Speed and Velocity (Tagalog)
TLDRThe video script introduces fundamental concepts of speed and velocity, using a relatable example of Joseph traveling to school by bus. It explains speed as the rate of distance covered over time, with units like miles per hour or kilometers per hour. The script further distinguishes between speed and velocity, emphasizing that velocity includes direction. By calculating the bus's speed and velocity based on given distances and time, the video illustrates average and instantaneous velocity, highlighting the difference between constant motion and variable speed. The summary effectively breaks down complex ideas into understandable segments, encouraging viewers to apply these concepts in real-life scenarios.
Takeaways
- 📏 Speed is defined as the rate of distance covered over a given time, expressed by the equation v = d/t (speed equals distance divided by time).
- 📐 Units of speed include miles per hour, kilometers per hour, and meters per second, allowing for various measurements depending on the context.
- 🚌 Example scenario: If a bus travels 4 kilometers in 2 hours, its speed is calculated as 2 km/h by dividing the distance (4 km) by the time (2 hours).
- 🔄 Velocity is a vector quantity that incorporates both speed and direction, following the formula v = displacement/time.
- 🧭 When considering the same bus example with a displacement of 3 kilometers northeast, the velocity is 1.5 km/h northeast, calculated by dividing displacement (3 km) by time (2 hours).
- 🔢 Average speed is the total distance traveled divided by the total time taken, which in the bus example equates to 2 km/h, calculated by dividing the total distance (4 km) by the total time (2 hours).
- 🔄 Average velocity, unlike average speed, takes direction into account and is calculated by dividing total displacement by total time. For the bus, it is 1.5 km/h northeast.
- 📌 Instantaneous speed is the speed at a specific point in time, such as reading from a speedometer, and can be with or without direction.
- 🚦 Instantaneous velocity is the instantaneous speed with direction, providing a more detailed understanding of an object's motion at a particular moment.
- 🏎️ Constant motion implies that an object travels the same distance for each second, maintaining a uniform pace. The bus example demonstrates constant motion at 75 km/h for both hours.
- 🌟 In summary, speed is a scalar quantity focusing on how fast an object moves, while velocity is a vector quantity that includes both speed and direction, providing a more comprehensive description of motion.
Q & A
What is the definition of speed?
-Speed is the rate of distance covered at a given time. It is calculated by dividing the distance traveled by the time taken to cover that distance, expressed as v = d/t. The units of measurement for speed include miles per hour, kilometers per hour, or meters per second.
How is speed calculated?
-Speed (v) is calculated using the formula speed equals distance (d) divided by time (t). For example, if a vehicle travels 4 kilometers in 2 hours, the speed is 2 kilometers per hour, calculated as v = 4 km / 2 hours.
What are the units of measurement for speed?
-The units of measurement for speed include meters per second (m/s), kilometers per hour (km/h), and miles per hour (mi/h). These units represent the distance an object travels in a specific amount of time.
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
-Speed is a scalar quantity that represents the rate of motion, while velocity is a vector quantity that includes both the rate of motion and the direction of movement. Speed does not indicate direction, whereas velocity does.
How is velocity calculated?
-Velocity (v) is calculated using the formula velocity equals displacement (d) divided by time (t). Displacement takes into account the direction of movement, so velocity provides both the rate and the direction of an object's motion. For example, if a bus has a displacement of 3 kilometers to the northeast in 2 hours, the velocity is 1.5 kilometers per hour northeast, calculated as v = 3 km / 2 hours.
What is average speed?
-Average speed is the total distance traveled divided by the total time taken. It is a scalar quantity and does not consider the direction of travel. For instance, if a bus travels 4 kilometers in 2 hours, the average speed is 2 kilometers per hour, calculated as v = total distance / total time.
What is average velocity?
-Average velocity is the total displacement divided by the total time taken. Unlike average speed, average velocity takes direction into account, making it a vector quantity. For example, if a bus has a displacement of 3 kilometers to the northeast in 2 hours, the average velocity is 1.5 kilometers per hour northeast, calculated as v = total displacement / total time.
What is instantaneous speed?
-Instantaneous speed is the speed of an object at a specific point in time. It can be measured using a device such as a speedometer, which shows the magnitude of the speed at a particular moment without indicating direction.
What is instantaneous velocity?
-Instantaneous velocity is the velocity of an object at a specific point in time, including both the magnitude and direction of the object's motion. It is a vector quantity and can be determined by calculating the velocity at an exact instant using calculus or by measuring it with specialized equipment.
What is constant motion?
-Constant motion refers to any type of motion where either the distance traveled by the object is the same for each second or the speed remains constant over time. For example, if a vehicle maintains a speed of 75 kilometers per hour for several hours without changing, it is in constant motion.
How can we convert between different units of speed?
-Different units of speed can be converted using conversion factors. For example, to convert kilometers per hour to meters per second, you can use the conversion factor of 0.2777777778 (1 km/h = 0.2777777778 m/s). Similarly, other conversions can be made using the appropriate factors, such as 1 mile per hour being equivalent to 0.44704 m/s.
Why is understanding the difference between speed and velocity important?
-Understanding the difference between speed and velocity is important because it allows us to accurately describe and analyze motion. Speed provides information about how fast an object is moving, while velocity gives us both the rate and direction of the object's movement, which is crucial in fields such as physics, engineering, and navigation.
Outlines
🚌 Understanding Speed and Velocity
This paragraph introduces the concepts of speed and velocity. Speed is defined as the rate of distance covered per unit of time, typically measured in miles per hour, kilometers per hour, or meters per second. The equation for speed is given by v = d/t, where v is speed, d is distance, and t is time. An example is provided where Joseph travels to school by bus, covering a distance of 4 kilometers in 2 hours, resulting in a speed of 2 kilometers per hour. Velocity, on the other hand, is a vector quantity that includes both speed and direction. The formula for velocity is v = d/t, with the understanding that displacement takes into account the direction of movement. Using the same scenario, if the bus travels 3 kilometers northeast, the velocity is calculated as 1.5 kilometers per hour in the northeast direction. The distinction between speed and velocity is emphasized, with speed being a scalar quantity and velocity being a vector quantity.
📐 Calculating Average and Instantaneous Speed
This paragraph delves into the calculation of average and instantaneous speed. Average speed is the total distance traveled divided by the total time taken, which in the case of the bus is 2 kilometers per hour, as the bus travels 4 kilometers in 2 hours. Average velocity, however, takes into account displacement and direction, resulting in the bus's average velocity being 1.5 kilometers per hour northeast, given a total displacement of 3 kilometers in 2 hours. Instantaneous speed refers to the speed at a specific moment in time, such as looking at a speedometer which might show 75 kilometers per hour. Instantaneous velocity similarly includes direction, and in the context of constant motion, it implies that the speed is uniform for each second. The example illustrates Joseph's bus traveling at a constant speed of 75 kilometers per hour for each hour, reinforcing the concept of constant motion.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡displacement
💡speed
💡velocity
💡units of measurement
💡average speed
💡average velocity
💡instantaneous speed
💡instantaneous velocity
💡constant motion
💡direction
💡formula
Highlights
Speed is defined as the rate of distance covered at a given time.
The equation for speed is given by speed equals distance divided by time (v = d/t).
Units of measurement for speed include miles per hour, kilometers per hour, and meters per second.
In the example, Joseph's bus travels 4 kilometers in 2 hours.
The speed of the bus is calculated as 2 kilometers per hour.
Velocity is a vector quantity that includes both speed and direction.
The formula for velocity is velocity equals displacement divided by time (v = d/t).
The bus's displacement is given as 3 kilometers northeast.
The velocity of the bus is calculated as 1.5 kilometers per hour northeast.
Average speed is the total distance traveled divided by the total time.
Average velocity takes into account both the magnitude and direction of the displacement.
The average speed of the bus is 2 kilometers per hour, considering the total distance traveled.
The average velocity of the bus is 1.5 kilometers per hour northeast, considering the total displacement and time.
Instantaneous speed is the speed at a specific point in time.
Instantaneous velocity is the velocity at a specific point in time, including direction.
Constant motion refers to motion where the distance traveled by the object is the same for each second.
Joseph's bus maintains a constant speed of 75 kilometers per hour for both hours.
The concept of constant motion is demonstrated by the bus traveling at a consistent speed throughout its journey.
The summary differentiates between speed, velocity, average speed, average velocity, and instantaneous velocity.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
Velocity and speed: Motion in One Dimension

Calculating average velocity or speed | One-dimensional motion | Physics | Khan Academy
Speed, Velocity and Distance Time Graphs - Physics - Science - Get That C In your GCSE and IGCSE
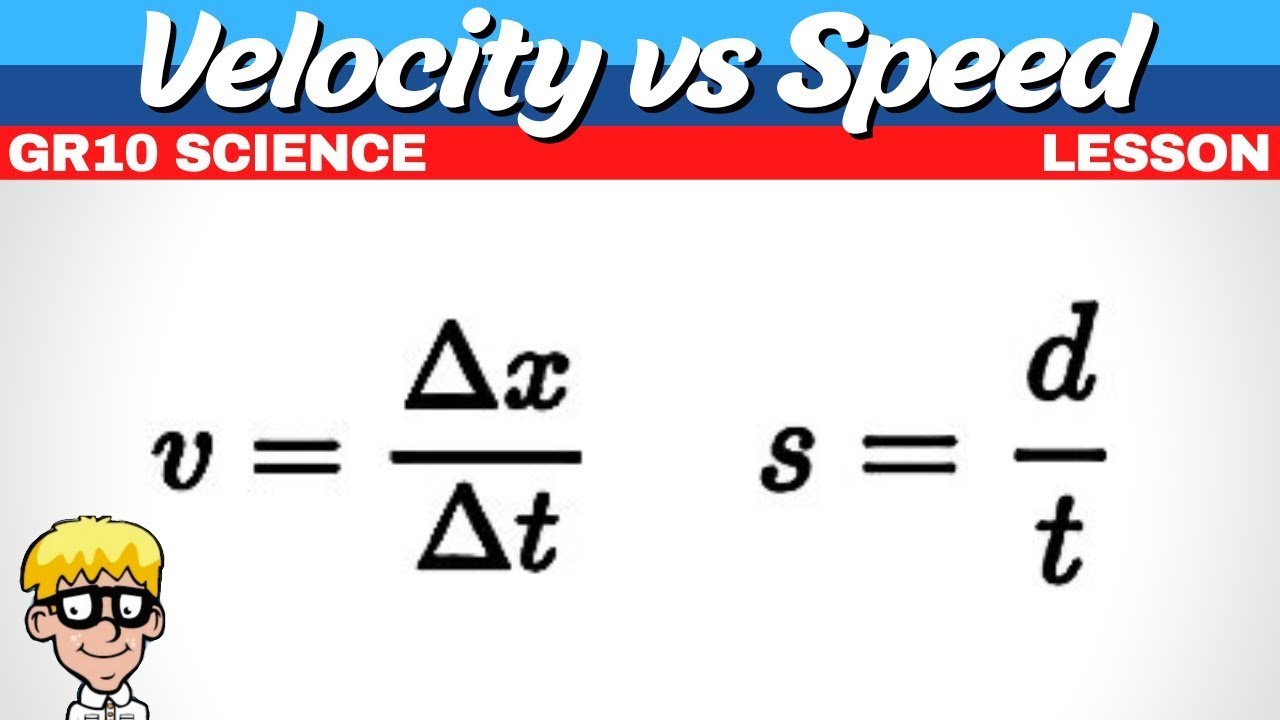
Velocity vs Speed Grade 10 Science

What is Velocity? Physics

Distance, Displacement, Speed and Velocity
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: