All physics explained in 15 minutes (worth remembering)
TLDRThe video provides a broad overview of key concepts in physics worth knowing, even for non-scientists. It covers classical mechanics and Newton's laws of motion and gravity which allow predicting motion; energy and thermodynamics involving conservation, entropy disorder, and usefulness for work; electromagnetism and how charges and magnets interact; Einstein's relativity theory showing time is relative and gravity bends space-time; and quantum mechanics with its probabilistic and uncertain nature prior to measurement. The goal is to explain physics concepts most applicable to everyday life and nature of reality, not comprehensive details, to impart useful knowledge to general viewers.
Takeaways
- 👨🎓 Physics is foundational to understanding the experimental sciences and engineering, impacting daily life significantly.
- 📊 Five critical areas of physics include classical mechanics, energy and thermodynamics, electromagnetism, relativity, and quantum mechanics.
- 📡 Newton's laws, particularly the second law (F=ma), provide a fundamental understanding of motion and forces in classical mechanics.
- 🔬 Energy, a central concept in physics, is conserved and can be transformed from one form to another, influencing work and power.
- 🥶 Thermodynamics explores energy flow, heat, and the concept of entropy, highlighting the inevitability of increasing disorder in closed systems.
- 🔭 Electromagnetism, governed by Maxwell's equations, explains the interaction between electric and magnetic fields and their effects on charged particles.
- 🚀 Einstein's theory of relativity (special and general) revolutionizes our understanding of time, space, and gravity, challenging classical physics norms.
- 📱 Quantum mechanics introduces a probabilistic approach to particle behavior, emphasizing the wave-particle duality and the uncertainty principle.
- 📈 Planck's quantization of energy, Heisenberg's uncertainty principle, and Schrödinger's wave function are pivotal in quantum mechanics.
- 📚 Learning platforms like the Great Courses Plus offer in-depth explorations of these physics concepts, making advanced knowledge accessible.
Q & A
What are the 5 broad areas of physics that the narrator highlights as important to know about?
-The 5 areas are: classical mechanics, energy and thermodynamics, electromagnetism, relativity, and quantum mechanics.
What is Newton's second law and why is it important?
-Newton's second law states that force equals mass times acceleration (F=ma). This allows us to predict the motion of objects by knowing the forces acting on them and their mass.
How does the narrator define energy and work?
-The narrator defines energy as a measure of how much work you can do. Work is force times distance traveled, which transfers energy from one form to another.
What does entropy measure and what does the second law of thermodynamics state about entropy?
-Entropy measures the disorder or randomness in a system. The second law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of an isolated system can never decrease over time.
What are the key concepts from electromagnetism that the narrator wants us to understand?
-The key concepts are: charges affect other charges, magnets affect other magnets, moving charges affect magnets, moving magnets affect charges. These interactions are governed by Maxwell's equations.
What were Einstein's two postulates that led to the theory of relativity?
-The two postulates were: 1) The speed of light is constant in all frames of reference 2) The laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames of reference moving at constant velocity.
What are the three main equations/principles of quantum mechanics highlighted?
-1) Planck's equation relating energy quanta to frequency 2) Heisenberg uncertainty principle 3) Schrodinger's equation and probability wave functions.
Why does the narrator say that entropy may be the only reason we experience a forward direction of time?
-Because entropy always increases in isolated systems, it provides an arrow of time, distinguishing the past from the future in the direction of increasing disorder.
What is a superposed state in quantum mechanics?
-A superposed state refers to a quantum system existing in multiple probable states simultaneously, as a probability wave function, prior to measurement.
How does the narrator describe Einstein's view of quantum mechanics?
-The narrator says Einstein largely resisted the implications of quantum mechanics, especially its probabilistic and non-deterministic nature.
Outlines
📖 Introducing core concepts to learn in physics
The video introduces some key physics concepts worth learning for daily life, across five areas: classical mechanics, energy and thermodynamics, electromagnetism, relativity, and quantum mechanics. It outlines Newton's laws of motion and gravity, highlighting key equations on force, work and energy. It explains concepts like entropy and relativity, and the probabilistic nature of quantum mechanics.
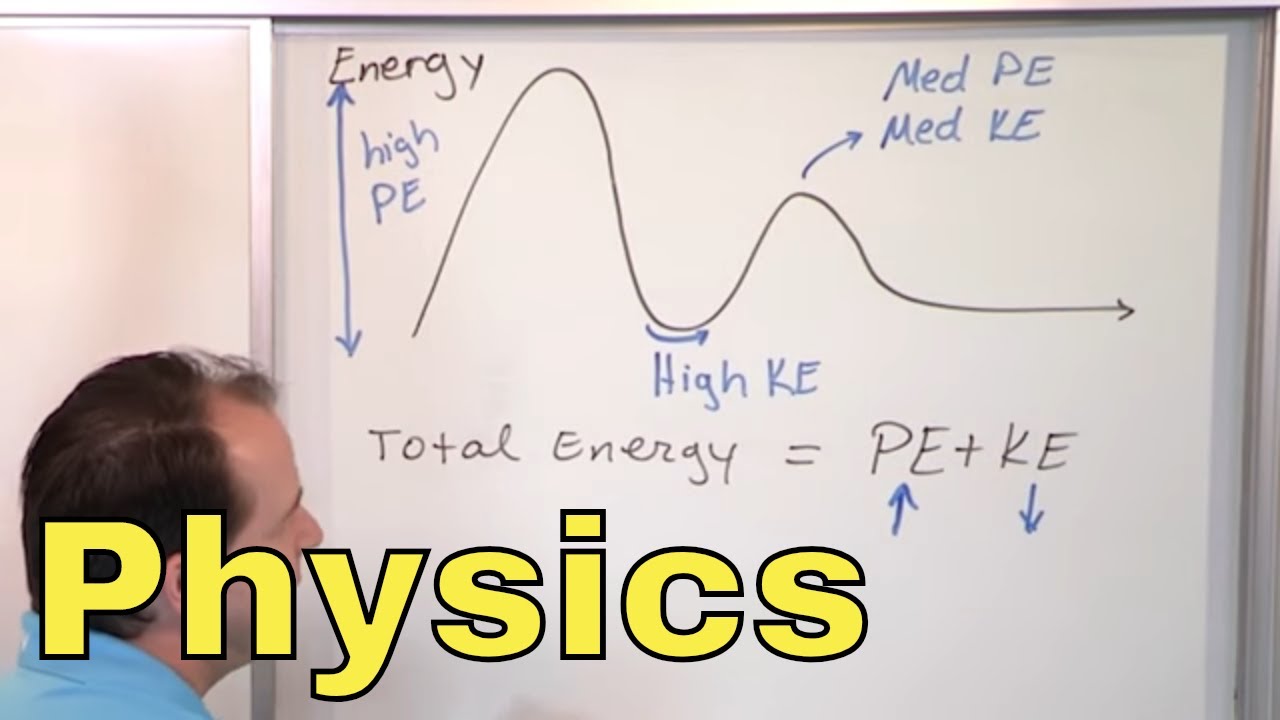
🔥 Understanding energy & thermodynamics
This paragraph introduces key energy concepts. It defines energy as the capacity to do work, with forms like kinetic and potential energy that can convert between each other. It discusses how energy powering motion can dissipate into heat, governed by the laws of thermodynamics. A key concept is entropy - quantifying disorder in a system - which always increases in an isolated system over time.
⚡ Grasping electromagnetism concepts
This section provides an overview of key concepts in electromagnetism using Maxwell's equations. It discusses charges, electric and magnetic fields, and how moving charges/fields can induce the other type of field. It introduces constants that determine the speed of light, setting context for Einstein's relativity theories.
⏱ Understanding Einstein's relativity
This introduces Einstein's special relativity, a revolutionary view where time and space depend on an observer's motion. It outlines key assumptions like constant speed of light. It describes how relative motion affects observations of time, enabling reconciliation of paradoxes. It also touches on general relativity - the curvature of spacetime by gravity.
🧠 Grasping the probabilistic quantum world
This section introduces key quantum concepts that represent a departure from classical physics. It outlines quantization of energy, uncertainty principle, and idea of quantum superposition expressed via wavefunctions. It describes the probabilistic and non-deterministic nature of quantum systems prior to measurement.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡physics
💡force
💡energy
💡electromagnetism
💡relativity
💡quantum mechanics
💡entropy
💡wavefunction
💡isolated system
💡paradigm shift
Highlights
Physics is at the core of reality and is the core basis of just about all of the experimental sciences.
Force equals mass times acceleration is a deceptively simple equation that has huge ramifications.
Energy is a measure of how much work you can do. Work is simply transferring energy from one form to another.
If you know all the forces acting on an object including friction, you can predict exactly where it will go.
Gravitational attraction diminishes rapidly as objects move apart because it's proportional to the inverse of distance squared.
Entropy, a measure of disorder, tells us some energy is more useful for doing work than others.
If you have a static charge, it will affect only other charges. If you have a moving charge, it will affect magnets.
Time was not fixed, it was relative - Einstein's crucial insight that shifted paradigms.
Einstein showed gravity and acceleration were equivalent - space-time itself must bend for light's path to be shortest.
Quantum particles have inherent uncertainty - you can't know both exact position and exact momentum.
Energy is quantized - it can only be emitted or absorbed in distinct quanta, not continuously.
Prior to measurement, quantum systems exist in superposed states - a set of probabilities.
An electron is everywhere at once - it is both here AND there.
Quantum weirdness is not a limitation of instruments, but of reality itself.
These are the concepts in physics most worth remembering for their impact on daily life.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

The Trouble with Gravity: Why Can't Quantum Mechanics explain it?

Carlo Rovelli: The nature of time
01 - Introduction to Physics, Part 1 (Force, Motion & Energy) - Online Physics Course

The Planck scale: Is there a fundamental limit to space and time?
How Quantum Entanglement Creates Entropy
24. Quantum Mechanics VI: Time-dependent Schrödinger Equation
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: