What Is the Difference Between Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential? | Physics in Motion
TLDRThe video script discusses the concept of electric potential energy, which is the energy stored by electric charges and can be converted into other forms like kinetic energy. It explains how this energy depends on the type and amount of charge, as well as the strength of the electric field. The script also introduces the concept of electric potential, or voltage, which is the electric potential energy per unit charge. Through examples and equations, it illustrates how electric potential energy and potential are calculated and their importance in everyday applications of electricity.
Takeaways
- 🌊 Gravitational potential energy is the energy stored in water, ready to be converted into kinetic energy for various applications like heating and powering electronics.
- 🔋 Electric potential energy is the energy stored by electric charges, which can be converted into electrical energy to power circuits and devices.
- 🔧 The amount of electric potential energy is crucial for electrical engineers to design circuits that provide the necessary power for a wide range of uses.
- 📈 Electric potential energy is a scalar quantity that can be positive or negative, depending on whether energy is lost or gained in a system.
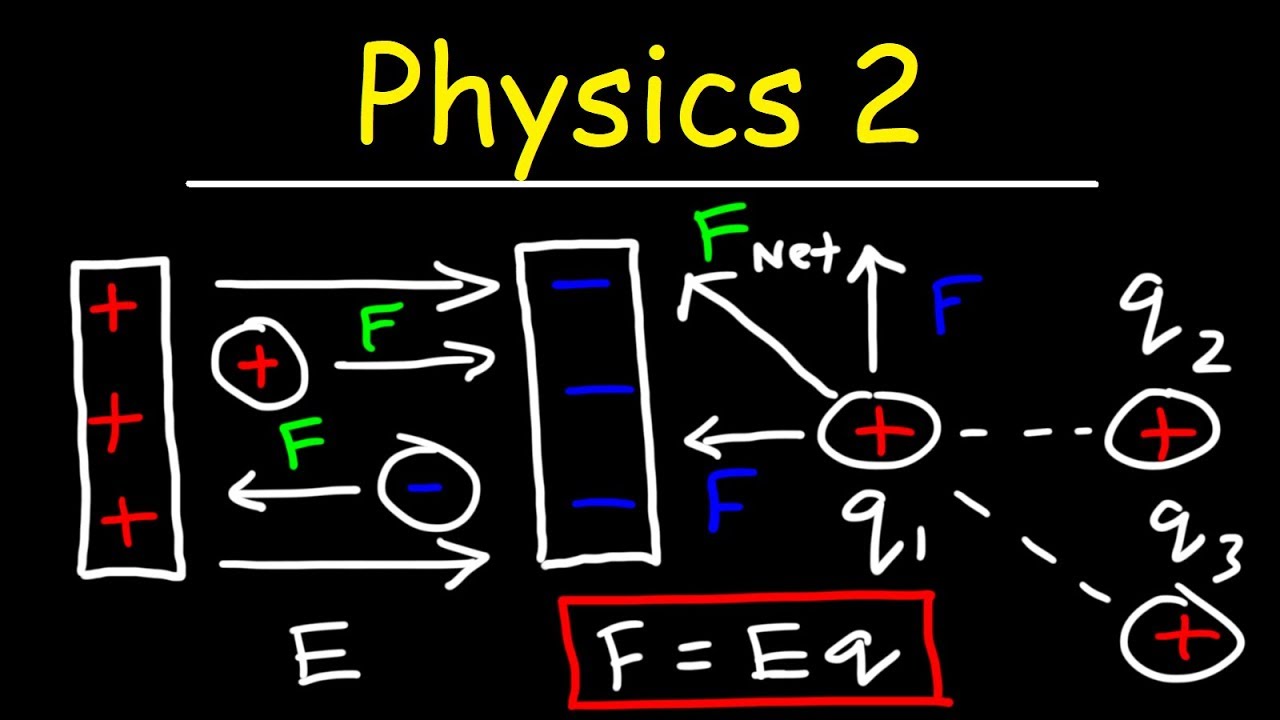
- 🔌 The electric potential energy depends on the type and amount of charge, as well as the strength of the electric field the charge is in.
- 📏 The formula for calculating electric potential energy is similar to that of gravitational potential energy, using Coulomb's constant and the product of charges divided by the distance between them.
- ⚡ The electric potential energy of a charge is negative when it is within a field created by an opposite charge, indicating that work must be done to keep them apart.
- 🔄 Electric potential energy is conservative, obeying the law of conservation of energy, where potential energy lost is gained as kinetic energy and vice versa.
- 🔄 When a charge moves from a region of high potential energy to low potential energy, it accelerates and converts potential energy into kinetic energy.
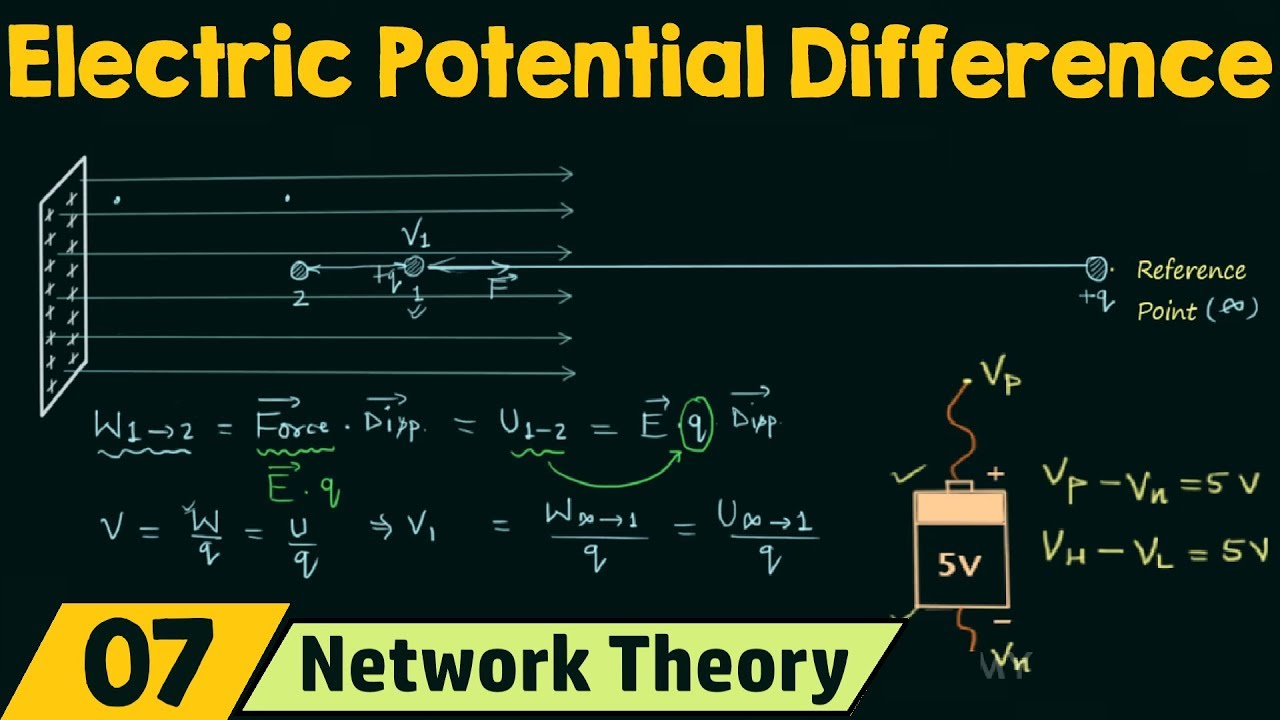
- 🔌 Electric potential (voltage) is the electric potential energy per unit charge and is a measure of the energy of a single unit of charge in an electric field.
- 🔌 The electric potential at a point in space due to multiple charges is the sum of the potentials created by each individual charge at that point.
Q & A
What is gravitational potential energy?
-Gravitational potential energy is the stored energy in an object due to its elevated position, which can be converted into kinetic energy under the influence of gravity.
How can gravitational potential energy be converted into hydroelectric power?
-Gravitational potential energy can be converted into hydroelectric power by allowing water stored at a height to flow down, driving turbines which in turn generate electricity.
What is electric potential energy?
-Electric potential energy is the energy stored by electric charges due to their position in an electric field, which can be converted into electrical energy.
What are the three factors that affect electric potential energy?
-The three factors that affect electric potential energy are the type of charge (positive or negative), the amount of charge, and the strength of the electric field.
How is electric potential energy related to work done by an electric field?
-Electric potential energy is the magnitude of work performed on a charged object by an electric field, giving the object the ability to do work.
What is the unit of measurement for both gravitational and electric potential energy?
-Both gravitational and electric potential energy are measured in Joules.
How can the electric potential energy between two charged objects be calculated?
-The electric potential energy between two charged objects can be calculated using the formula: Electric potential energy = k * (product of charges) / distance between them, where k is Coulomb's constant.
What happens to electric potential energy when a charge moves in the direction opposite to the electric field?
-When a charge moves in the direction opposite to the electric field, it is moving up the field and gaining electric potential energy, as more work is required to maintain this position against the field.
What is the relationship between electric potential energy and electric potential?
-Electric potential energy refers to the total energy stored by all charges in an electric field, while electric potential (or voltage) is the electric potential energy per unit charge.
How is electric potential calculated at a point in space due to multiple charges?
-The electric potential at a point in space due to multiple charges is the sum of the potentials created by each individual charge at that point.
What is the significance of electric potential being a scalar quantity?
-Since electric potential is a scalar quantity, it is easy to add together the potentials from multiple charges to find the total potential at a given point in space.
How does the law of conservation of energy apply to electric potential energy?
-The law of conservation of energy applies to electric potential energy in that whatever an object loses in potential energy, it gains in kinetic energy, and vice versa, ensuring that the total energy remains constant.
Outlines
🌊 Gravitational and Electric Potential Energy
This paragraph introduces the concept of gravitational potential energy stored in water and its conversion to kinetic energy for various uses. It then transitions to electric potential energy, which is energy stored by electric charges. The importance of understanding electric potential energy in circuit design is emphasized, and the paragraph delves into the factors that affect electric potential energy, such as charge type, amount, and electric field strength. The concept is further explained through a calculation example involving charges and electric fields, highlighting the significance of the sign of charges in determining the work required to maintain their separation.
🔋 Conversion of Electric Potential Energy to Kinetic Energy
This section discusses the transformation of electric potential energy into kinetic energy, using the analogy of a ball moving downhill to explain the concept. It establishes that electric potential energy is conservative, obeying the law of conservation of energy. The paragraph outlines scenarios affecting electric potential energy, such as the position of charges relative to each other and their movement within an electric field. It also compares electric potential energy to gravitational potential energy, drawing parallels between the two. The equation for electric potential energy stored by a charge between two charged plates is derived and compared to the equation for gravitational potential energy.
🔌 Electric Potential and its Calculation
The final paragraph focuses on electric potential, which is the electric potential energy per unit charge, and its relationship to voltage. It clarifies the difference between electric potential energy and electric potential. The paragraph explains how electric potential depends on the amount of charge creating the potential and the distance from that charge. The concept is further illustrated through an example of calculating electric potential at a point in space due to multiple charges. The paragraph concludes by reinforcing the importance of understanding electric charges and their energy content for harnessing electric power in everyday applications.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Gravitational Potential Energy
💡Electric Potential Energy
💡Charge
💡Electric Field
💡Work
💡Kinetic Energy
💡Conservation of Energy
💡Electric Potential
💡Coulomb's Law
💡Scalar Quantity
💡Voltage
Highlights
Gravitational potential energy is introduced as a form of energy stored in water, ready to do work.
Gravitational potential energy can be converted to kinetic energy and used for various applications like heating and powering electronics.
Electric potential energy is energy stored by electric charges and is crucial for electrical engineers in designing circuits.
Electric potential energy is the energy a charge in an electric field possesses to do work and can be positive or negative.
The electric potential energy depends on the type of charge, the amount of charge, and the strength of the electric field.
Electric potential energy is measured in Joules, the same units as gravitational potential energy.
A calculation example is provided to demonstrate how to find the electric potential energy stored by a charge.
Work must be done on the system to keep charges apart, and the electric potential energy signifies this ability.
Electric potential energy can decrease and convert into kinetic energy, similar to gravitational potential energy.
Electric potential energy is conservative and obeys the law of conservation of energy.
The electric potential energy of a charge near another positive charge is high, while near a negative charge, it is low.
Electric potential is the electric potential energy per unit charge and is also known as voltage.
The electric potential at a point in space depends on the amount of charge creating the potential and the distance from that charge.
The electric potential at a point due to multiple charges is the sum of the potential of each individual charge.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: