ten.
Conversion of liters to kiloliters and the simplification of fractions by canceling zeros.
Detailed explanation of converting centimeters to millimeters and the use of intermediate units like meters.
The process of converting kiloliters to milliliters through a two-step conversion involving liters.
Explanation of converting millimeters to meters by recognizing the relationship between these units.
The method of converting centigrams to milligrams and then to grams, emphasizing the step-by-step approach.
Conversion of milliliters to liters with an explanation of simplifying the process by canceling zeros.
The process of converting kilograms to centigrams through intermediate conversions to grams and milligrams.
Emphasis on the simplicity and convenience of the metric system for unit conversions, especially in scientific and engineering applications.
The importance of practice in mastering the method of metric unit conversions and its long-term utility in various fields.
The introduction of part two of the lesson, promising more practice and reinforcement of the concepts learned.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: