Chapter 1: SI unit review | CHM 214 | 002
TLDRThis video delves into the fundamentals of analytical chemistry, focusing on chemical measurements and the importance of using SI units. It reviews key SI units such as meters for length, kilograms for mass, seconds for time, amperes for electrical current, kelvins for temperature, and moles for the amount of substance. The video also touches on derived units like hertz for frequency, newtons for force, pascals for pressure, joules for energy, and watts for power. The aim is to refresh the viewer's memory of these units to ensure a solid understanding for further studies in chemistry.
Takeaways
- 📚 Introduction to Analytical Chemistry: The video begins with an introduction to analytical chemistry, setting the stage for the topics to be covered.
- 📈 Review of General Chemistry: The content serves as a review for those who have taken general chemistry recently, and a refresher for those who haven't in a while.
- 📐 Importance of Units in Measurement: The script emphasizes the importance of using specific units when discussing measurements in chemistry, particularly the SI units.
- 🌐 SI Units for Basic Quantities: The video lists the seven base SI units, which include units for length (meter), mass (kilogram), time (second), electric current (ampere), thermodynamic temperature (kelvin), amount of substance (mole), and luminous intensity (candela).
- 🔍 Specific SI Units for Common Measurements: The script highlights specific SI units such as meter for length, kilogram for mass, second for time, ampere for electric current, kelvin for temperature, and mole for the amount of substance.
- 🎥 Derived Units in the SI System: The video mentions derived units, which are created from the base SI units, such as hertz for frequency, newton for force, pascal for pressure, joule for energy, and watt for power.
- 👀 Frequency and Spectroscopy: The concept of frequency, measured in hertz, is introduced with a focus on its application in spectroscopy when studying light.
- 💡 Connection to Physics: The script connects chemistry concepts to physics by mentioning units like newton (force) and joule (energy), which may be familiar from physics classes.
- 📊 Practical Application of Units: The video briefly touches on the practical use of units like pascal for pressure and watt for power, indicating their relevance in specific scientific contexts.
- 🎓 Ensuring Understanding: The purpose of reviewing these units is to ensure that everyone is on the same page and has a clear understanding of the measurements used in chemistry.
Q & A
What is the main focus of this video?
-The main focus of this video is to review chemical measurements, specifically the use of SI units in the context of analytical chemistry.
Why is it important to review these units?
-It is important to review these units to ensure that everyone has a solid understanding of the basic measurements used in chemistry, as it forms the foundation for more complex concepts.
What does the SI unit for length measure?
-The SI unit for length, the meter, is used to measure the extent of something in one dimension.
What is the SI unit for mass and why is the kilogram interesting?
-The SI unit for mass is the kilogram, which is interesting because it is a base unit and not a gram, showing the defined starting point for mass measurements.
How is the SI unit for time determined?
-The SI unit for time is the second, which measures the duration of events or processes.
What is the significance of the ampere in the SI system?
-The ampere is the SI unit for electrical current, representing the flow of electric charge through a conductor per unit time.
What does the kelvin measure in the SI system?
-The kelvin is the SI unit for temperature, representing the absolute temperature scale which starts at absolute zero, the lowest possible temperature.
What is the mole used to estimate in chemistry?
-The mole is used to estimate the amount of substance, representing the number of particles (such as atoms or molecules) in a sample.
What is the relevance of frequency in spectroscopy?
-In spectroscopy, frequency is relevant because it relates to the energy of light and other electromagnetic radiation, allowing scientists to analyze and identify substances based on their light absorption or emission characteristics.
How is the newton related to force?
-The newton is the SI unit for force, which is calculated as mass times acceleration (kg·m/s²), representing the push or pull acting upon an object.
What is the role of the joule in energy measurements?
-The joule is the SI unit for energy, representing the work done or the transfer of heat, and is equivalent to a newton times a meter (N·m).
How is power defined in the SI system?
-Power in the SI system is defined as the rate at which energy is used or transferred, measured in watts, which is one joule per second (J/s).
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Analytical Chemistry and SI Units
The video begins with a warm welcome to the educational content, setting the stage for an exploration of analytical chemistry with a focus on chapter one, which revisits chemical measurements. The instructor emphasizes the importance of understanding and recalling fundamental concepts from general chemistry, acknowledging the varying time since exposure to these topics for different viewers. The central theme of the paragraph is the introduction of SI (International System of Units) and their application in scientific measurements. The instructor discusses the various SI units for length (meter), mass (kilogram), time (second), electrical current (ampere), temperature (kelvin), and the amount of substance (mole). The paragraph also touches on other units such as frequency (hertz), force (newton), pressure (pascal), energy (joule), and power (watt). The purpose is to review these units to ensure a shared understanding among viewers as they continue their study of chemistry.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Analytical Chemistry
💡Chemical Measurements
💡SI Units
💡Length
💡Mass
💡Time
💡Electrical Current
💡Temperature
💡Amount of Substance
💡Derived Units
💡Frequency
Highlights
Introduction to Analytical Chemistry
Review of chemical measurements
Use of SI units in class
SI unit for length - meter
SI unit for mass - kilogram
SI unit for time - second
SI unit for electrical current - ampere
SI unit for temperature - kelvin
SI unit for amount of substance - mole
Frequency unit - hertz
Derived unit for force - newton
SI unit for pressure - pascal
SI unit for energy - joule
SI unit for power - watt
Review of units used in chemistry
Ensuring everyone is on the same page with unit usage
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
SI Units Quiz | 40 Questions | International System of Units (SI) | Physics Quiz
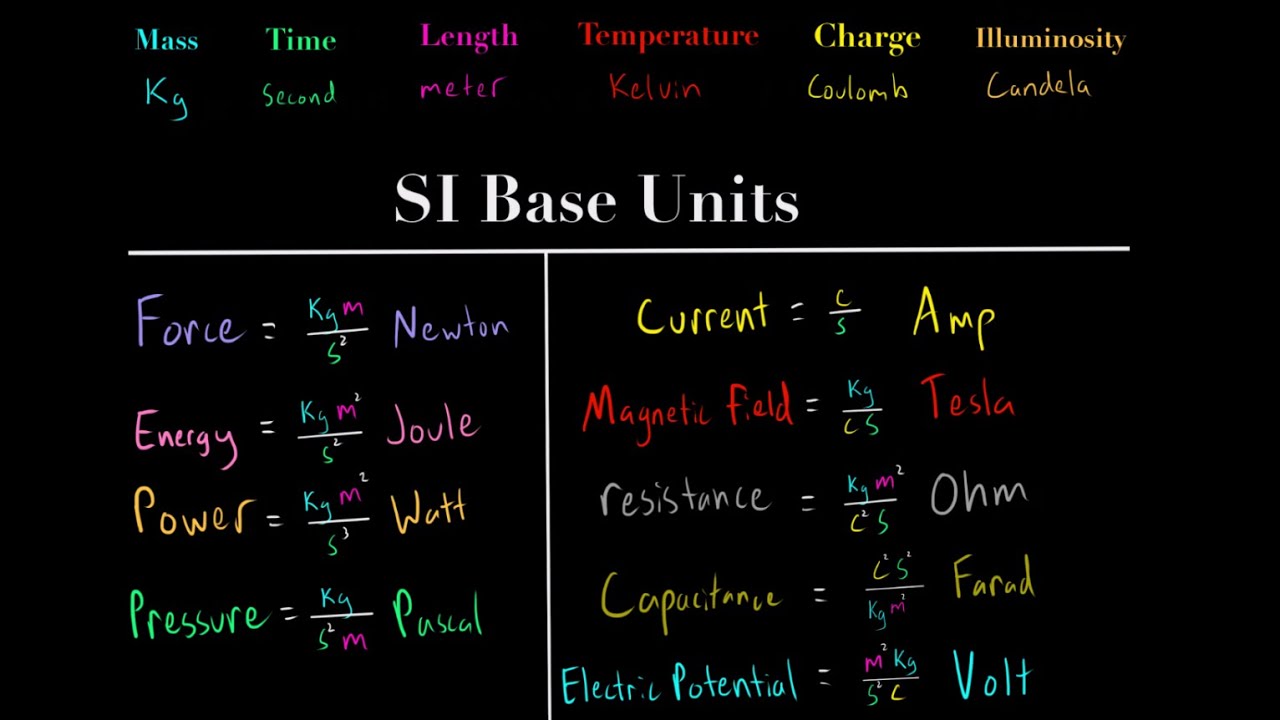
Understanding the SI Units (meters, seconds, kg, kelvin, coulomb, candela) MCAT Physics Chemistry

SI Base Units and Derived Units - Physics and Chemistry
UNITS & PHYSICAL QUANTITIES | Physics Animation
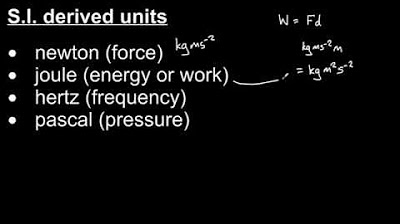
S.I. base units and derived units

College Physics 1: Lecture 4 - Units and Unit Conversions
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: